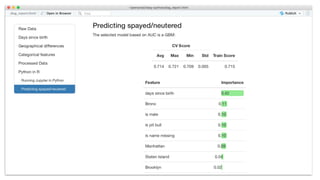
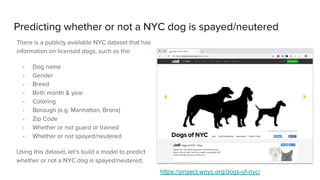
This document summarizes Kelli-Jean Chun's presentation on using Python and R for data science. It discusses data science roles, provides an overview of Python and R, compares them for different use cases, and outlines a plan to predict whether NYC dogs are spayed/neutered using both languages. R will be used for exploratory data analysis and visualization, while Python with Scikit-learn, Pandas and NumPy will be used to build and evaluate a predictive model. The languages will be connected using rpy2 to load data from R into Python and reticulate to run Python code in RMarkdown.



![What is R?
Python R
Indexing starts at 0 1 :)
Loops for i in range(3):
print(i)
for (i in 0:2){
print(i)
}
List/Vector [0, 1, 2, 3] c(0, 1, 2, 3)
Data Frames import pandas as pd
pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2], 'B': [3, 4]})
data.frame('A' = c(1,2), 'B' = c(3,4))
When typical people say
this, they usually refer to
Type of snake Letter in the alphabet
“R is a language and environment for statistical computing and graphics.”
Source: https://www.r-project.org/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/turbochargeyourdatasciencewithpythonandr-181105003815/85/Turbocharge-your-data-science-with-python-and-r-4-320.jpg)





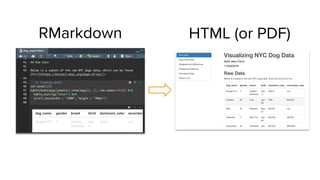

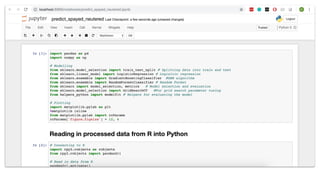

![R in Python with rpy2
Loading the data frame of NYC dogs that was processed in R into Python
can be done with rpy2
import rpy2.robjects as robjects
from rpy2.robjects import pandas2ri
# Read in data from R
pandas2ri.activate()
readRDS = robjects.r['readRDS']
df = readRDS('data/dogs_proc.RDS')
df = pandas2ri.ri2py(df)
R function to read R’s
RDS files](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/turbochargeyourdatasciencewithpythonandr-181105003815/85/Turbocharge-your-data-science-with-python-and-r-16-320.jpg)