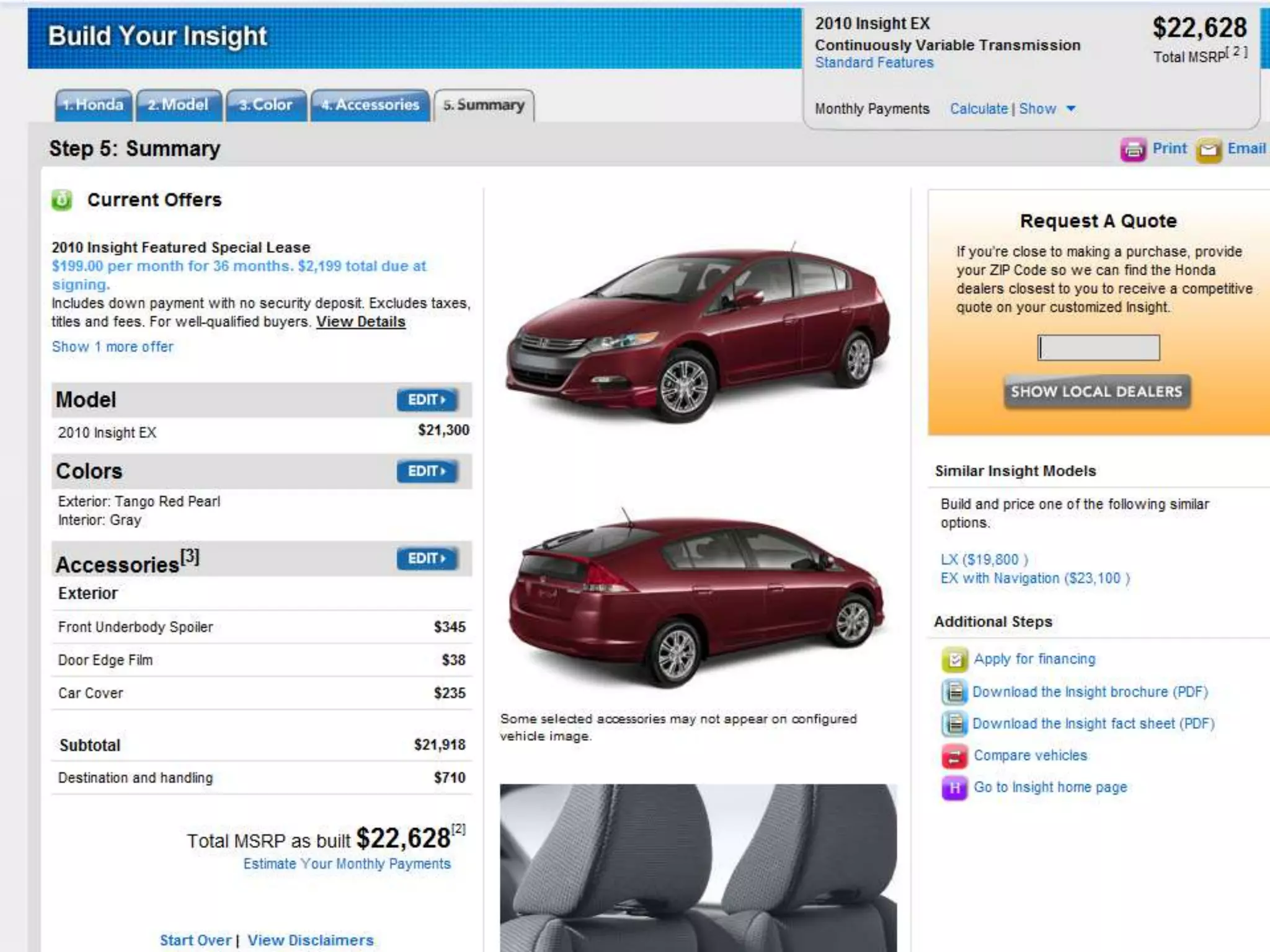
1) The document discusses emerging trends in digital technologies and service innovation, including new economic, social, and business models driven by advances in digitization and the web.
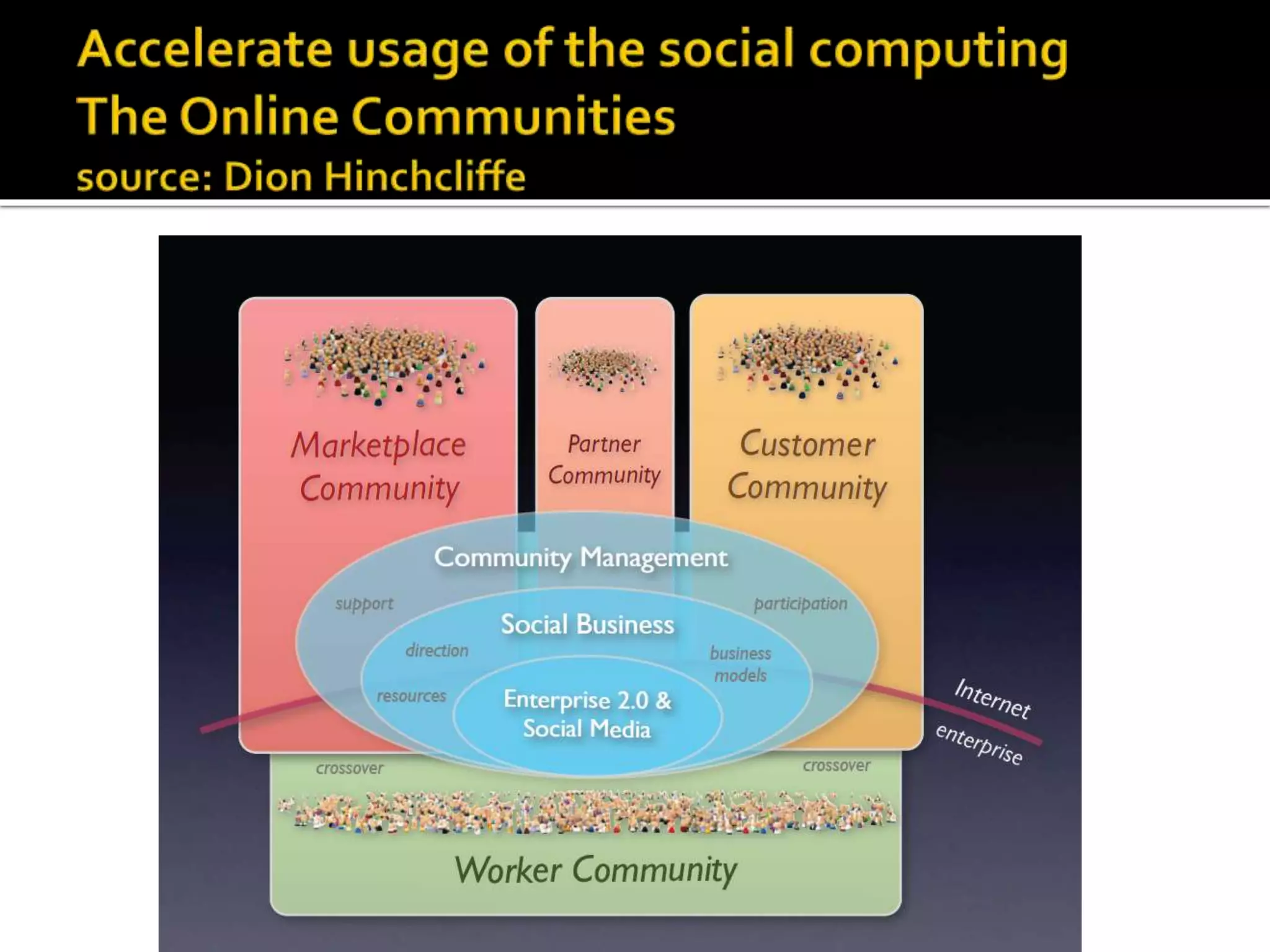
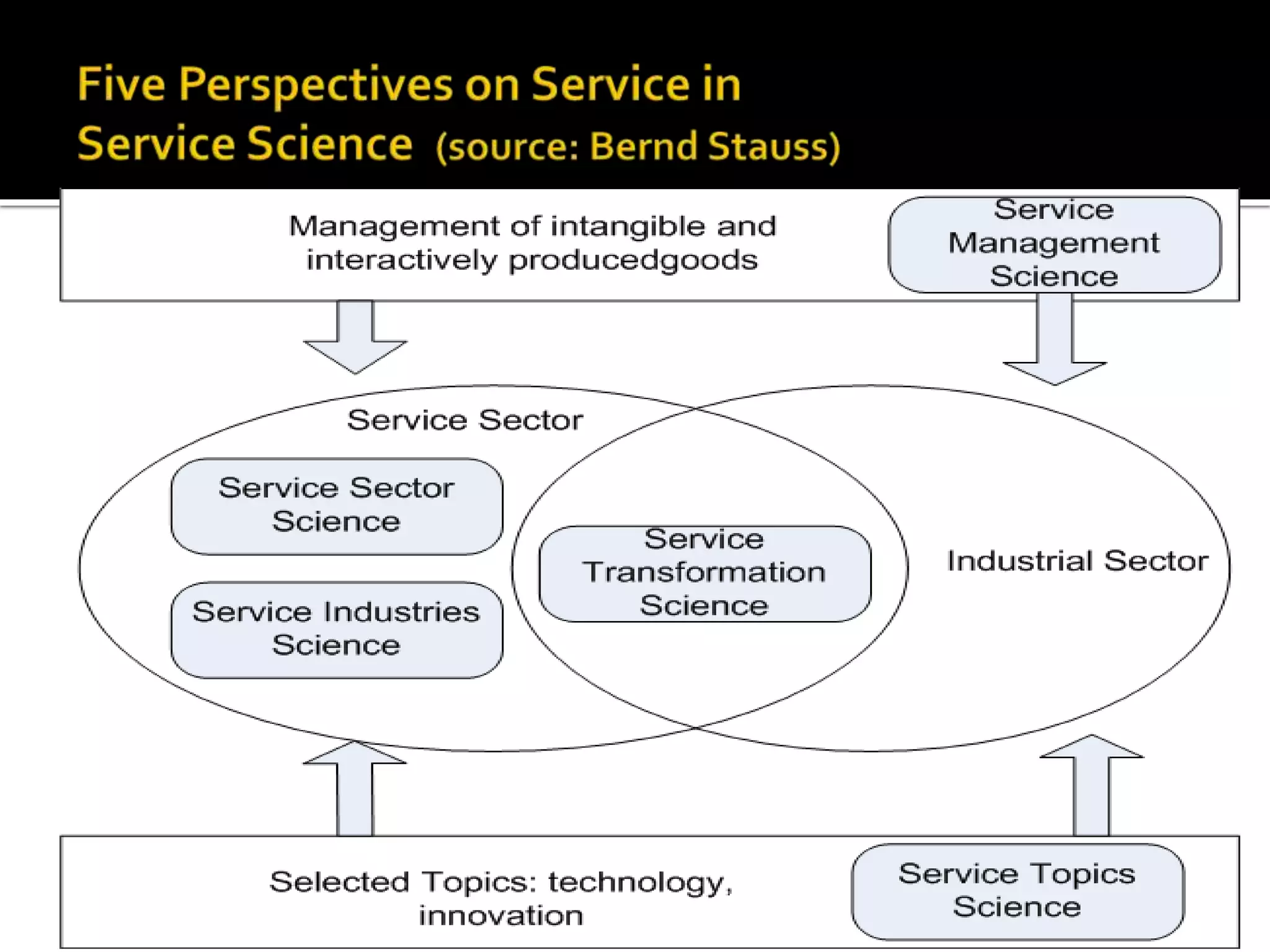
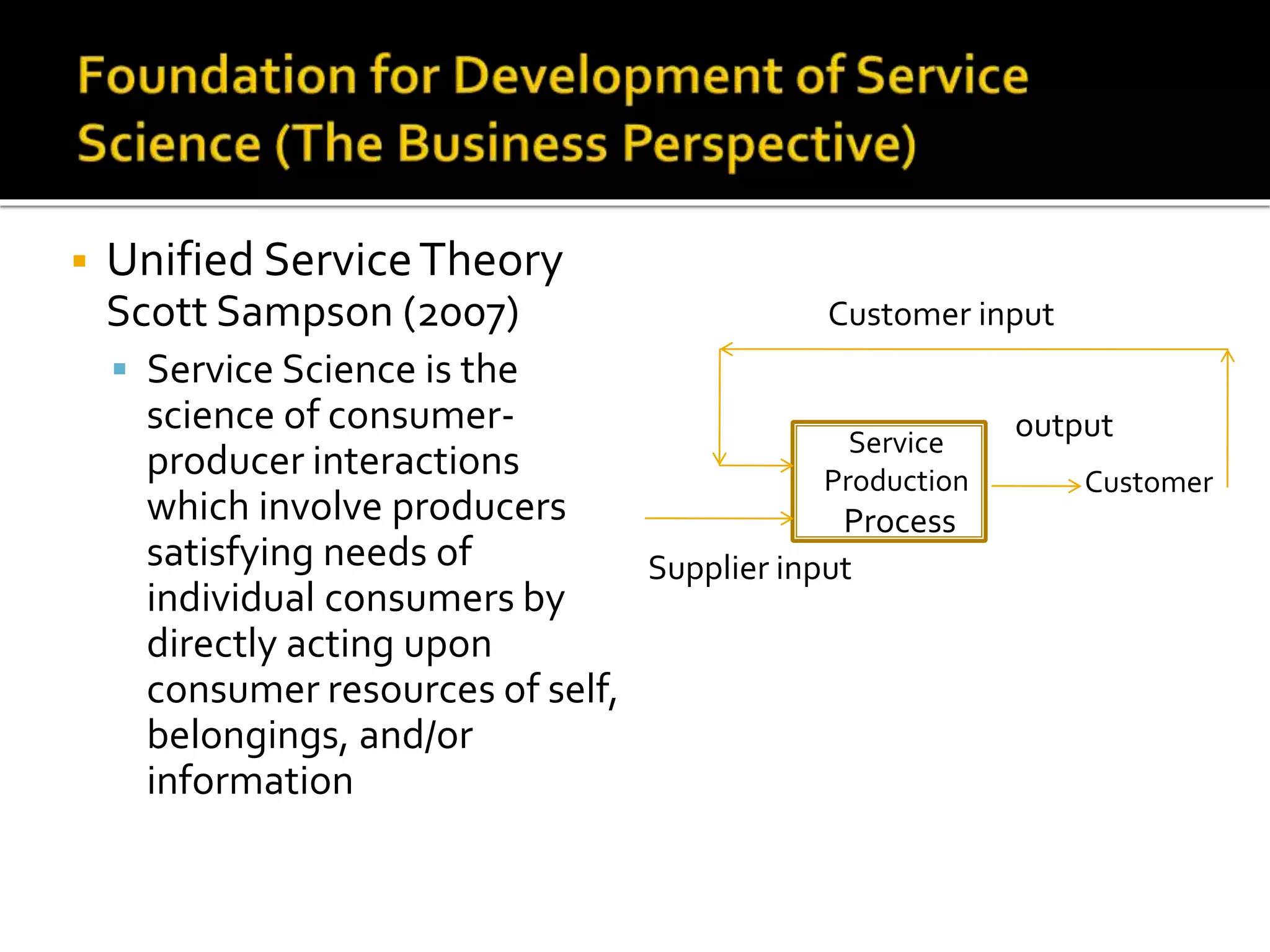
2) Key topics covered include service science, the importance of technological enhancement and applying social computing to services, and case studies of companies innovating their services through smart products and transforming their business models.
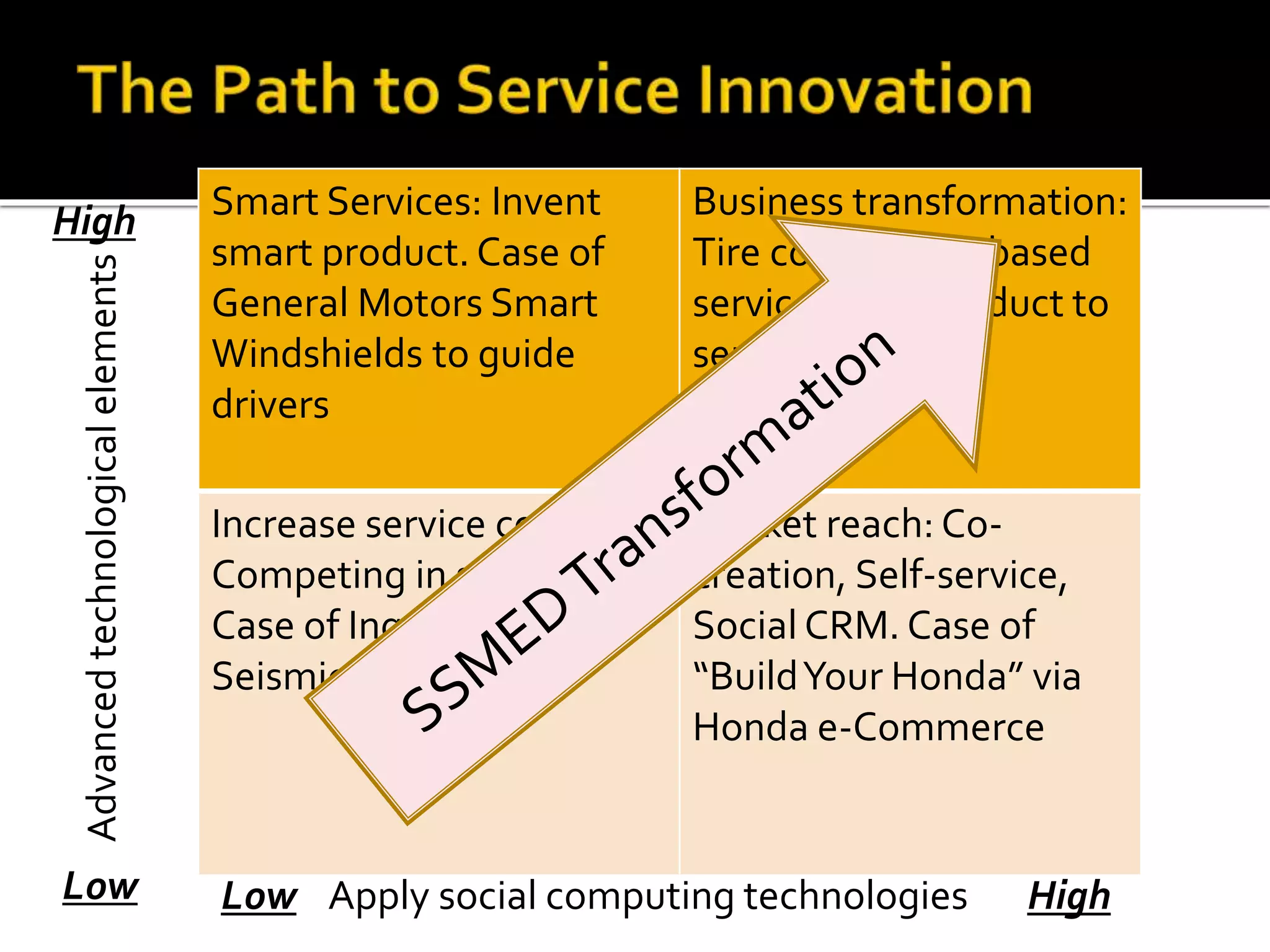
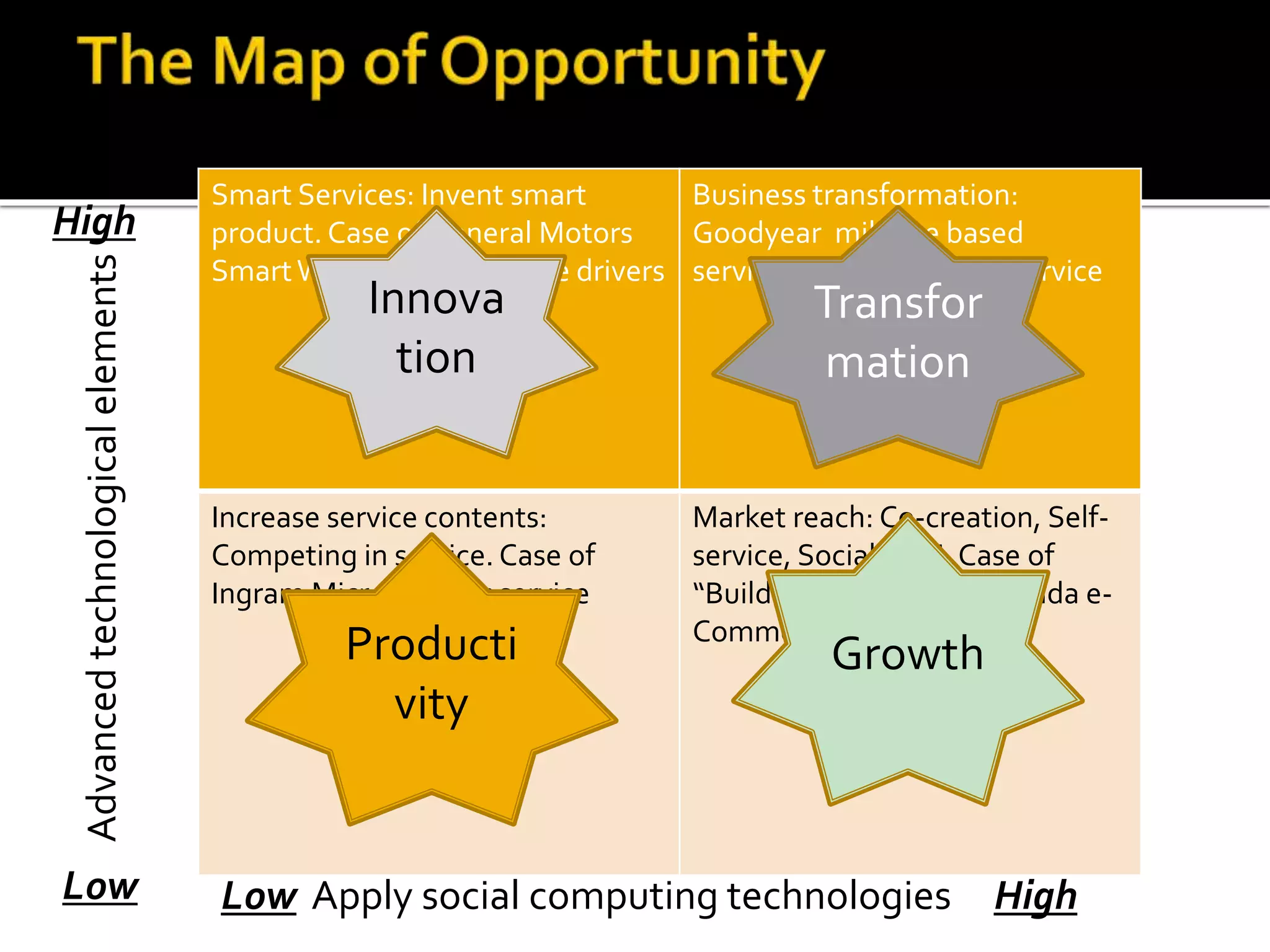
3) The presentation maps different approaches to service innovation along axes of technological enhancement versus applying social computing and outlines remaining challenges in service science, management, engineering, and design.