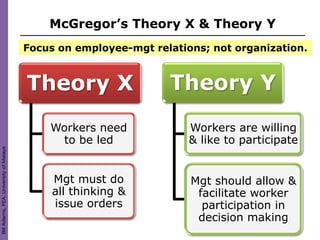
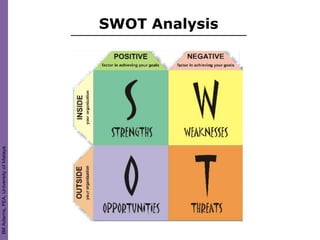
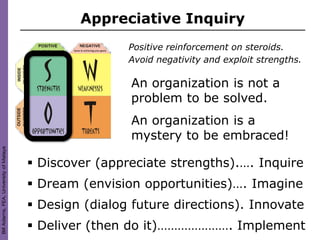
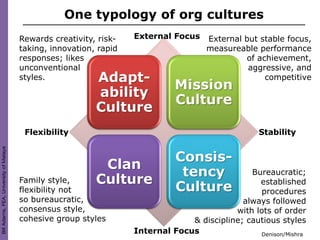
Organization culture theory argues that to change organizations, one must change their underlying culture. Culture is determined by shared values, norms, and traditions that guide employee behavior. Leaders play a key role in establishing and changing an organization's culture. Various models describe how to analyze and understand organizational culture, such as identifying shared behaviors, language, decision-making processes, and symbols that embody a culture. Appreciative inquiry focuses on identifying strengths within a culture to facilitate positive change.

![Organization Culture Theory
[Classics book turned to strong advocacy!]
Boomed since the early 1980s reform efforts to
change organizations.
To change orgs must change the culture!
Claims that the rational model rarely works.
Bill Adams, FEA, University of Malaya
Big management reform approaches (like Total
Quality Management) all require changed culture.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/um8organizationculture-100309201244-phpapp02/85/UM-8-Organization-Culture-2-320.jpg)

![“Symbolic Management”
[Influenced by “postmodern” philosophy
& “The Social Construction of Reality”]
Lots of uncertainty exits in many organizations.
People use symbols as tools for reducing ambiguity.
[OK, sure, symbols are important.]
“The interpretation of what is happening in organi-
Bill Adams, FEA, University of Malaya
zations is more important than what is actually
happening.”!!!
“If people believe things are real,
they are real in their consequences.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/um8organizationculture-100309201244-phpapp02/85/UM-8-Organization-Culture-4-320.jpg)
![[Schein] Organizational Culture
Culture guides our behavior.
Culture = the “personality” of a group.
Culture = “pattern of shared basic assumptions”
Ingrained, unthinking, nonnegotiable assumptions
Group has a shared history, things in common.
Bill Adams, FEA, University of Malaya
Role of leaders in establishing & changing culture.
New members “socialized” into the culture.
In large organizations, may be subcultures.
Importance of learning the culture when new!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/um8organizationculture-100309201244-phpapp02/85/UM-8-Organization-Culture-5-320.jpg)
![[Schein] Describing aspects of culture
(“Observables associated with culture”)
Behavioral regular- Group norms Rules of the game
ities (language, (implicit standards (unwritten rules for
customs, rituals) and values) “getting along”)
Habits of thinking Shared meanings Root metaphors/
(shared paradigms) (intra-org lingo) shared symbols
Embedded skills Formal rituals
Bill Adams, FEA, University of Malaya
Climate (feeling &
(special practices (group traditions for
group atmosphere)
passed along) “passages”)
Espoused values Formal philosophy
(announced values) (broad principles)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/um8organizationculture-100309201244-phpapp02/85/UM-8-Organization-Culture-7-320.jpg)
![[Martin] Manifestations of Culture: “Cultural Forms”
Rituals
Other
Content
Stories
Culture
Bill Adams, FEA, University of Malaya
Bldg.,
Décor, Jargon
Dress
Humor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/um8organizationculture-100309201244-phpapp02/85/UM-8-Organization-Culture-8-320.jpg)
![[Ouchi “Oh’chi”] Z Organization (aka Japanese Mgt.)
Lifetime employment
Low turnover rates
Increased job commitment
Company-specific skills
Slow promotions but “wandering around” moves
Long-range staff development (& generalists)
Bill Adams, FEA, University of Malaya
Use but not obsessed by quantitative analysis
Consensus decision-making & staff cohesion
Importance of warm holistic relationships
Attitude/symbols of egalitarianism and trust](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/um8organizationculture-100309201244-phpapp02/85/UM-8-Organization-Culture-9-320.jpg)
![[Ouchi “Oh’chi”] Z Organization (aka Japanese Mgt.)
Disadvantages of “Type Z”:
● The “clan” can be “clanish” toward
“outsiders” (xenophobic, sexist, racist!)
● Cultural conformity resists valuable innovations
Bill Adams, FEA, University of Malaya
● Loss of external professionalism (inward looking)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/um8organizationculture-100309201244-phpapp02/85/UM-8-Organization-Culture-10-320.jpg)