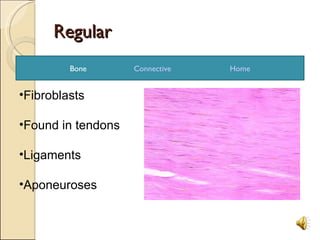
There are four main types of tissues in the human body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues cover and line body surfaces, and can be simple or stratified. Connective tissues are found throughout the body and include bone, cartilage, blood, adipose, and fibrous tissues that connect and support other tissues. Muscle tissues include skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle. Nervous tissues are made up of neurons and neuroglia and are responsible for processing and transmitting information.