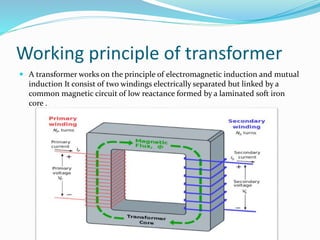
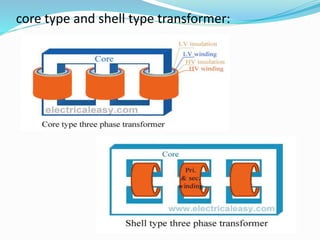
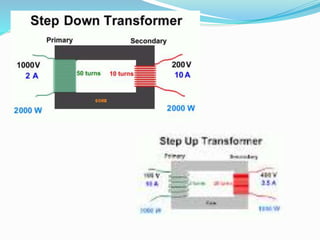
The document provides an overview of transformers, which are devices that transfer electrical power between circuits with a change in voltage or current but no change in frequency. It explains the working principle based on electromagnetic induction, types of transformers, and their applications in various fields. Additionally, the document contrasts ideal transformers with practical ones, highlighting their differences in efficiency and losses.