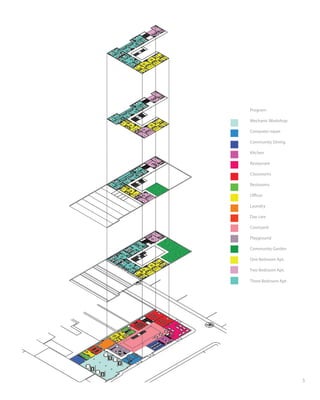
1) The document presents a master's thesis project that aims to address Mexico City's housing problem through designing a building in the Atlampa neighborhood.
2) The building would provide both housing and vocational education opportunities for low-income residents. It would include classrooms, workshops, a restaurant, and apartments of various sizes.
3) The goal is to help improve residents' quality of life by providing housing, work, education, recreation, and social engagement through public spaces integrated into the design.