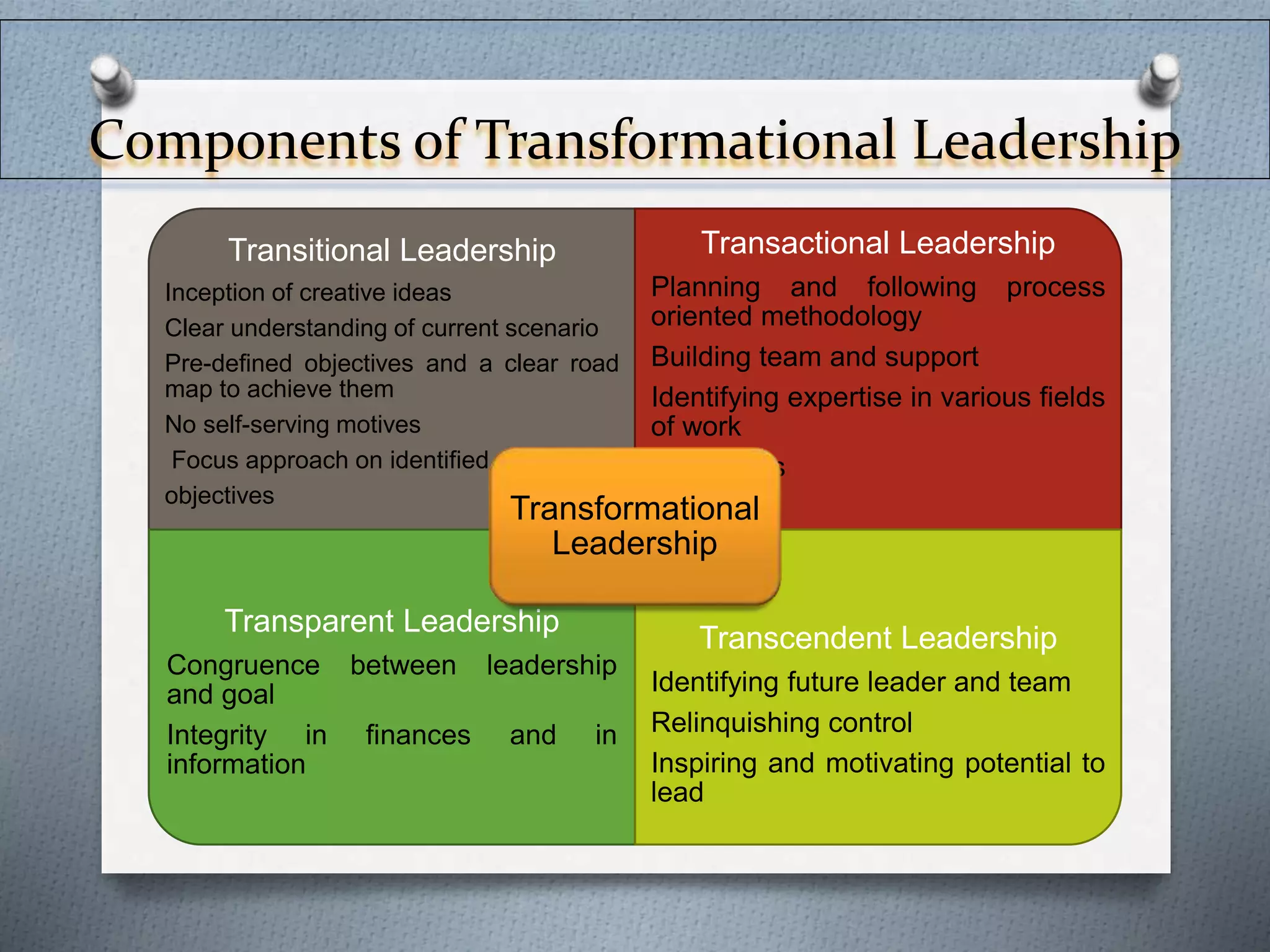
Transformational leadership theory aims to inspire followers to accomplish more than expected by raising morale and motivating followers to consider group goals over self-interest. The theory was first proposed in the 1970s and further developed by Bass in the 1980s, identifying four components of transformational leadership: idealized influence, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation, and individualized consideration. Transformational leadership can increase performance, job satisfaction, and develop future leaders compared to transactional leadership. However, it also lacks conceptual clarity and depends on the ability of leaders to demonstrate transformational behaviors.