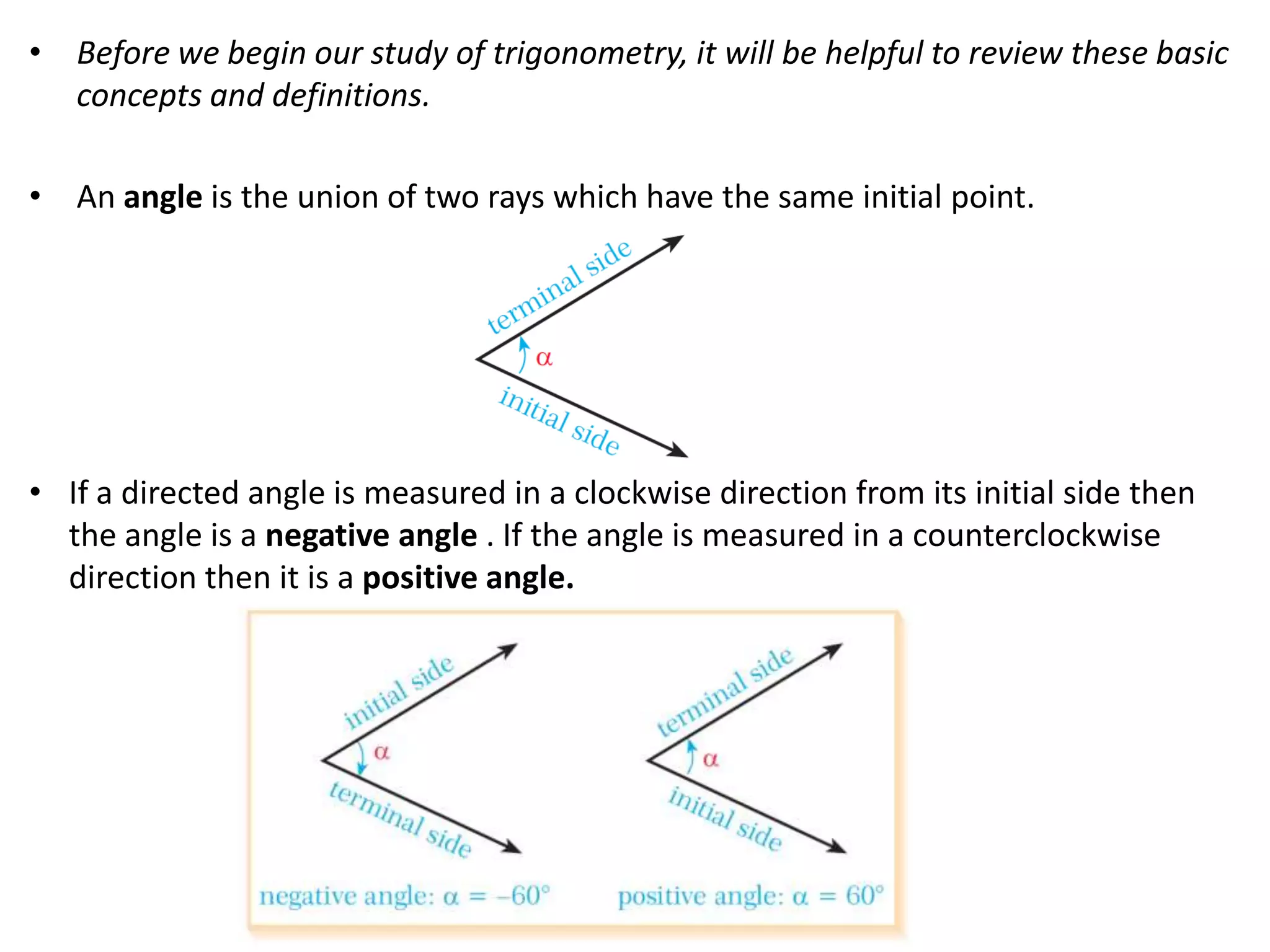
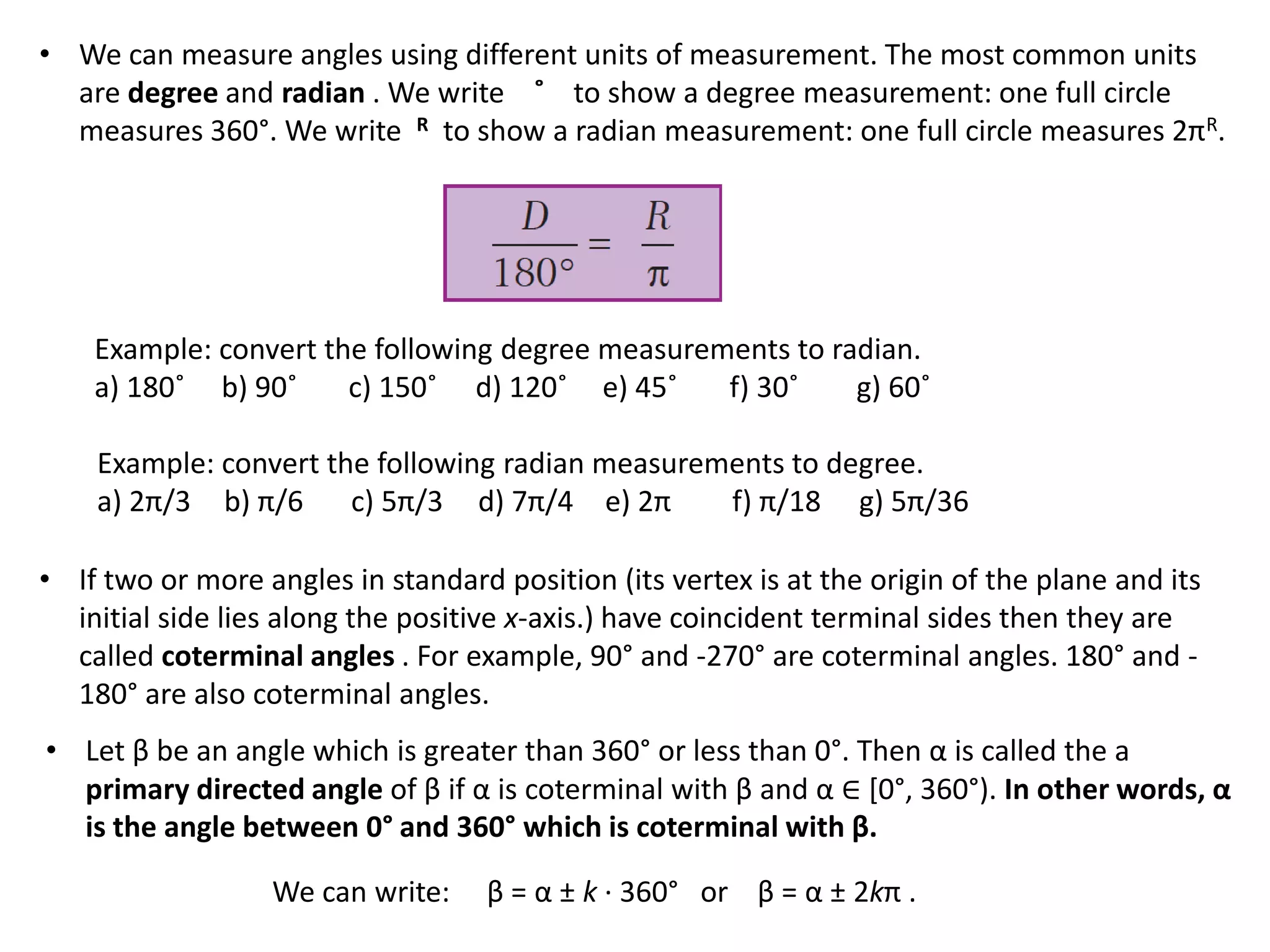
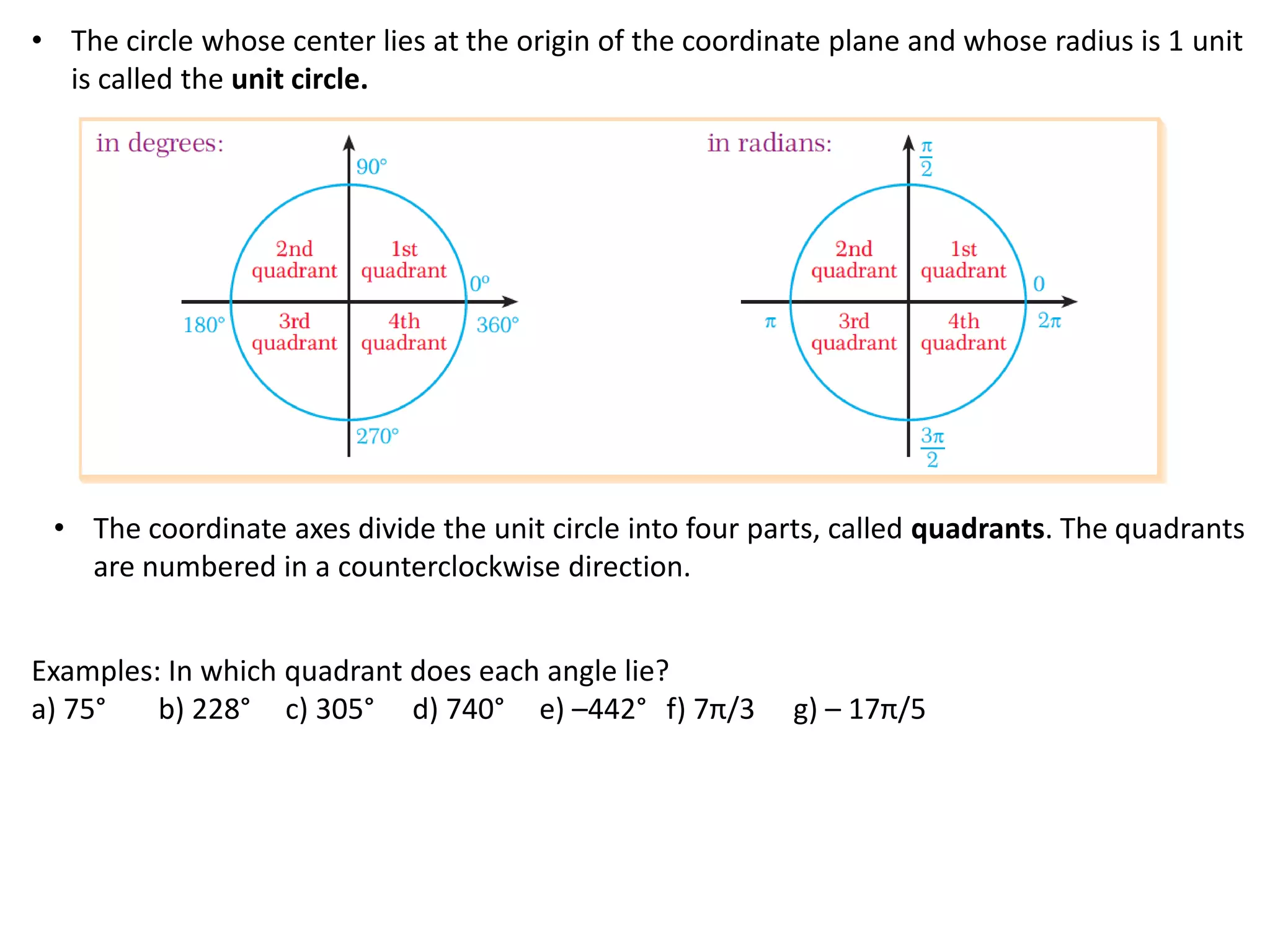
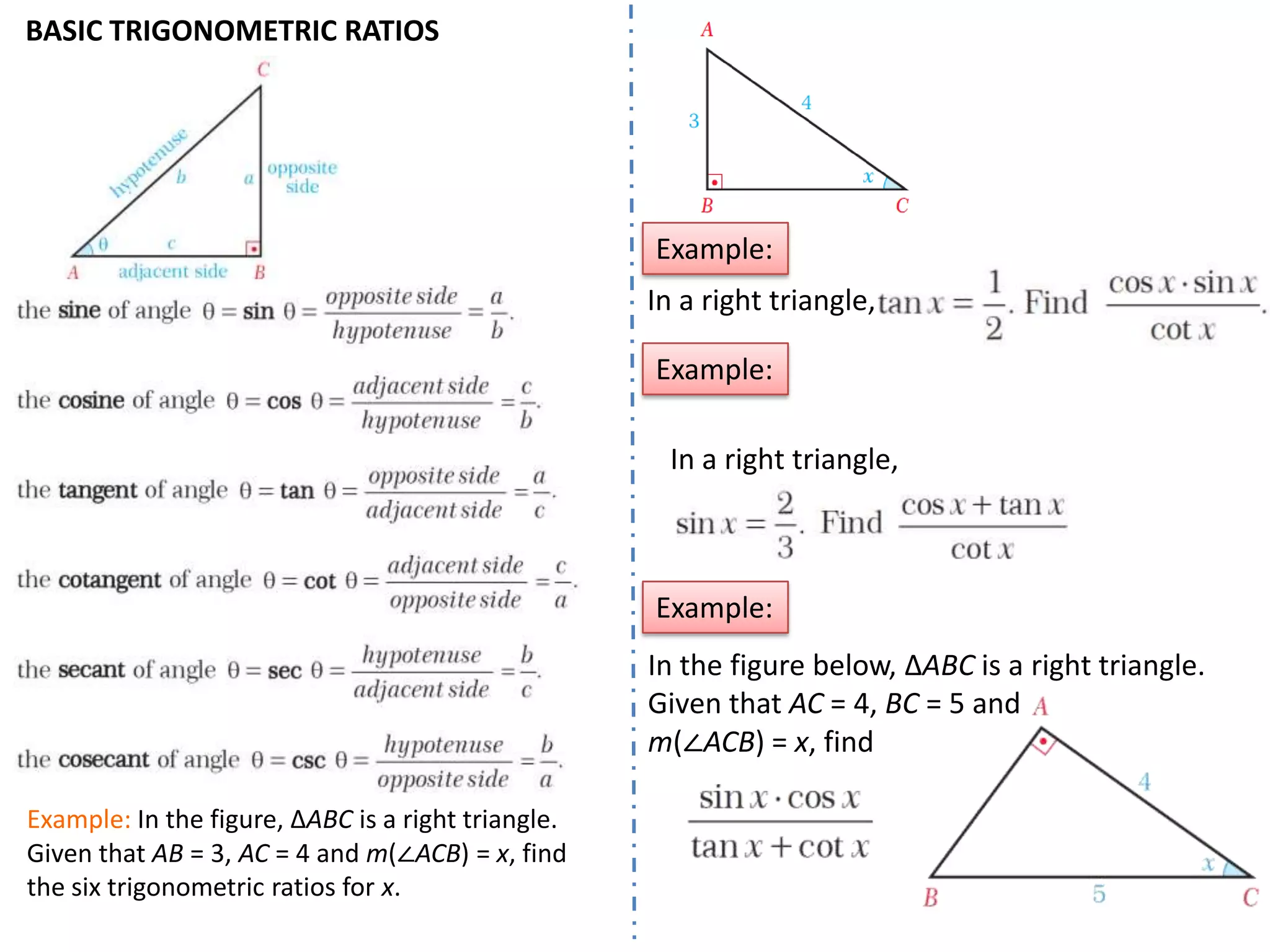
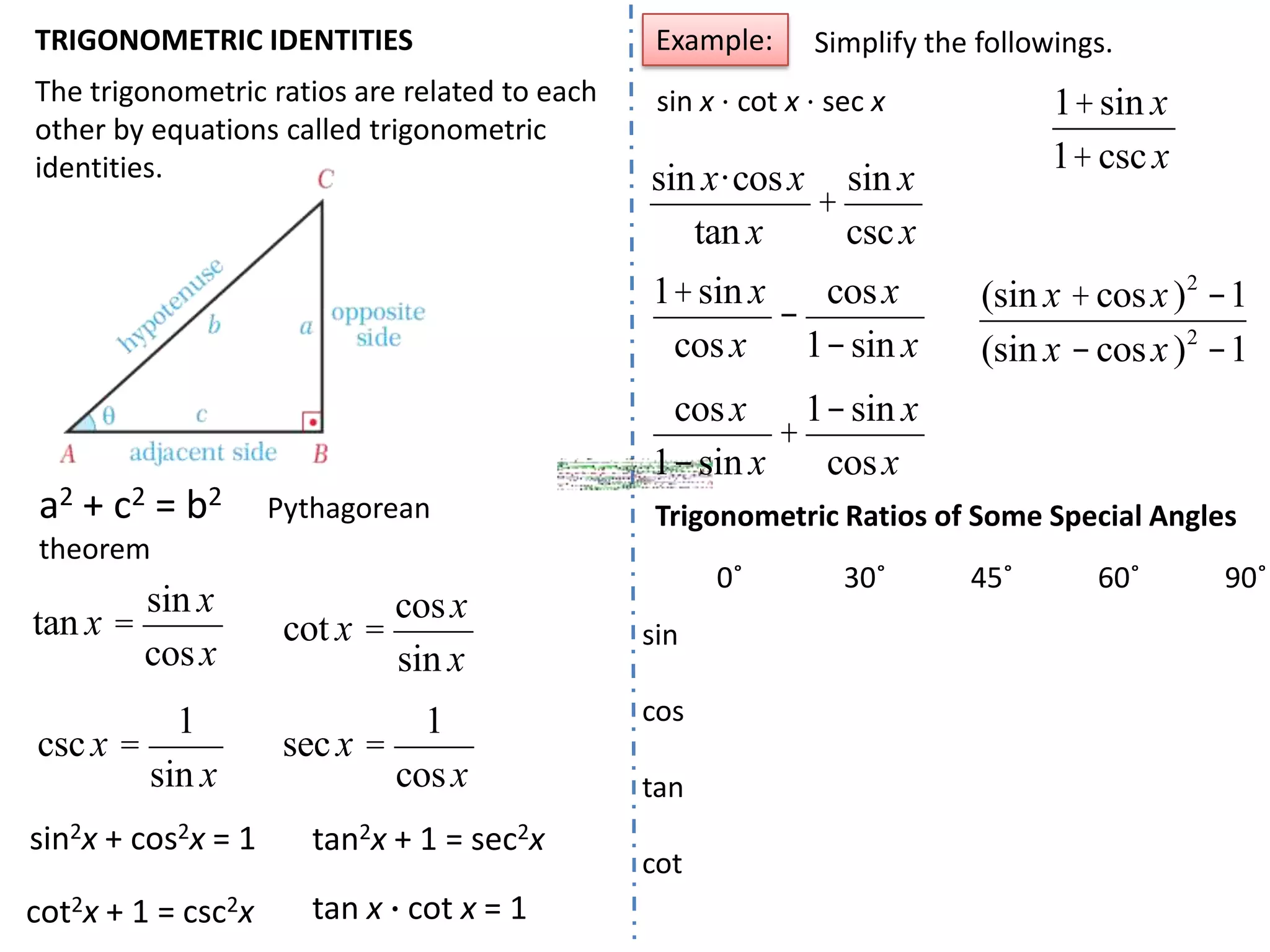
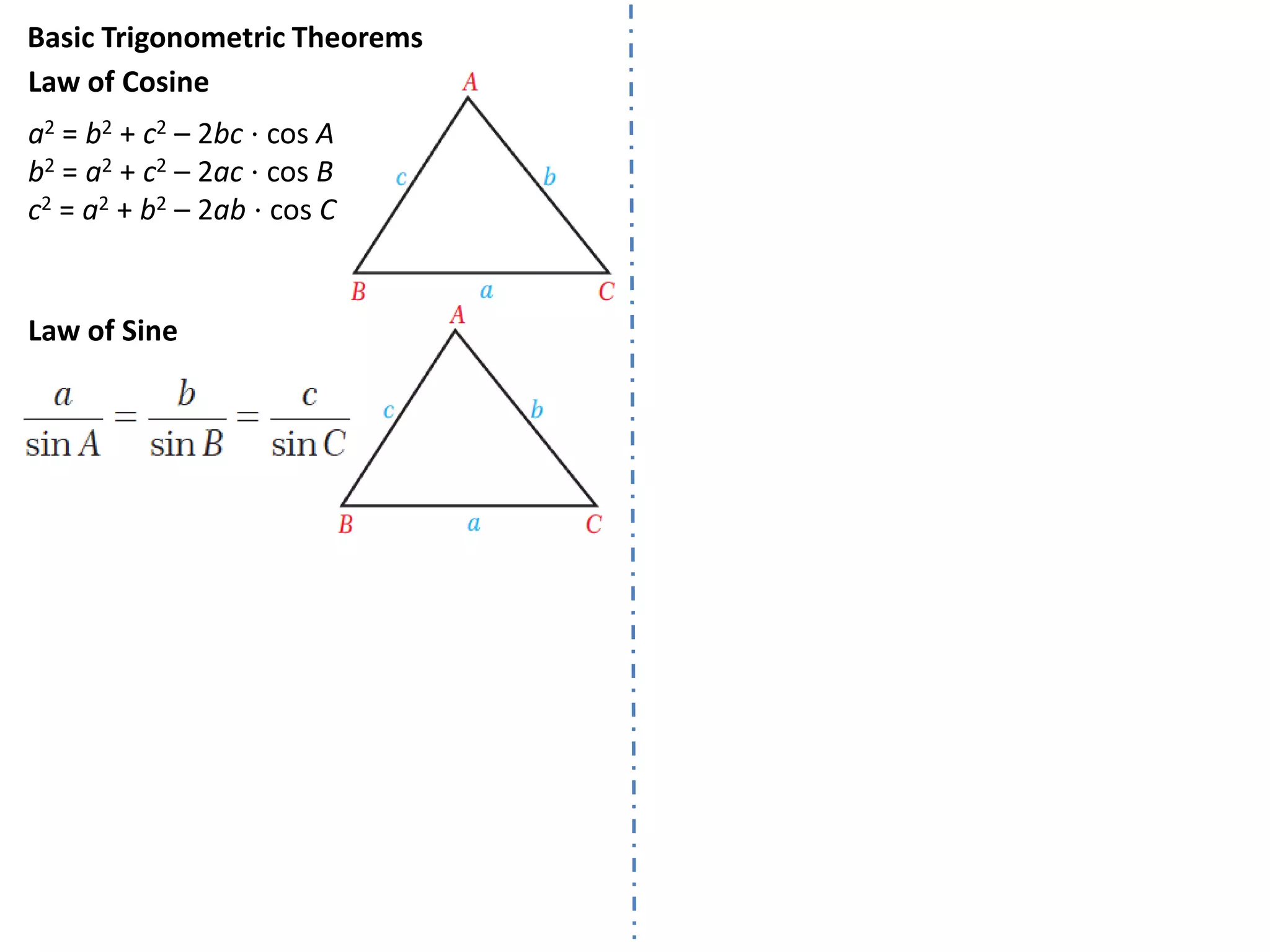
Trigonometry involves measuring angles and relationships between sides and angles of triangles. There are six trigonometric ratios - sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant and cosecant - that relate the measures of sides and angles. Angles can be measured in degrees or radians and converted between the two units. Important trigonometric identities relate the ratios to each other and allow trigonometric functions of combined angles to be simplified.