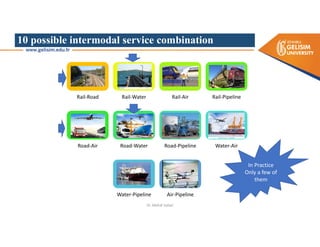
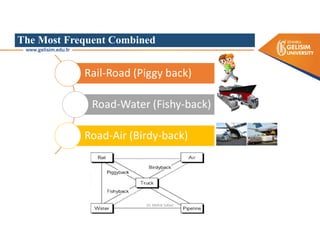
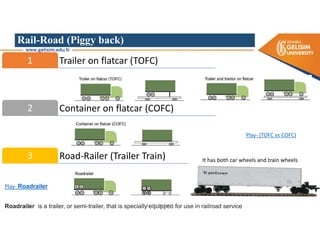
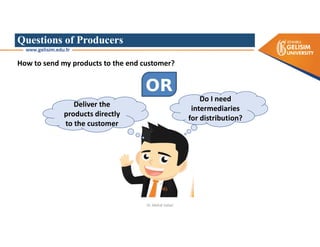
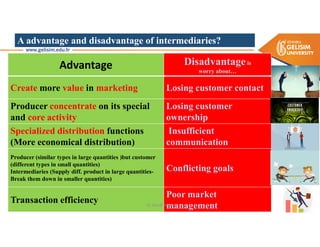
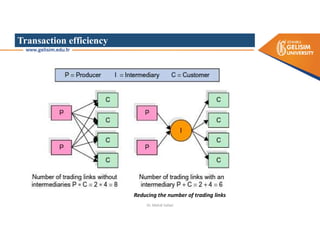
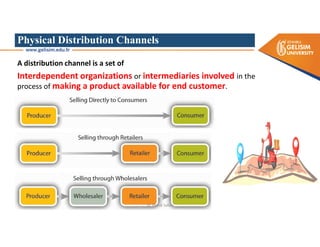
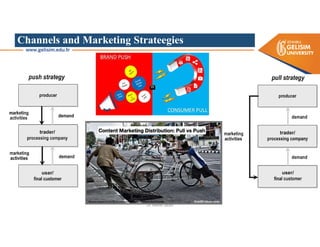
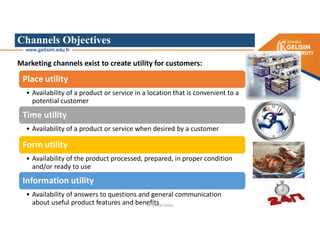
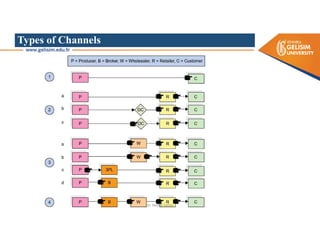
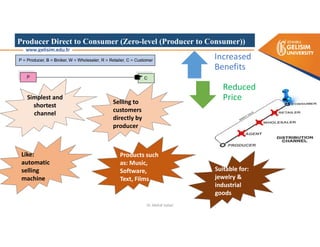
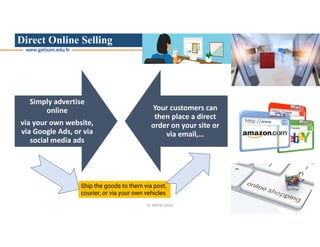
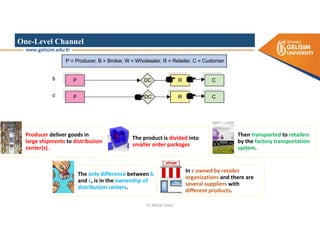
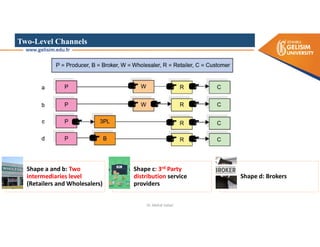
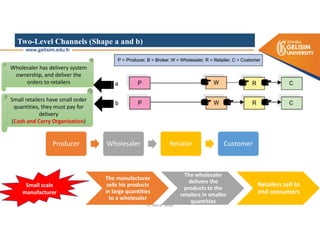
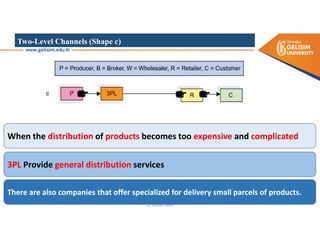
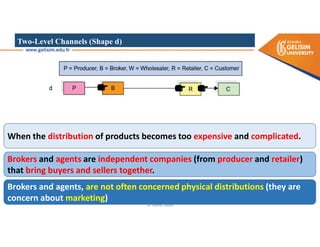
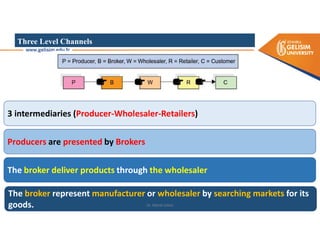
The document discusses various intermodal transportation options and their combinations, including rail-road, rail-water, rail-air, and rail-pipeline. It notes that in practice, only a few of the 10 possible combinations are commonly used, with the most frequent being rail-road, road-water, and road-air. The document then provides more details on rail-road transportation in the forms of trailer on flatcar, container on flatcar, and roadrailer.