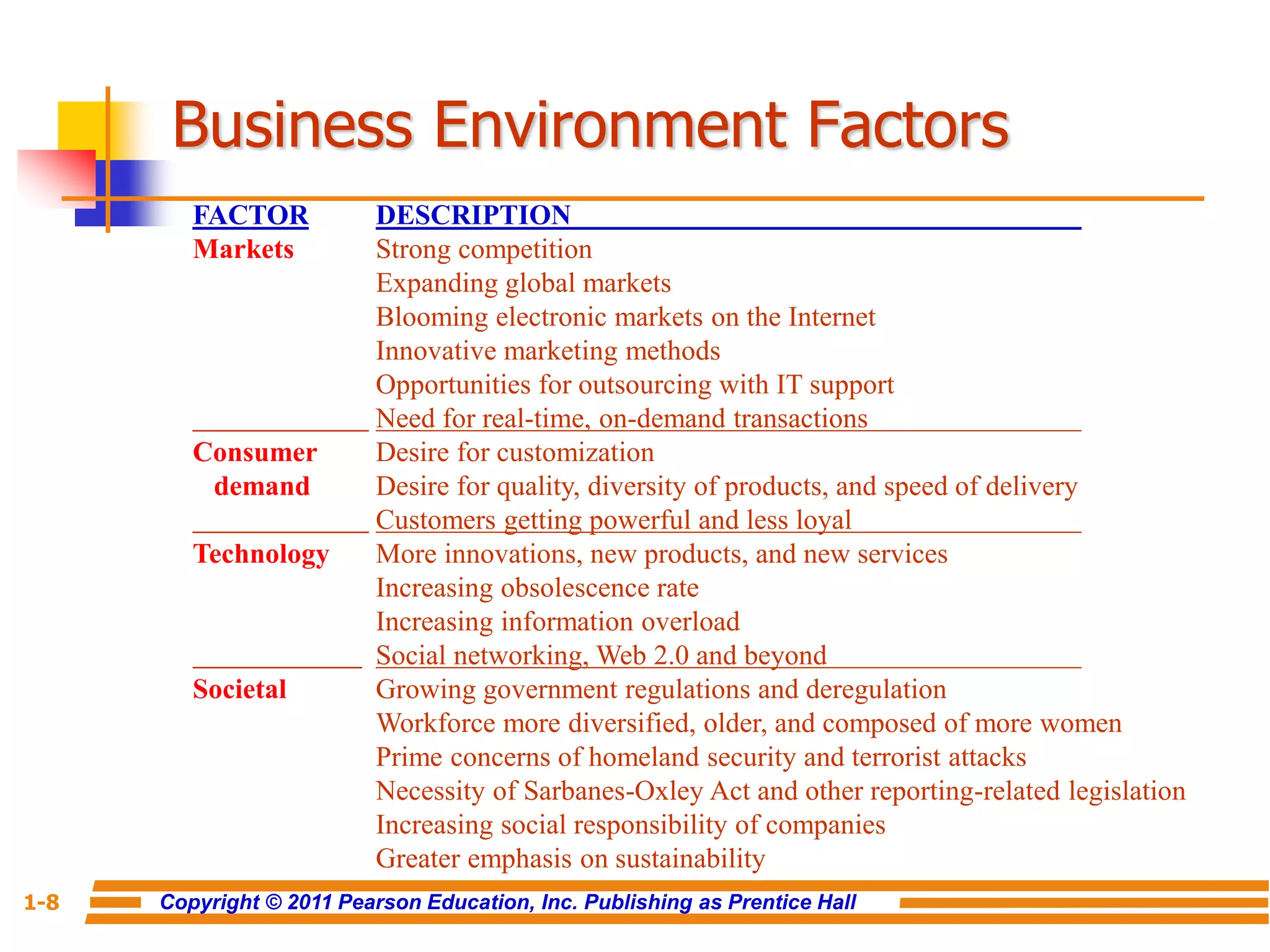
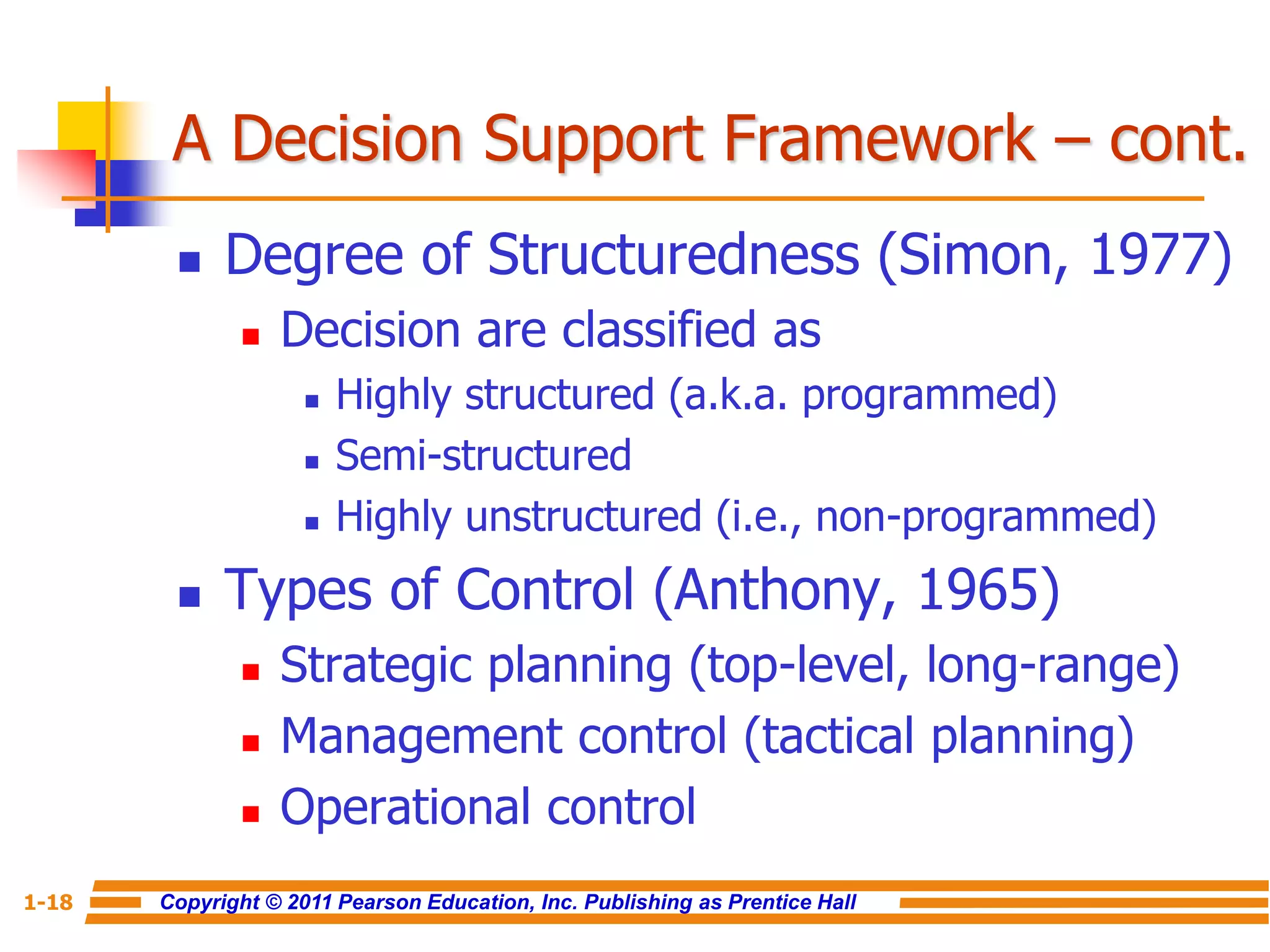
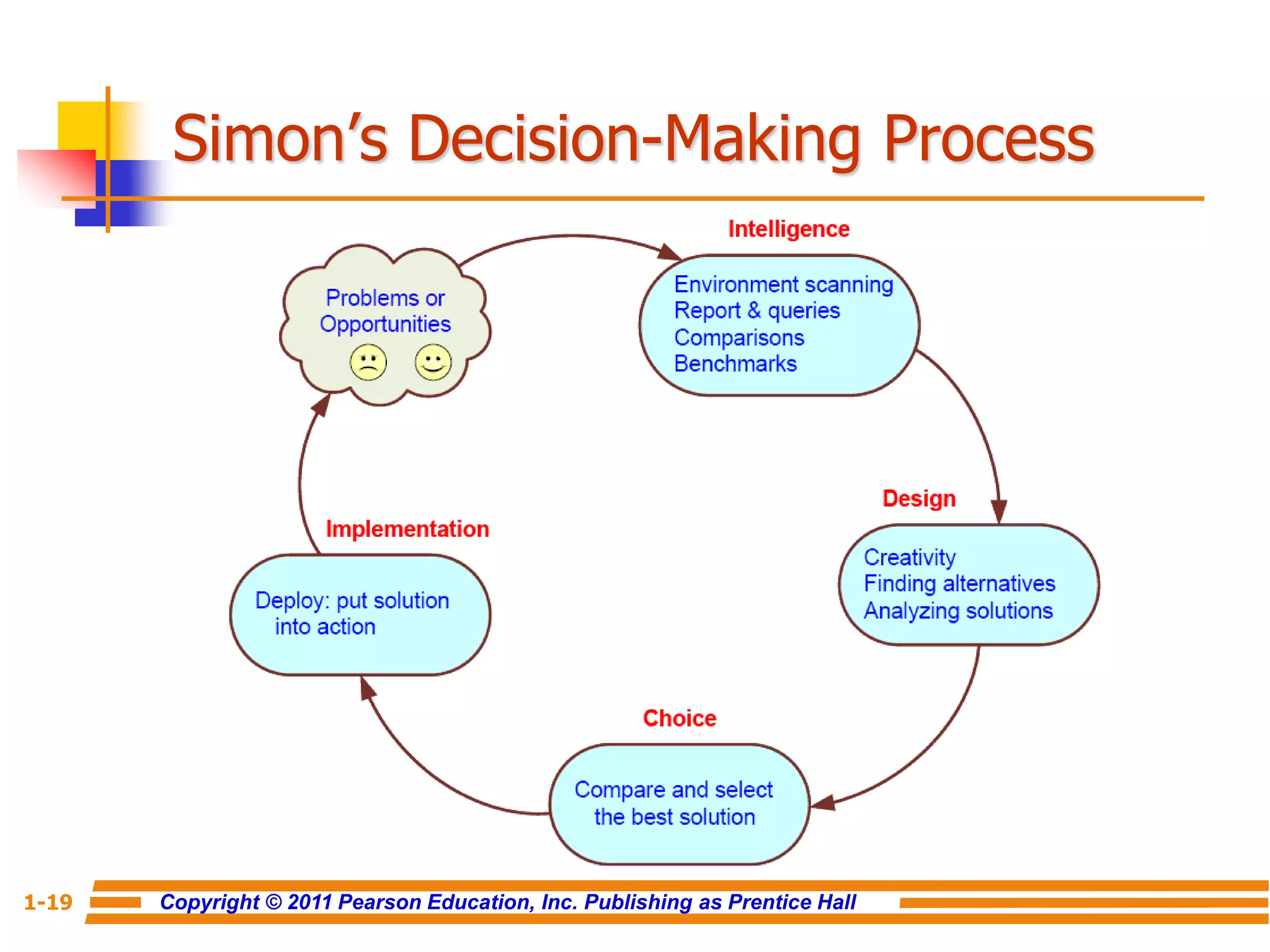
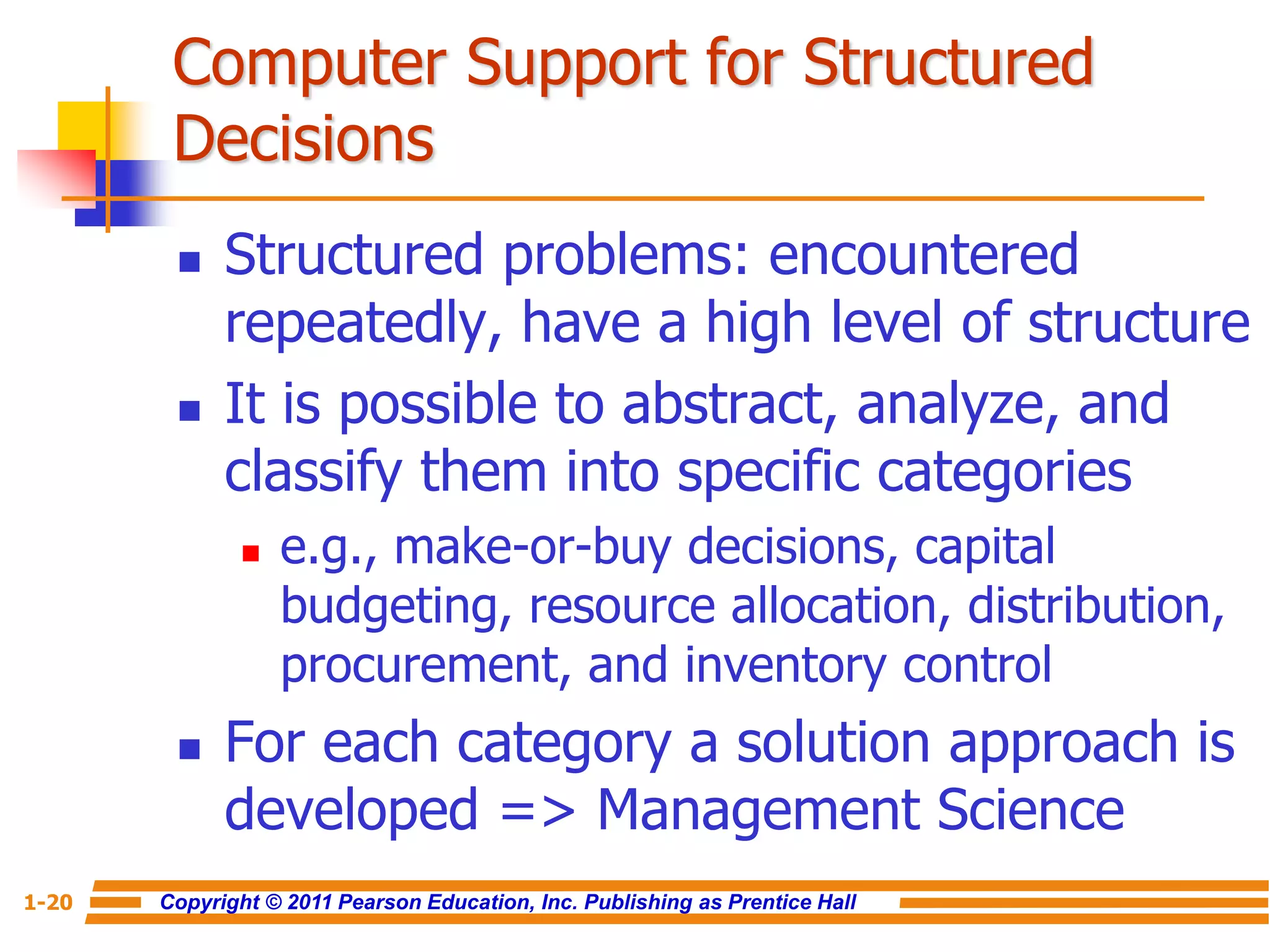
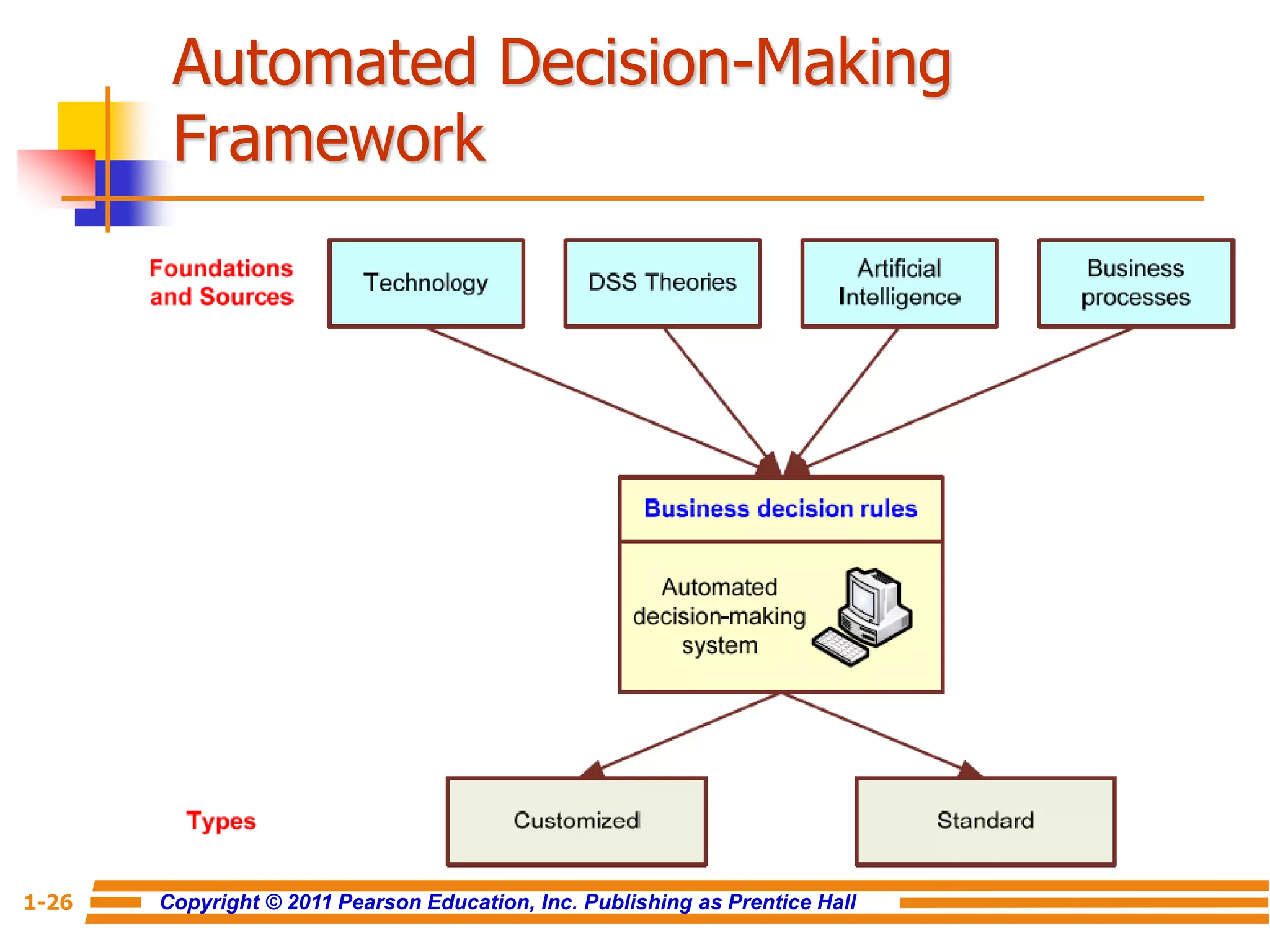
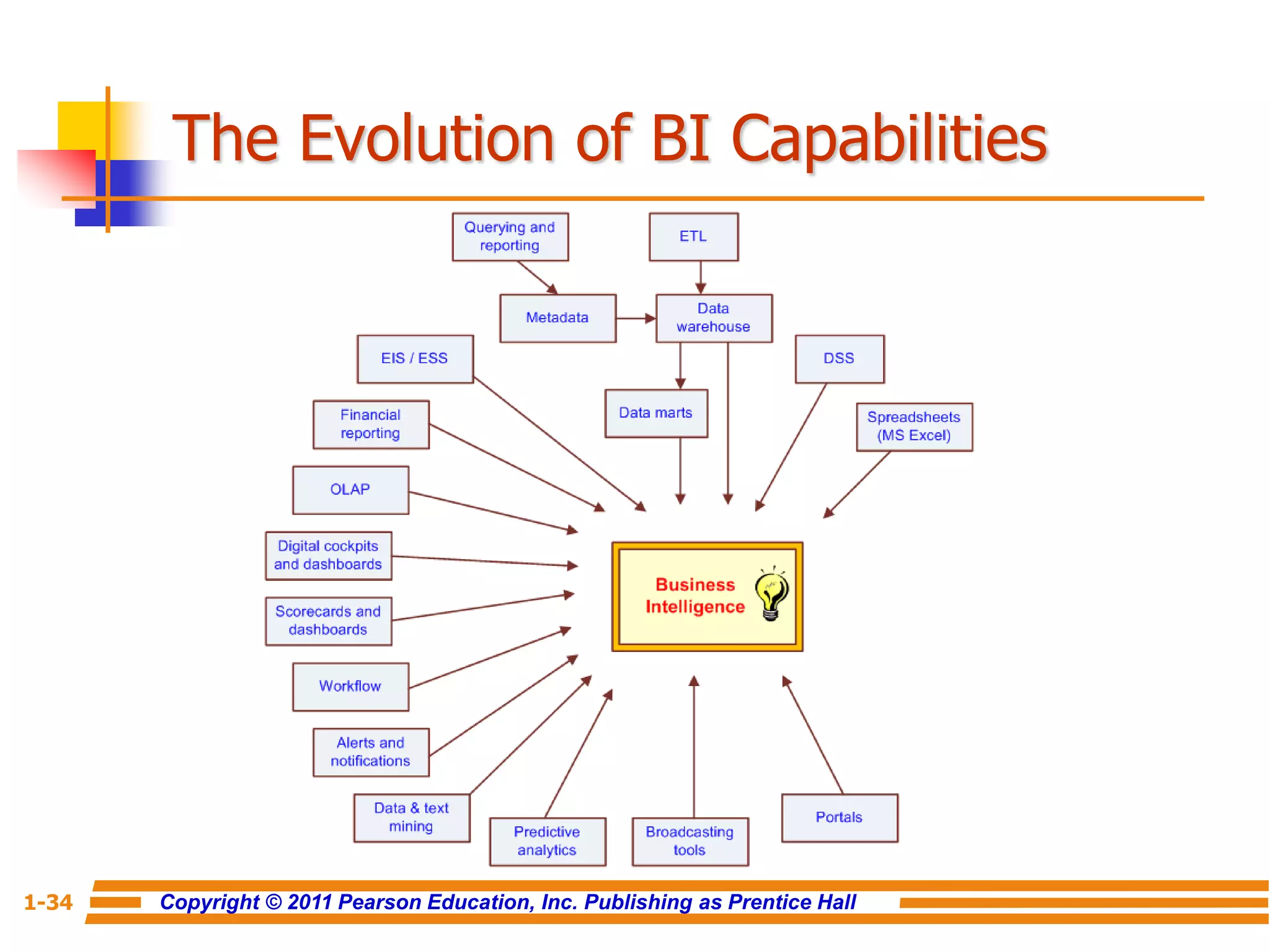
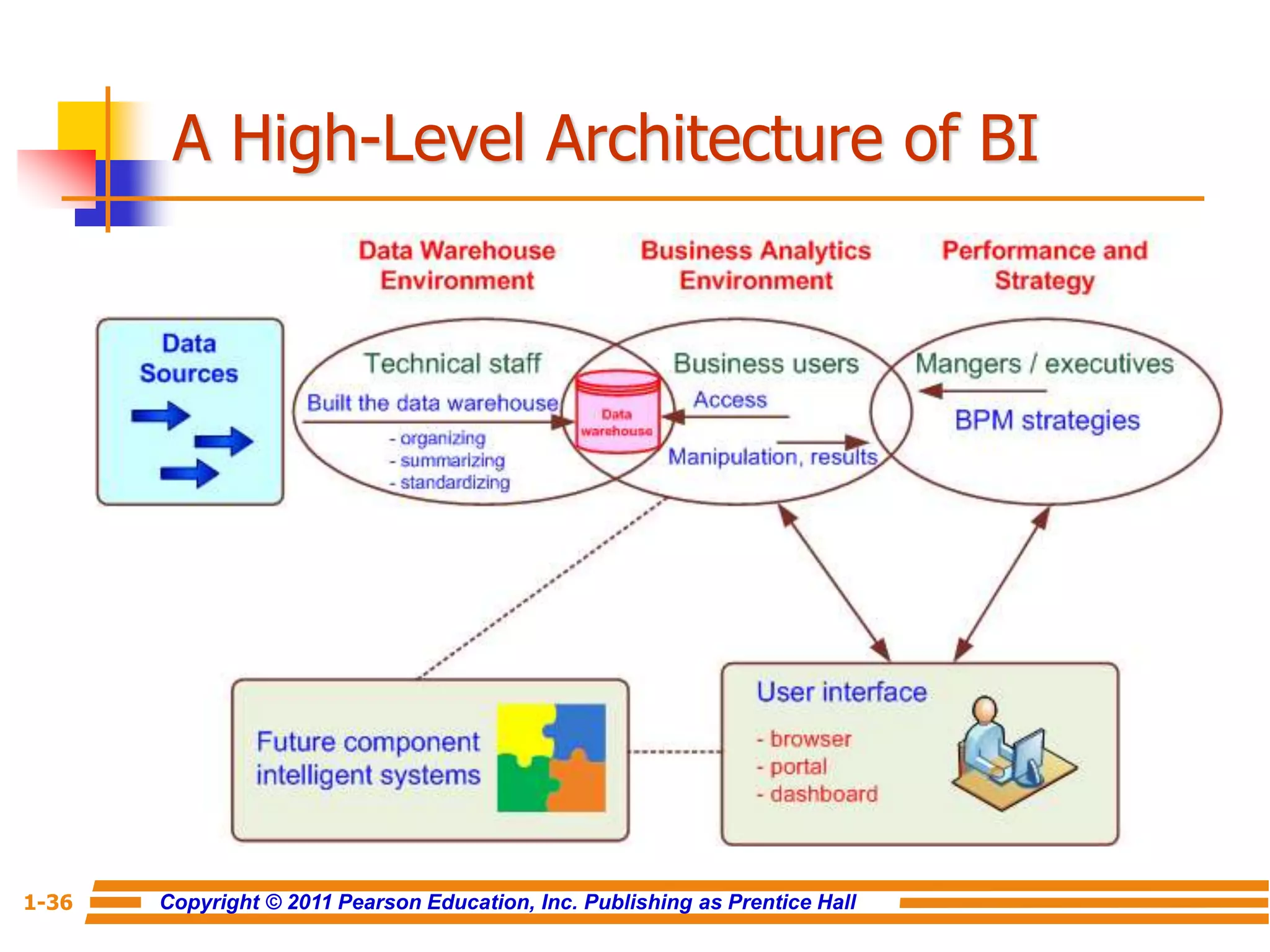
This document discusses decision support systems and business intelligence. It covers the changing business environment that necessitates computerized decision support. It defines decision support systems and describes their evolution into broader business intelligence approaches. The key components of decision support systems and business intelligence architectures are also outlined, including data warehouses, analytics, and user interfaces. Various types of decision support systems and styles of business intelligence are described.