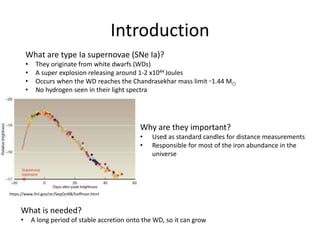
Type Ia supernovae result from a white dwarf reaching the Chandrasekhar mass limit of 1.44 solar masses through accretion from a binary companion. The document discusses the history of understanding the progenitor system of Type Ia supernovae, including early theories of single degenerate systems and double degenerate mergers, as well as observations ruling out some candidates like super soft X-ray sources and favoring others like recurrent novae. However, the exact progenitor remains uncertain, with the current leading theories involving either a single degenerate or double degenerate system.


![Necessary Components (2)
Single degenerate scenario (SDS):
• The WD accretes matter from a sub-giant,
main sequence, red giant star or AGB star
Double degenerate scenario (DDS):
• The WD accretes matter from another
WD before colliding
Cataclysmic Variable (CV) [Any star]:
1. Roche lobe is filled, accretion occurs through
the Lagrangian point
Symbiotic Variable (SB) [RG or AGB only]:
1. Roche lobe isn’t filled, accretion occurs only via
strong winds
http://www.daviddarling.info/images/contact_binary.jpg
http://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cms/cpg15x/albums/userpics/typeiaprogenitor1.jpg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/typeiasupernovae-150529071322-lva1-app6892/85/Type-ia-supernovae-5-320.jpg)




