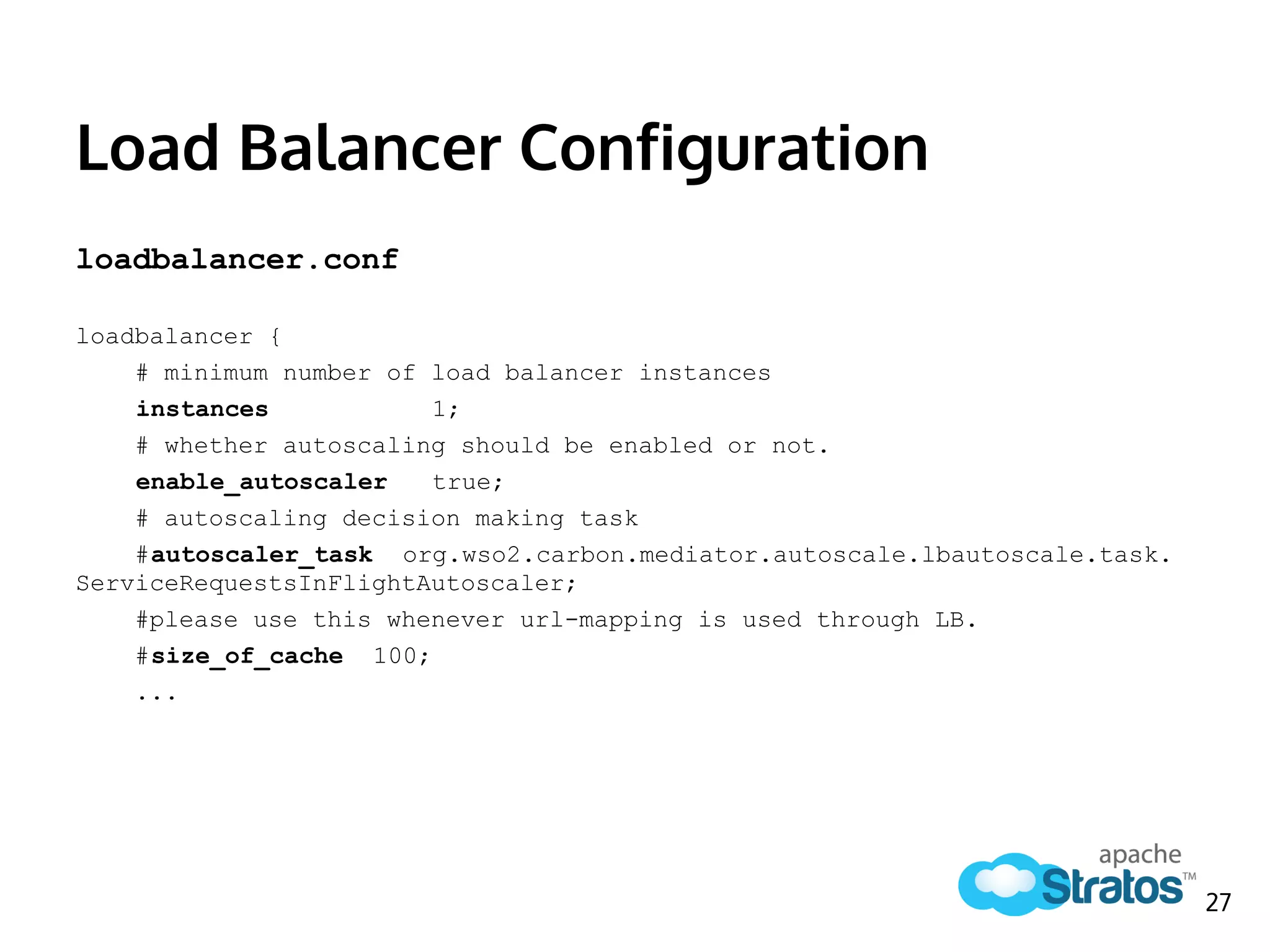
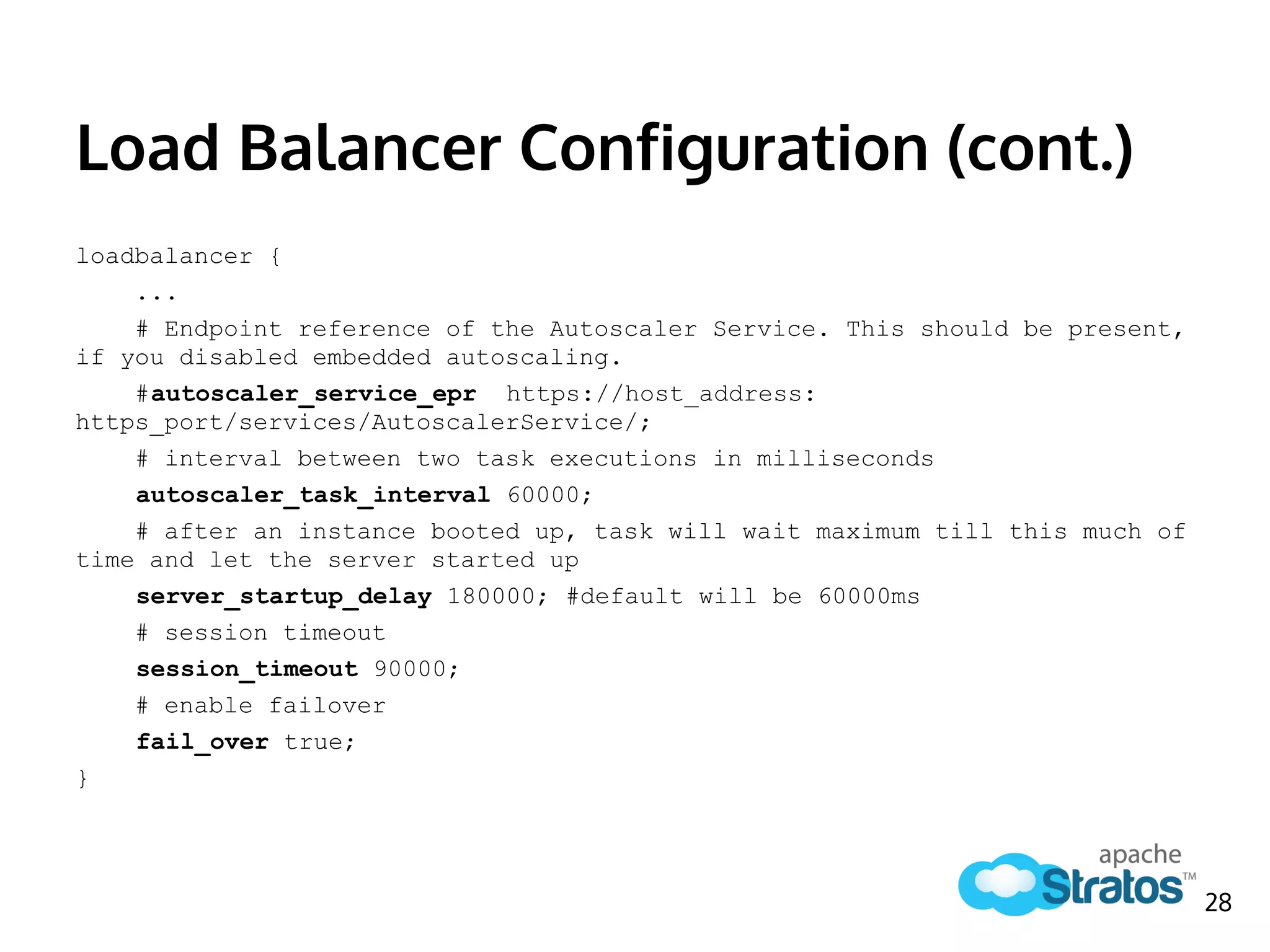
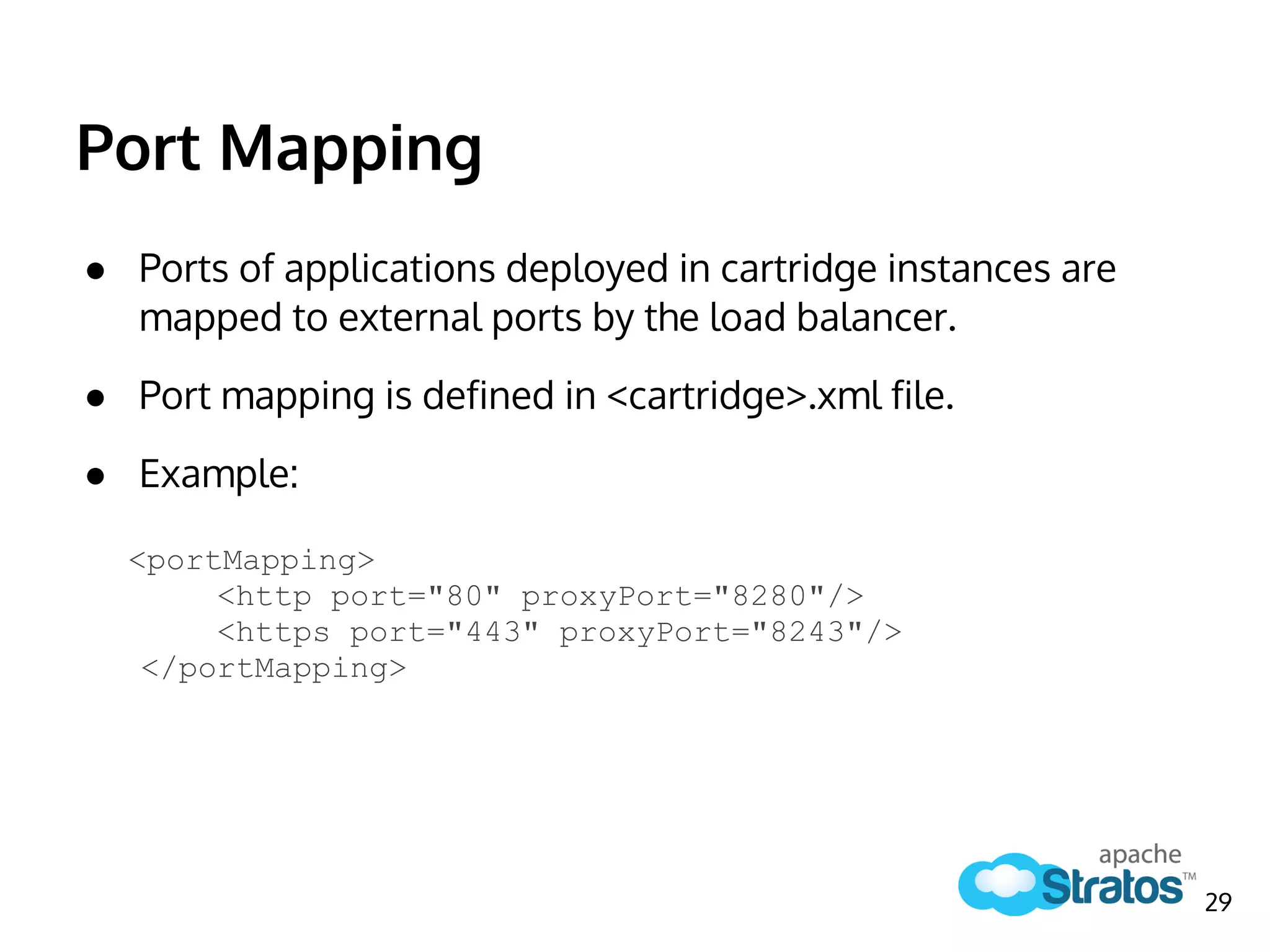
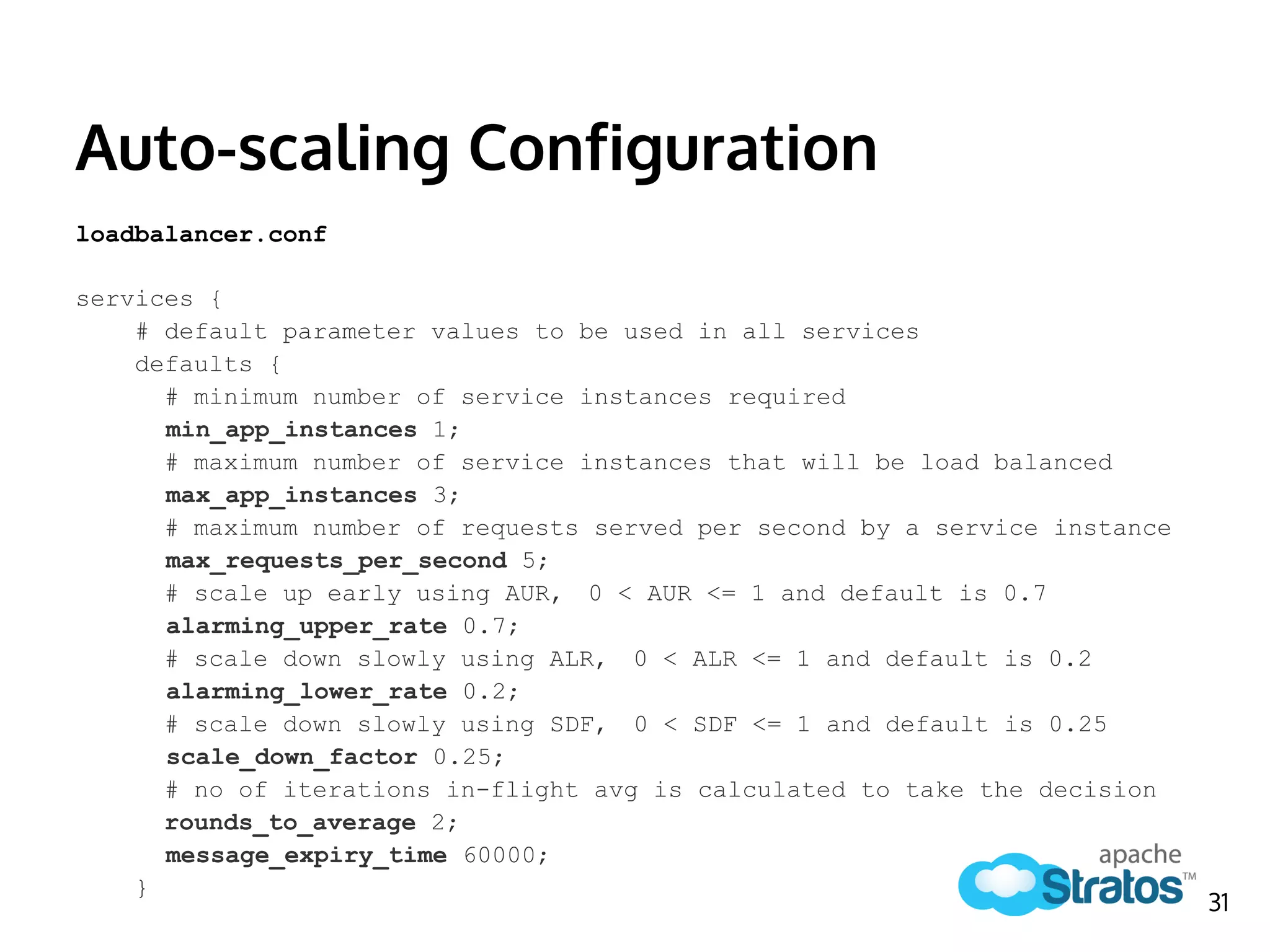
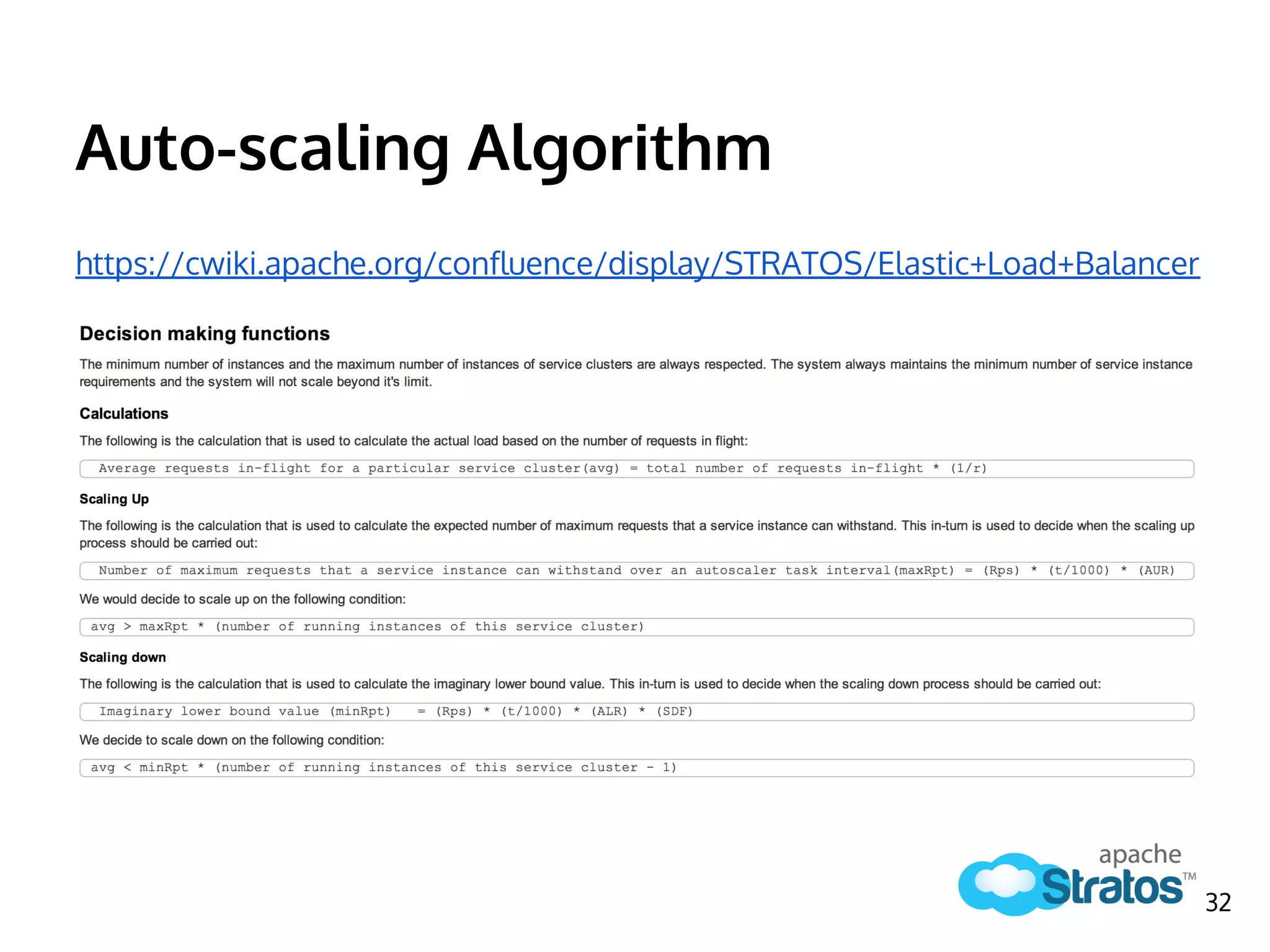
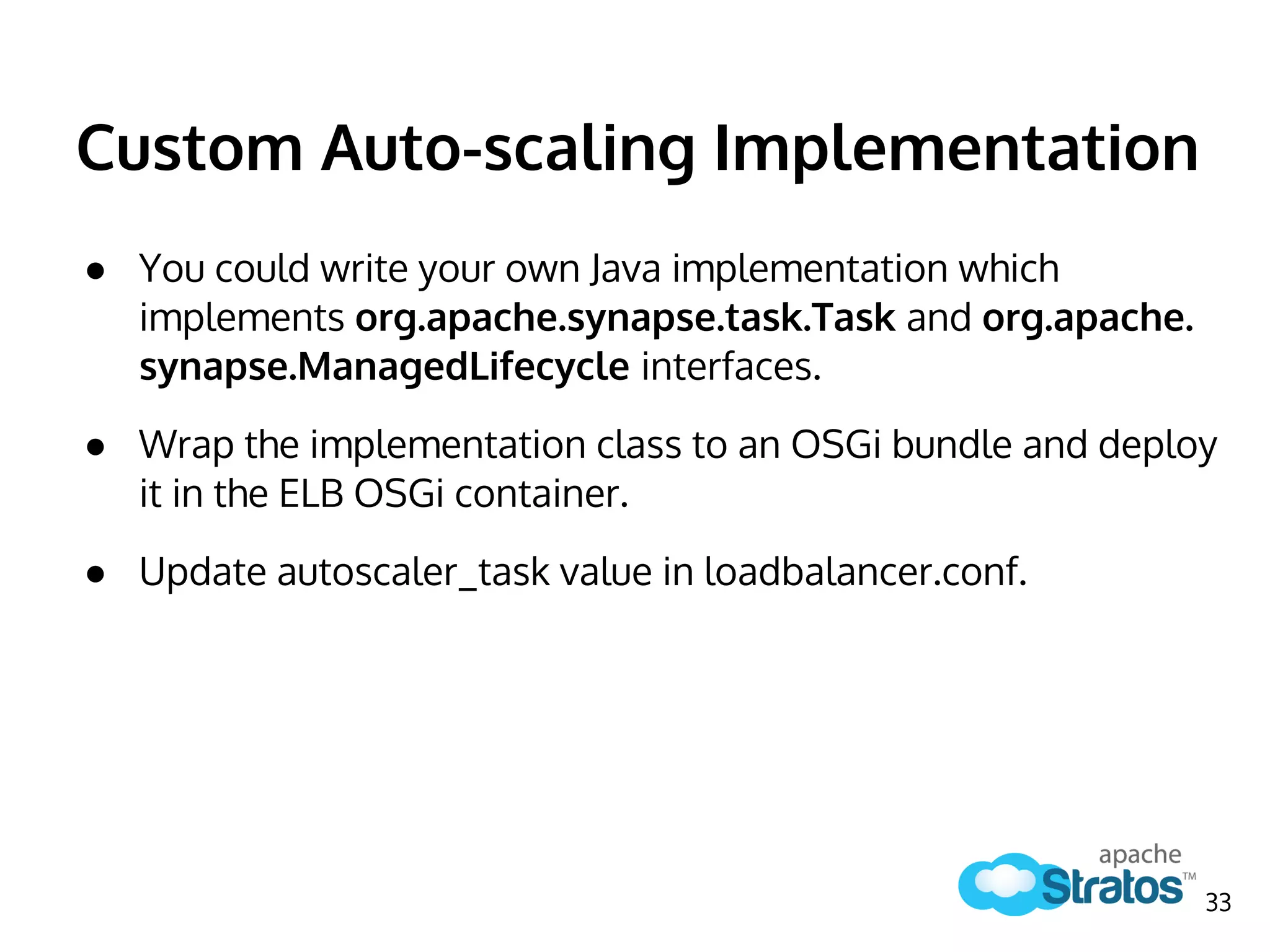
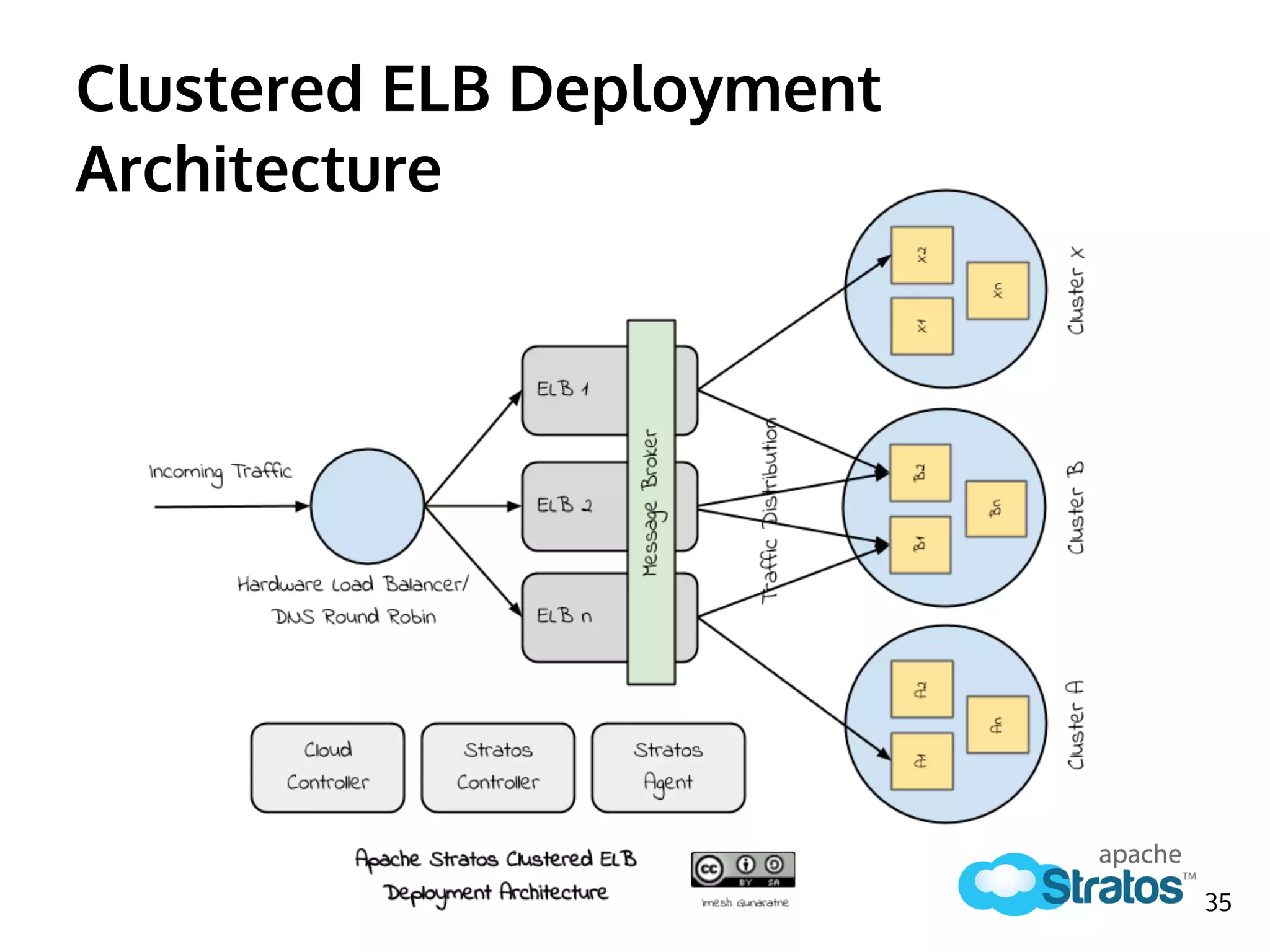
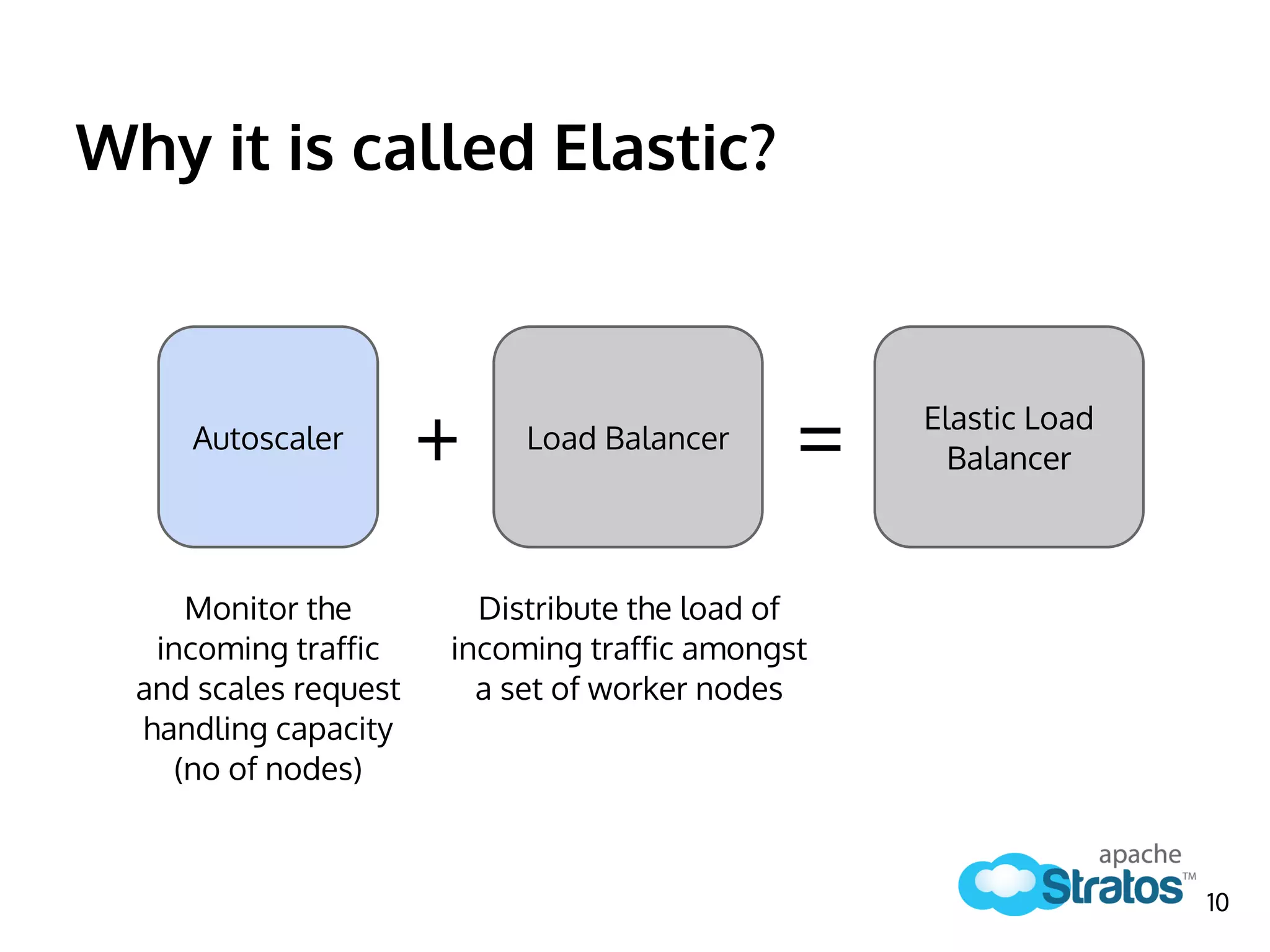
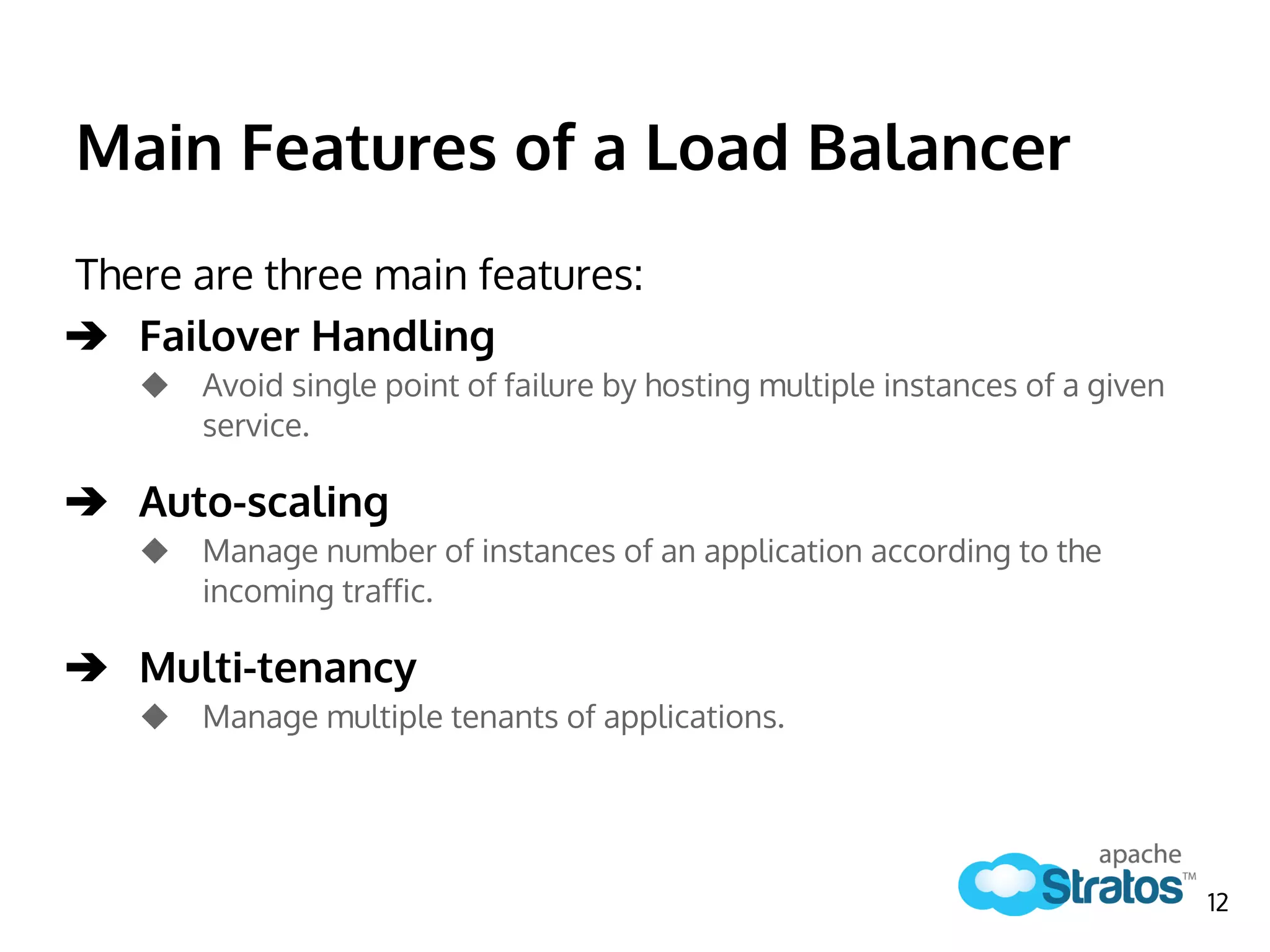
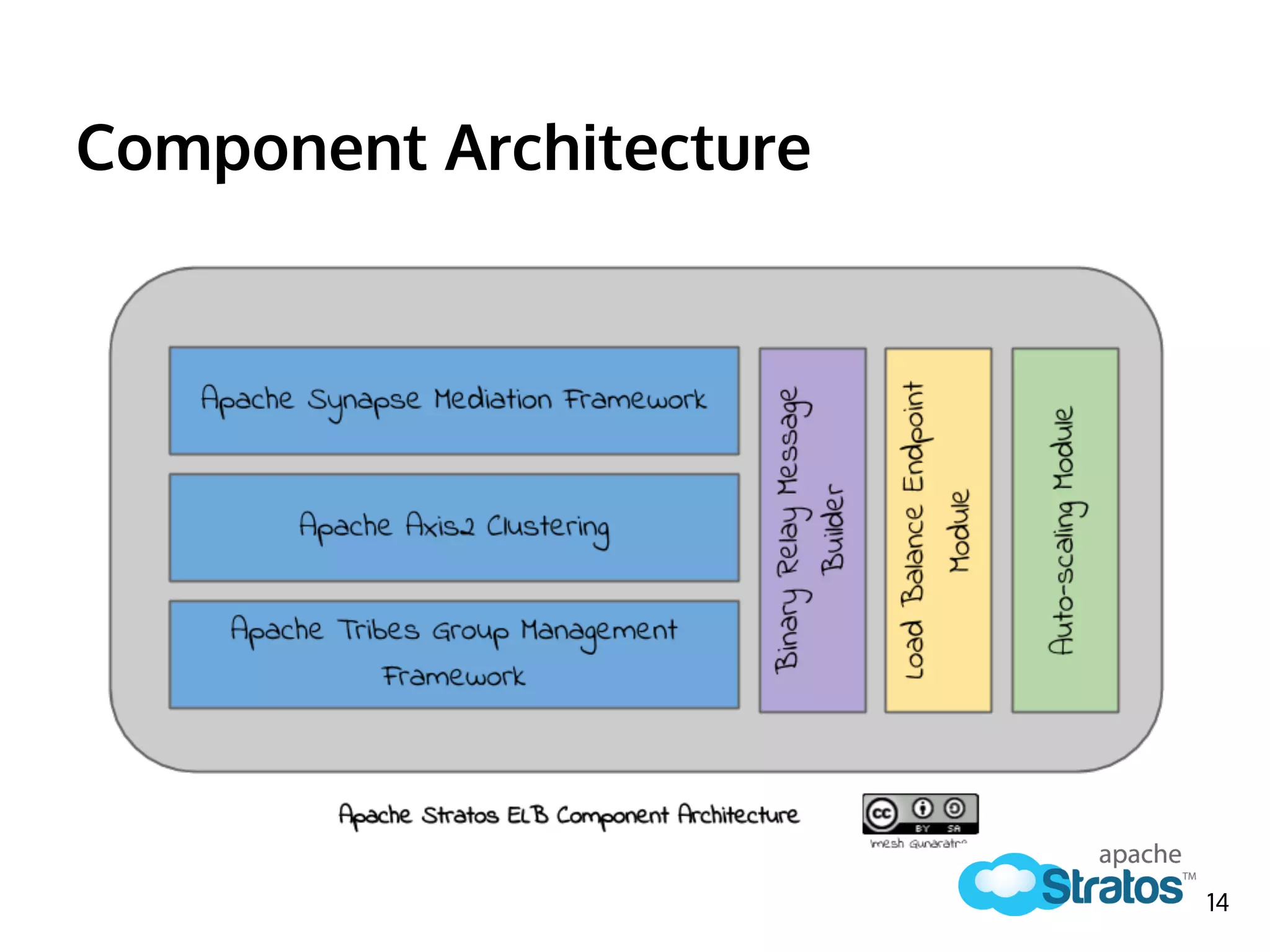
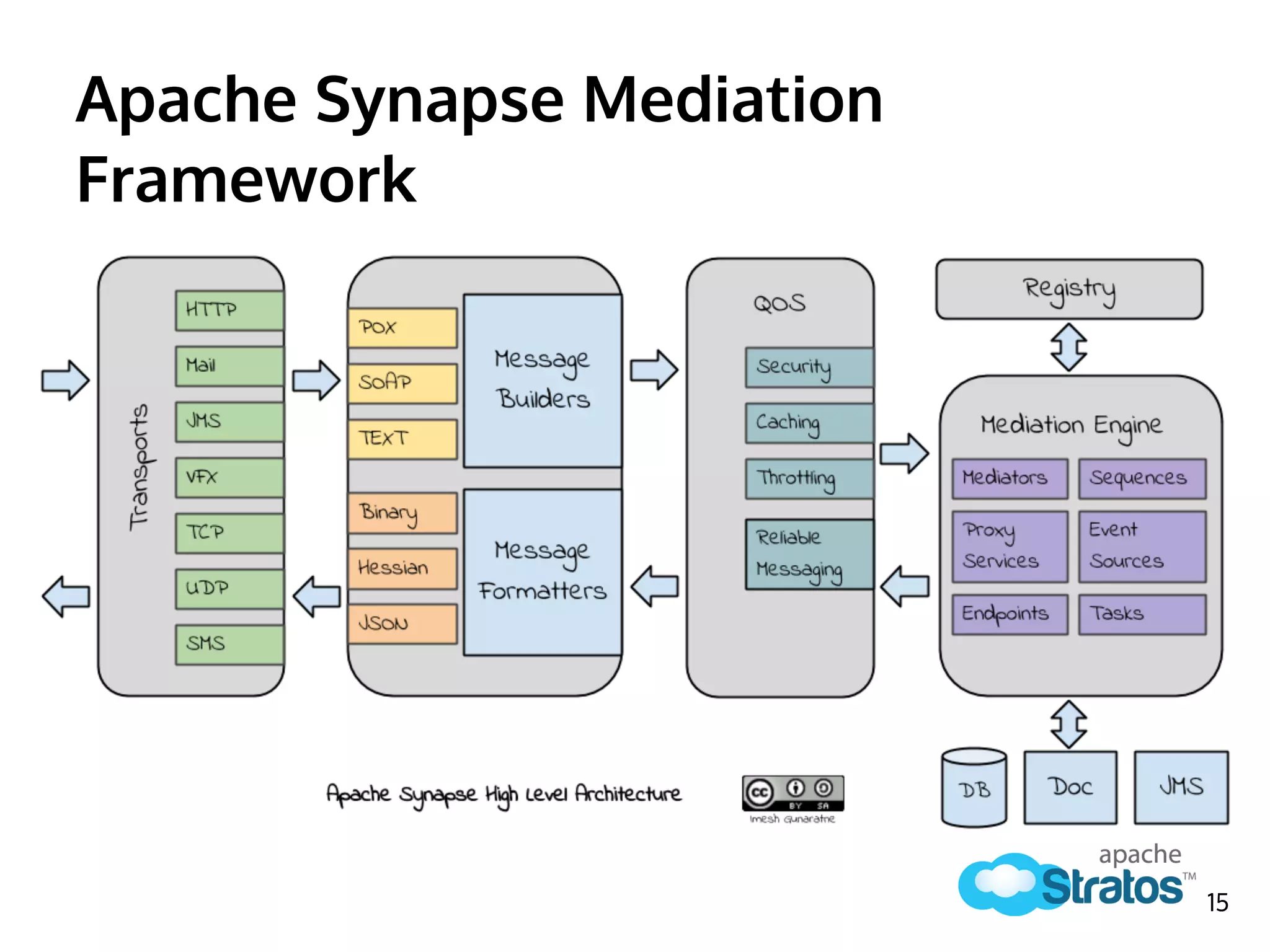
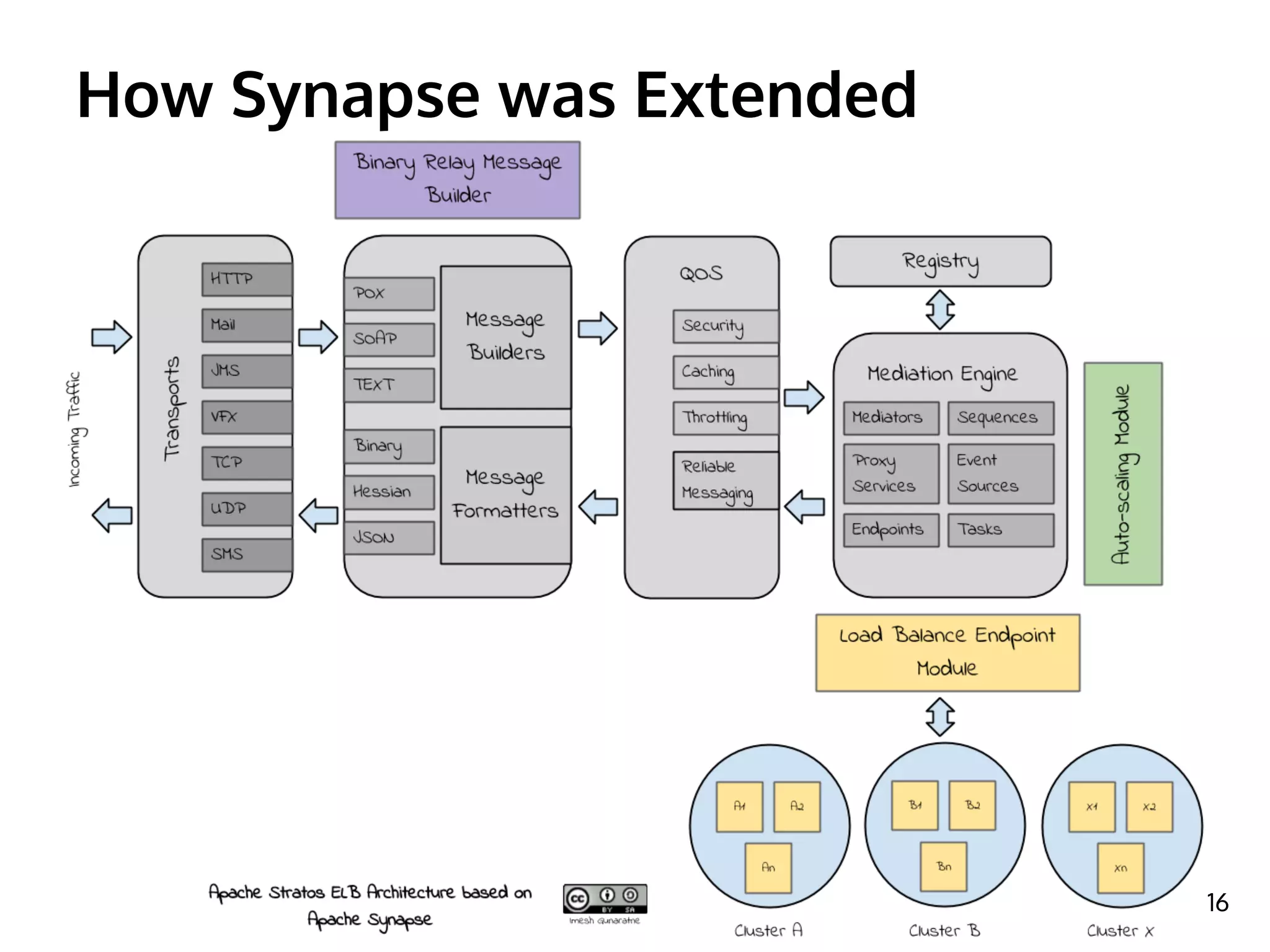
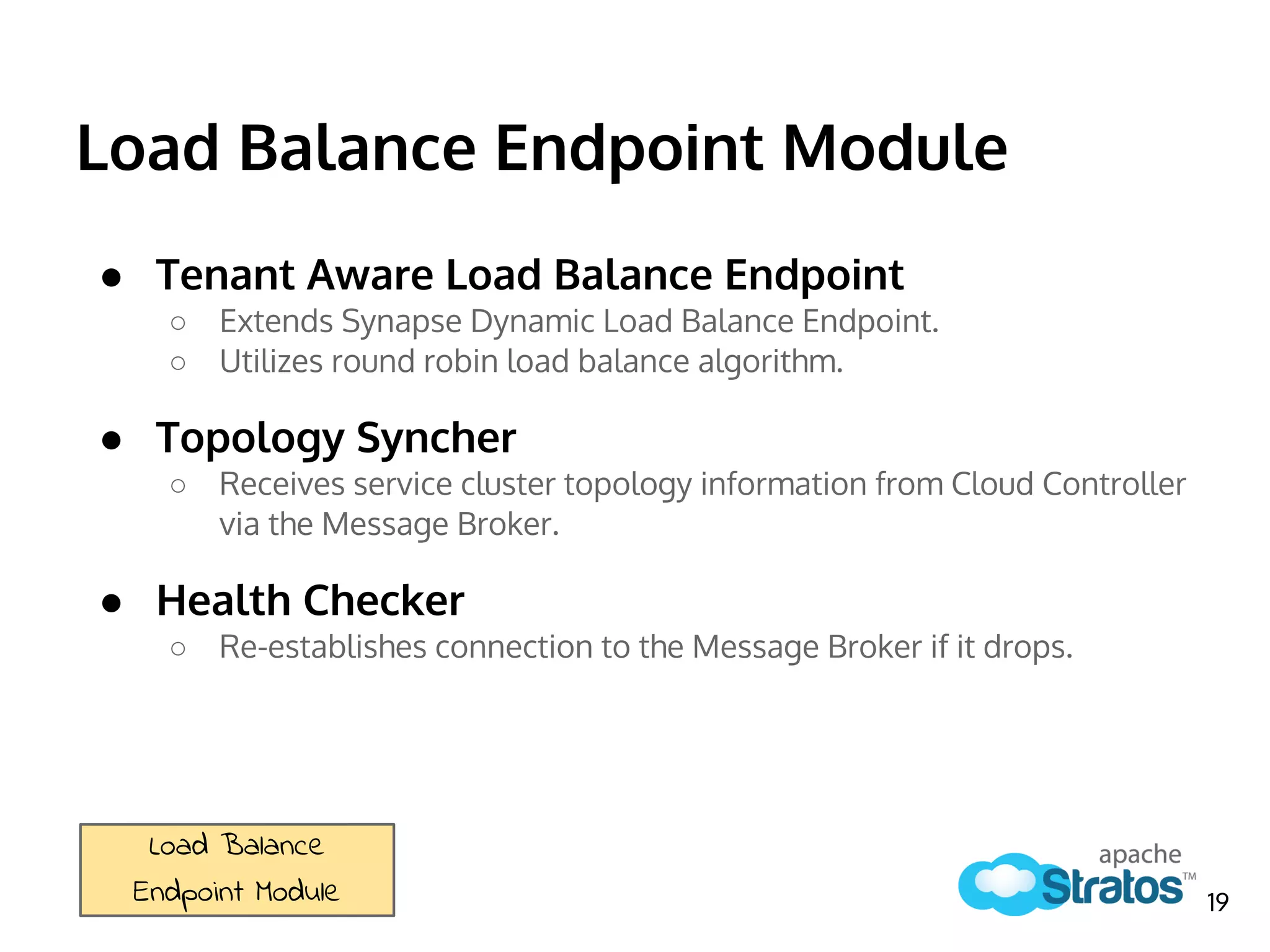
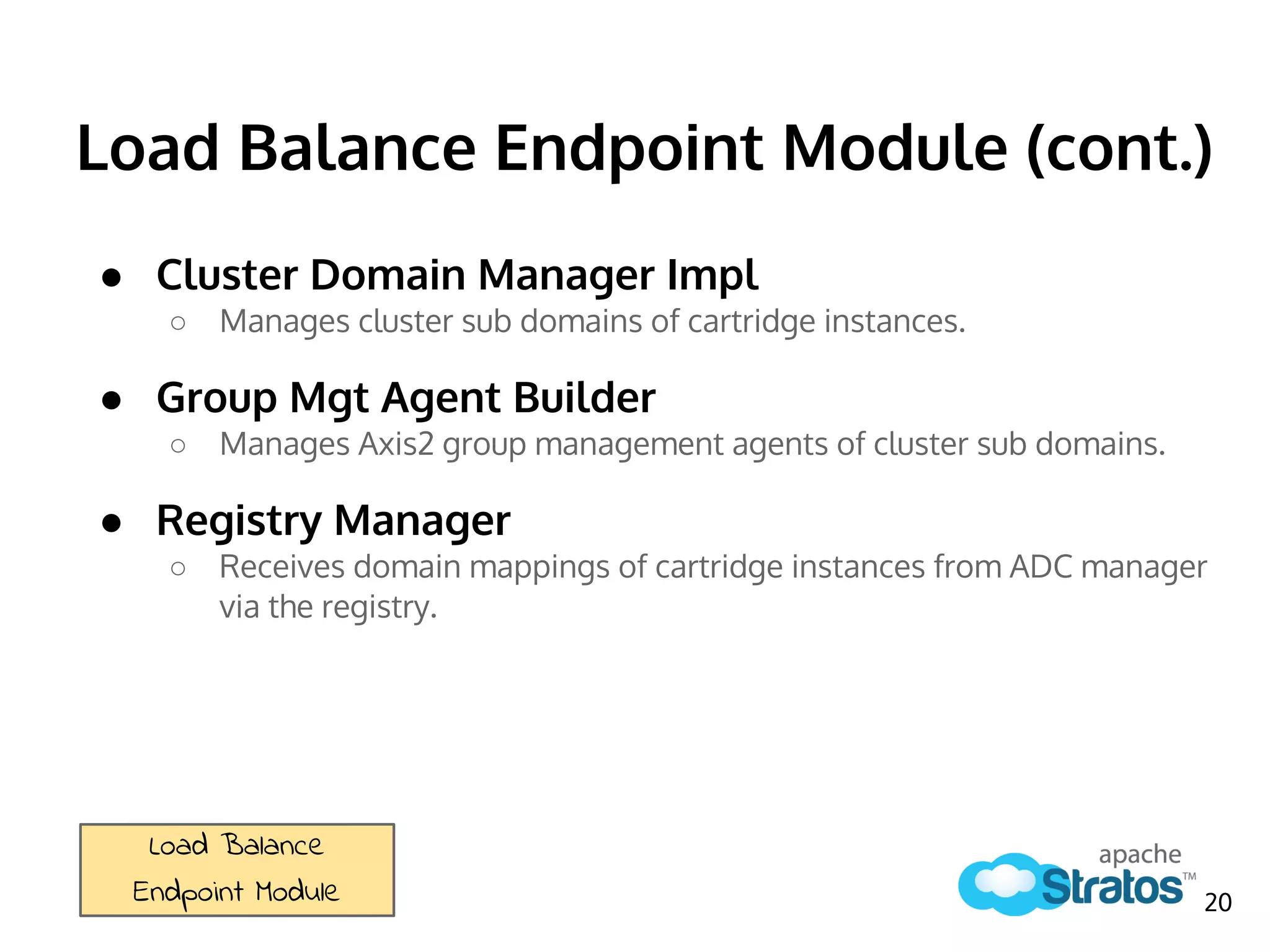
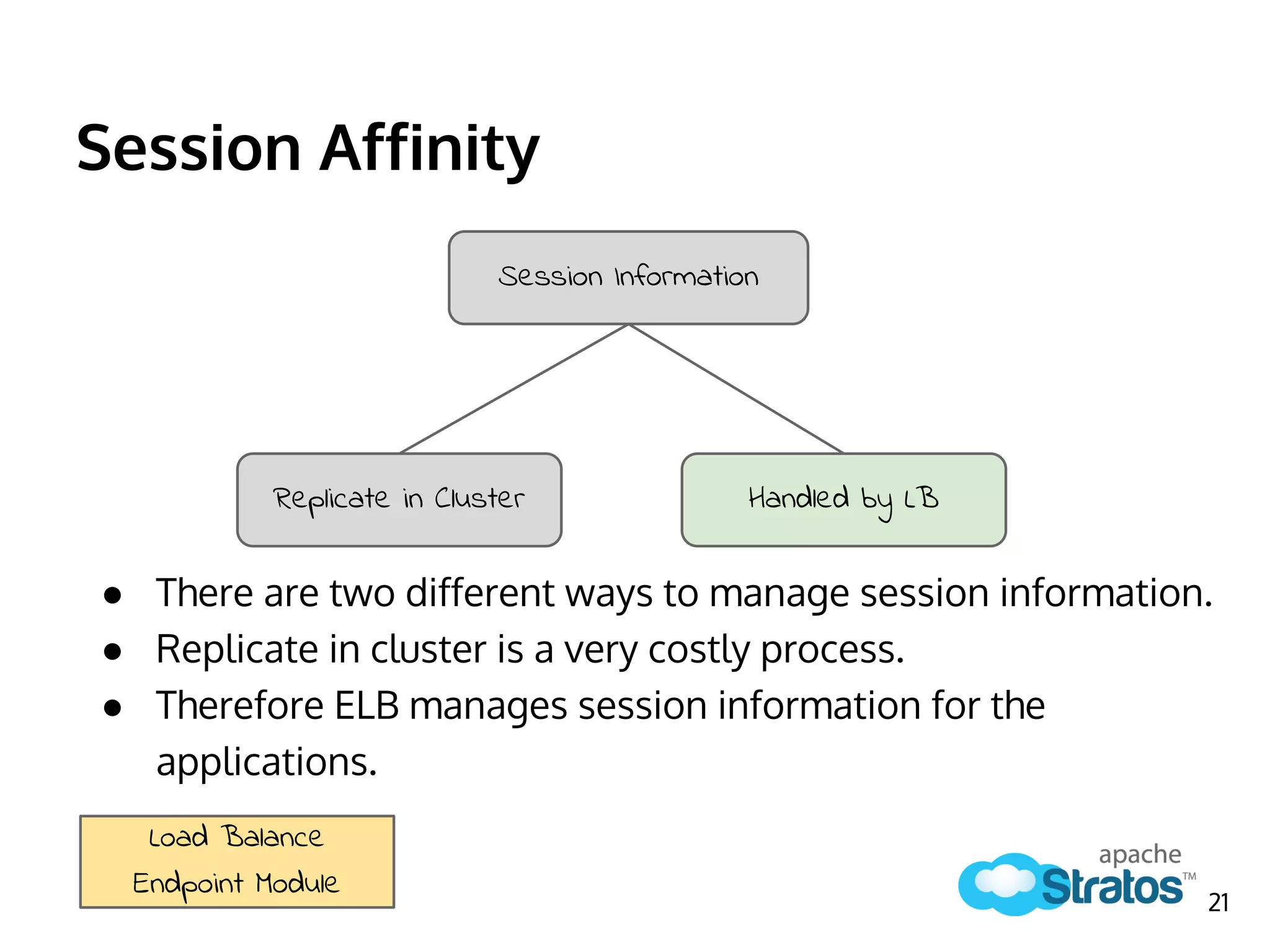
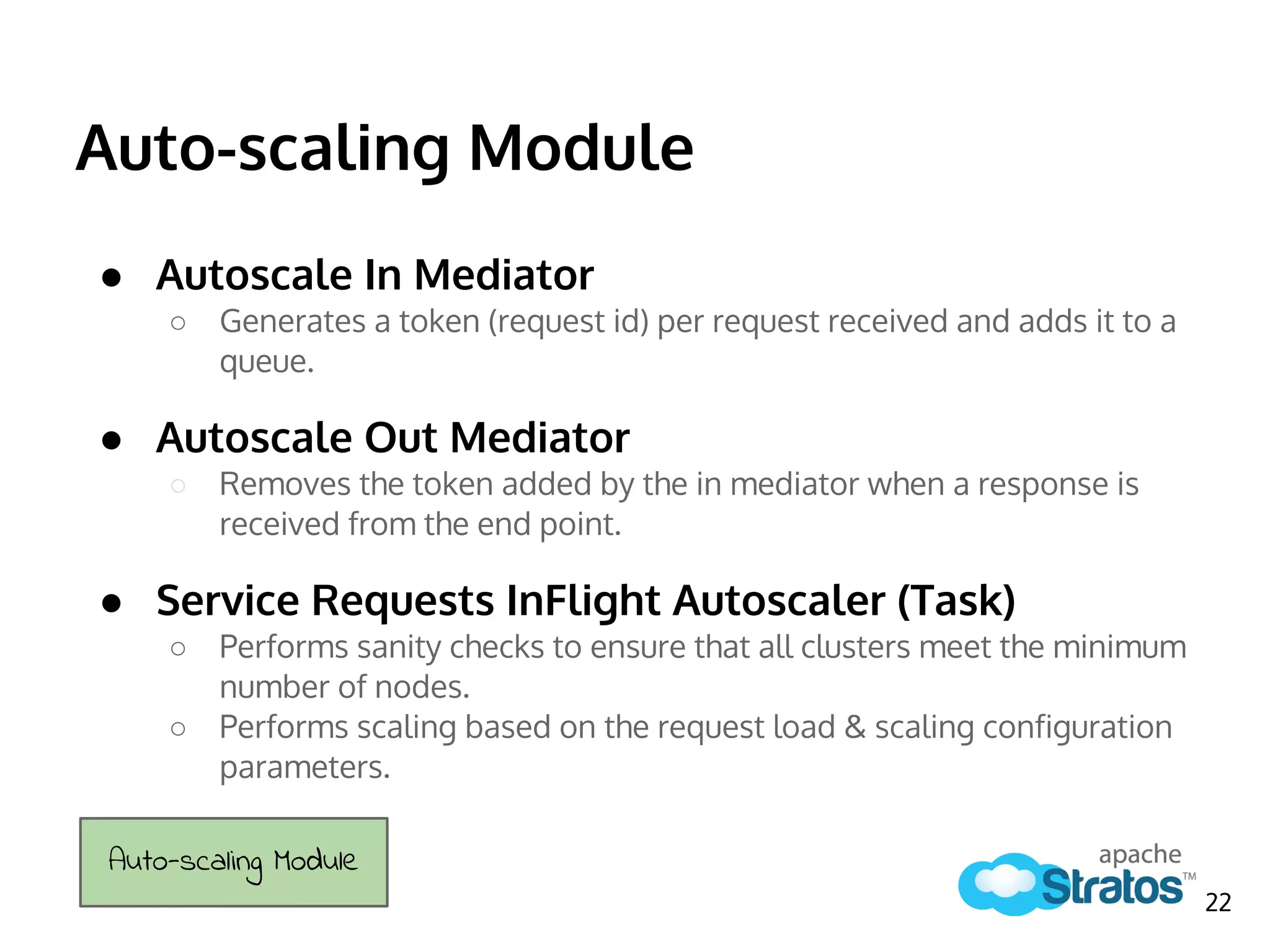
The document discusses the role of the Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) in Apache Stratos PaaS. It describes how the ELB uses components like Synapse, Axis2, and Tribes to distribute incoming traffic across backend nodes and auto-scale capacity. The ELB handles load balancing, failover, auto-scaling, and multi-tenancy. It integrates with Stratos by receiving topology information, load balancing requests to cartridge instances, and auto-scaling the number of instances based on traffic.






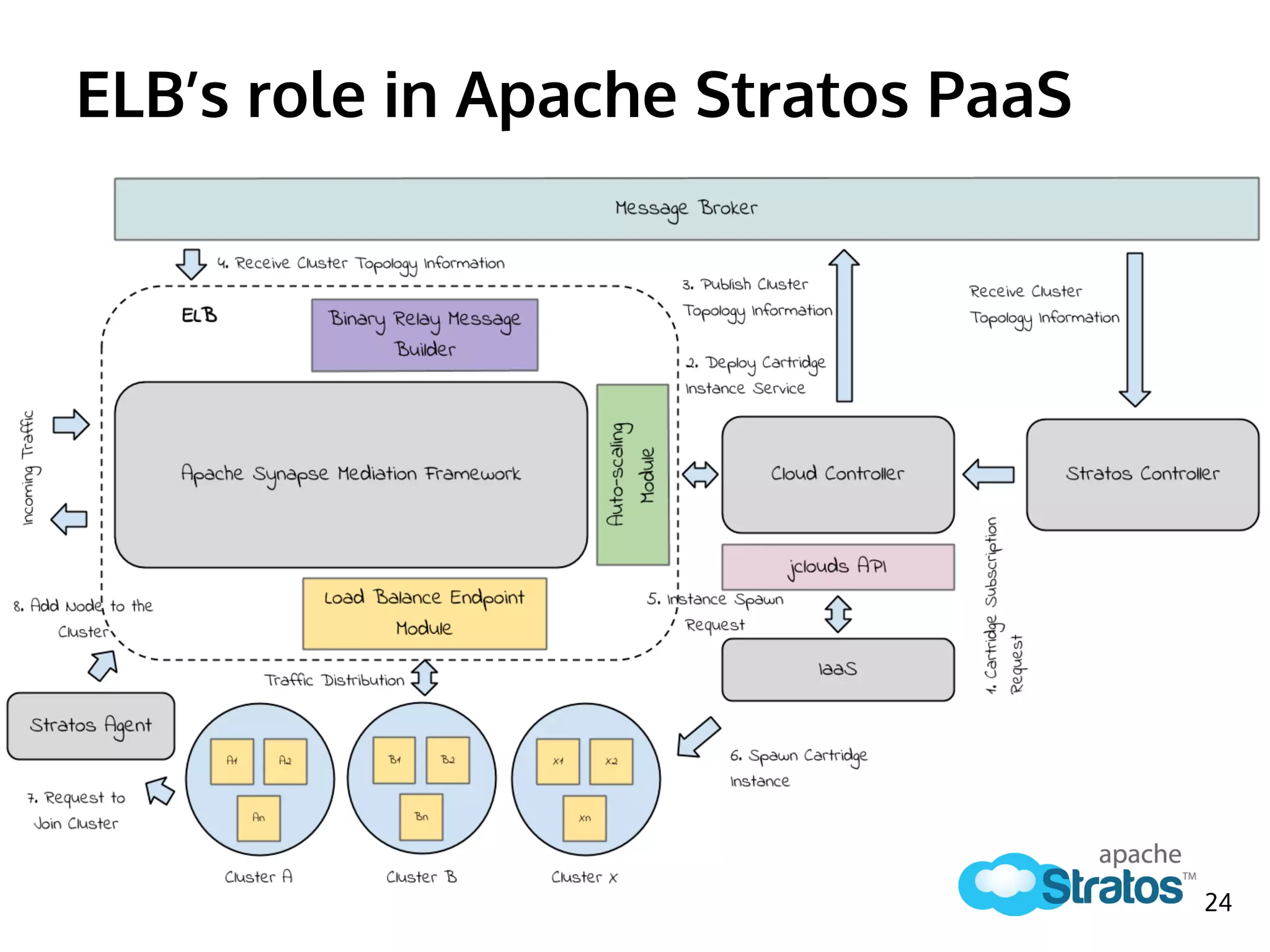
![Cartridge Subscription Workflow
1. [SC -> CC] Send Cartridge Subscription Request
2. [CC] Deploy Cartridge Instance Service
3. [CC -> MB] Publish Cluster Topology Information
4. [MB -> ELB] Receive Cluster Topology Information
5. [CC -> jclouds] Instance Spawn Request
6. [jclouds -> IaaS] Spawn Cartridge Instance
7. [Cartridge -> Agent] Request to Join Cluster
8. [Agent -> ELB] Add Node to Cluster
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theroleofelasticloadbalancer-apachestratos-130827225359-phpapp01/75/The-Role-of-Elastic-Load-Balancer-Apache-Stratos-25-2048.jpg)
![1. [Client -> ELB] Send request message
2. [ELB] Identify cluster & tenant using message header
3. [ELB] Add request to a list
4. [ELB -> Node] If session exists, send message
5. [ELB] If not store session information
6. [ELB -> Node] Apply algorithm & send message
7. [ELB -> Node] Handle failover
8. [Node -> ELB] Send response
9. [ELB -> Client] Send response and remove request from list
10. [ELB] Scale number of cartridge instances
Load Balancing Workflow
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theroleofelasticloadbalancer-apachestratos-130827225359-phpapp01/75/The-Role-of-Elastic-Load-Balancer-Apache-Stratos-26-2048.jpg)