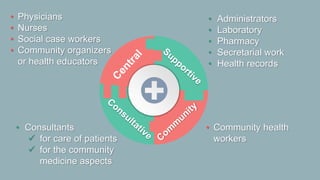
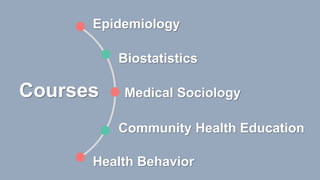
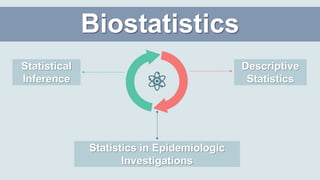
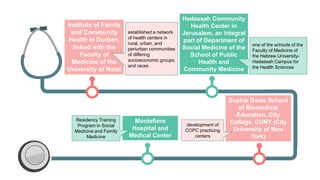
This document discusses the training needed for community-oriented primary care (COPC). It states that COPC requires practitioners trained in a unified approach to community medicine and primary health care. It also discusses the importance of COPC training facilities being attached to university health science faculties. The document outlines the types of training needed for various roles in COPC, including epidemiology, biostatistics, medical sociology, and clinical experience in community health care, family health care, and working with a health team. It provides examples of COPC training centers linked with medical schools and schools of public health.