This document describes different types of twins:
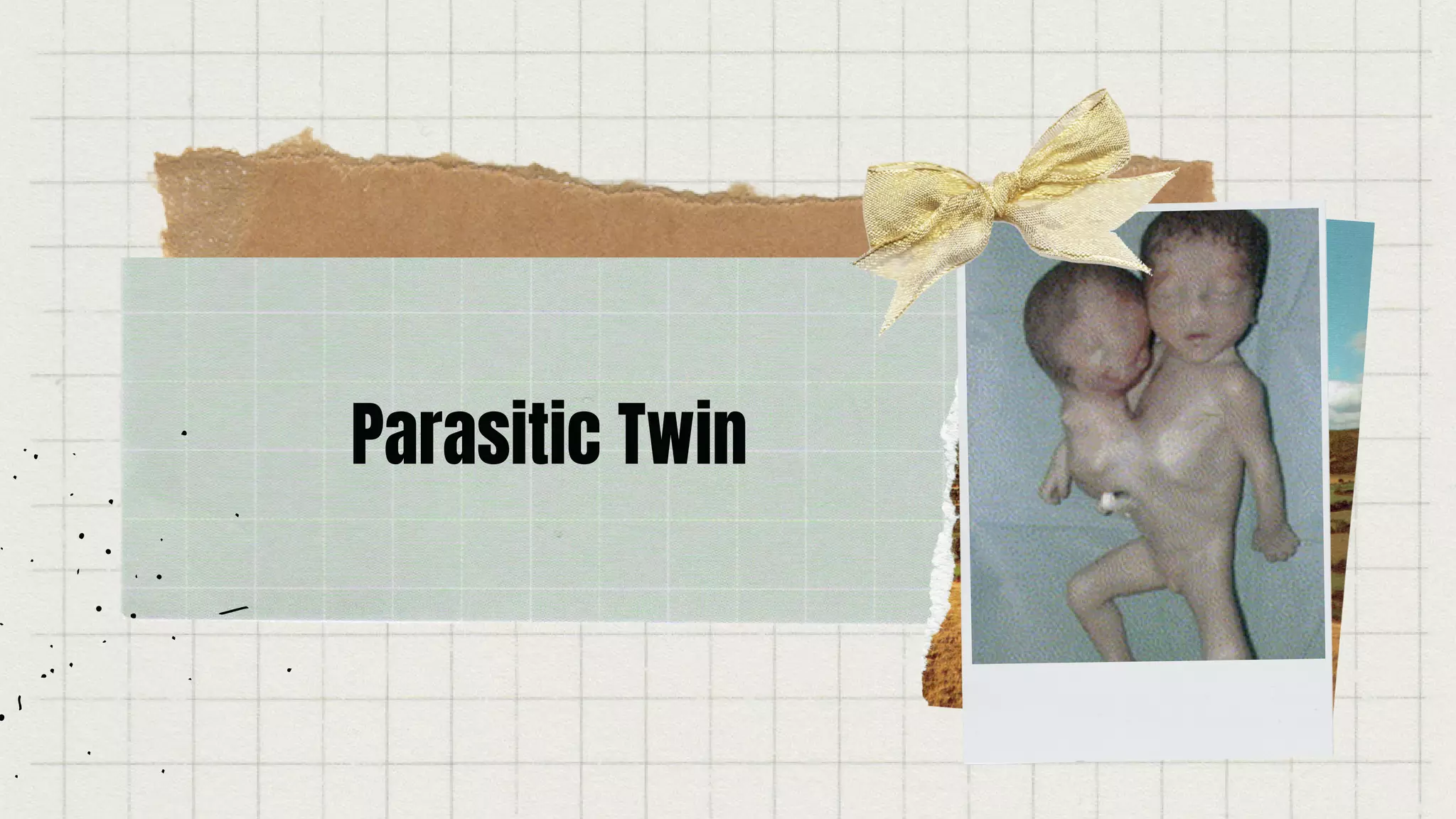
Identical twins have identical genetic material and are always the same sex. Non-identical twins develop from separate eggs and have only a 50% chance of sharing the same traits. Mirror twins are exact physical replicas of each other but features may be opposite sides of the body. Conjoined twins share body parts or organs. Parasitic twins are physically attached but never fully develop and cannot survive alone. Semi-identical twins share the mother's genes but only half the father's genes.