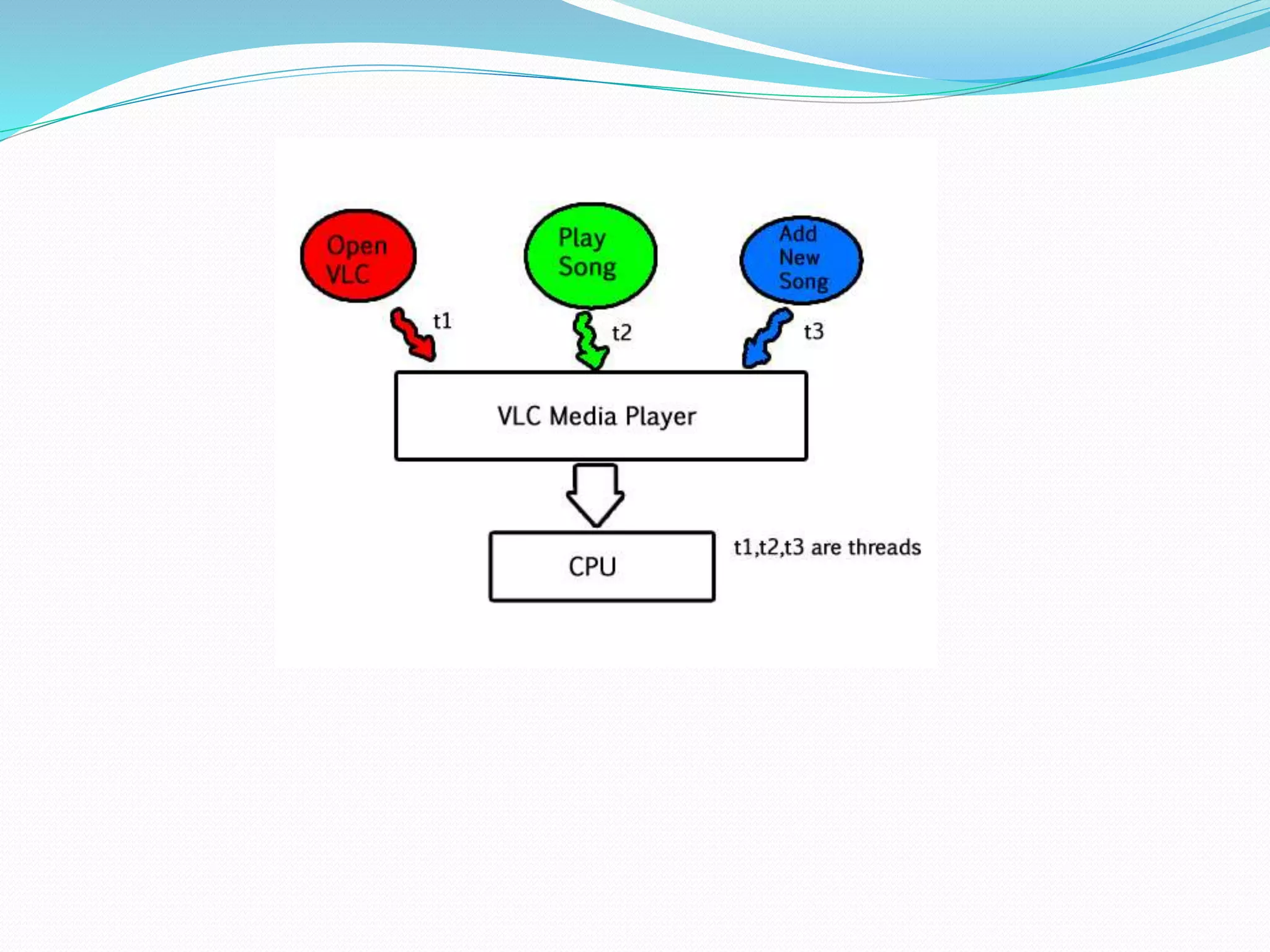
The document discusses various types and evolution of operating systems, including multi-programming, multiprocessing, multi-tasking, multi-threading, distributed operating systems, real-time operating systems, time-sharing operating systems, and batch operating systems. It explains how these systems manage multiple processes and tasks, highlight their differences, advantages, and use cases, particularly in terms of resource utilization and performance. Key concepts include CPU sharing, context switching, and the importance of time constraints in real-time systems.