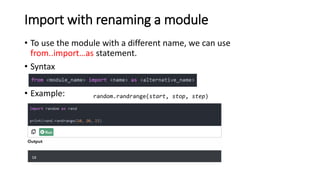
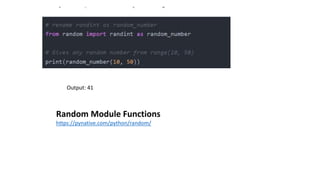
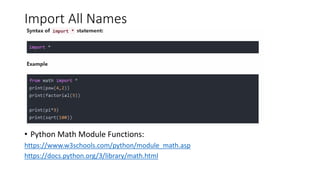
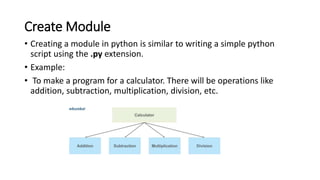
The document discusses Python modules, emphasizing their importance in organizing code and functionality, with distinctions between built-in and user-defined modules. It also highlights how to import modules and their various capabilities, including data manipulation, statistical analysis, and data visualization using the pandas library. Additionally, it covers applications of pandas in data cleaning, exploration, preparation, and analysis, along with its integration with other libraries for enhanced data insights.