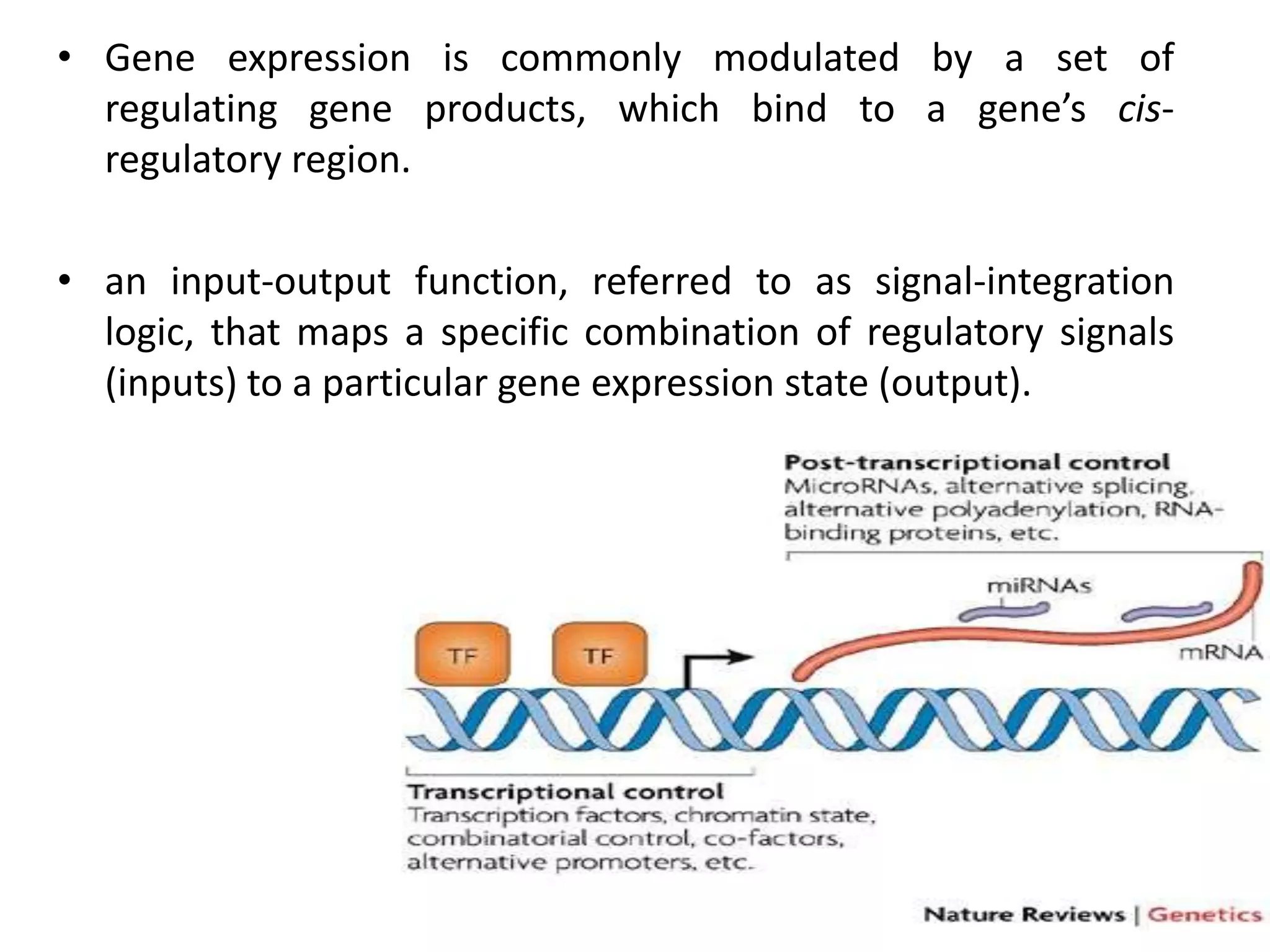
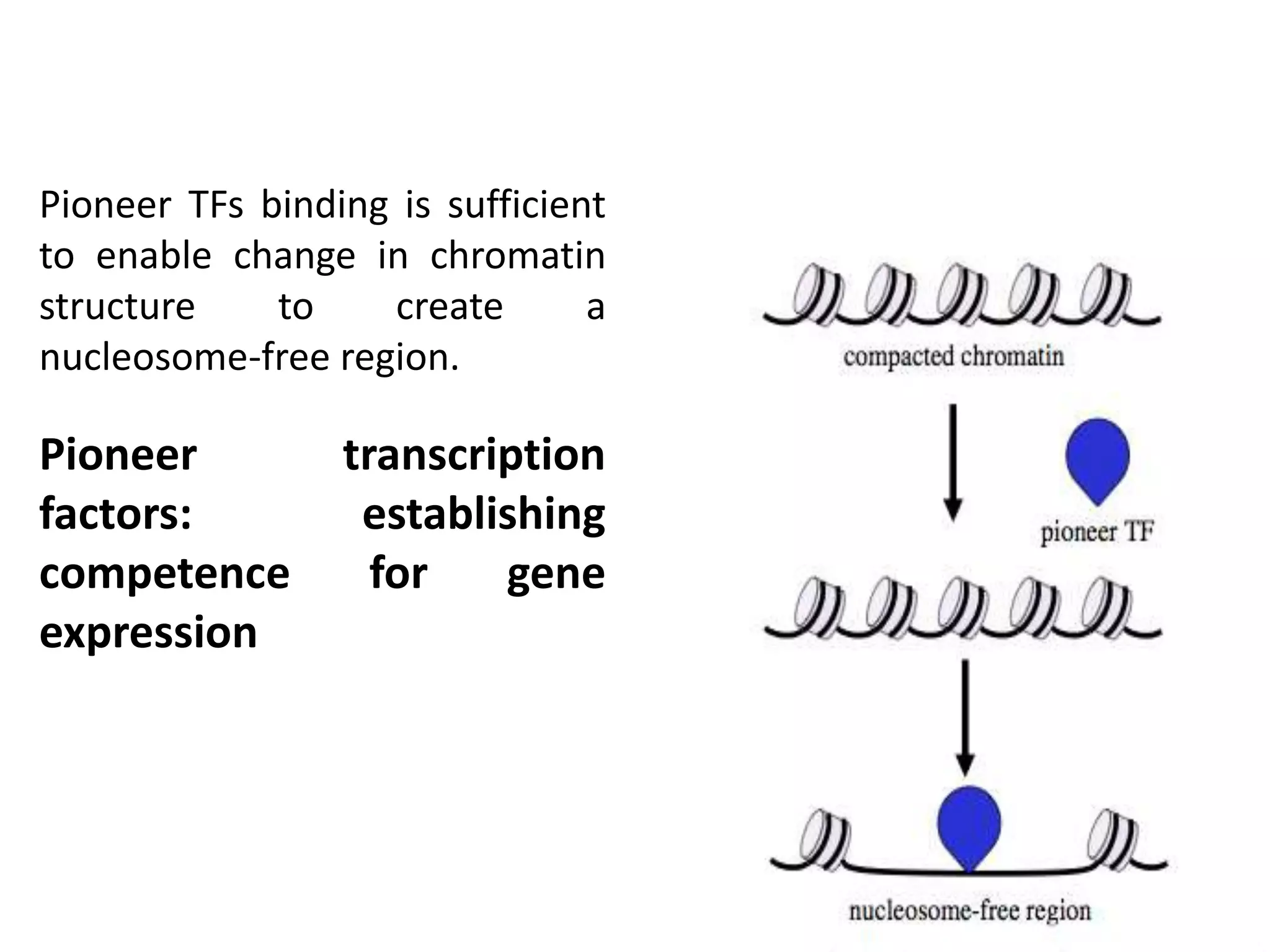
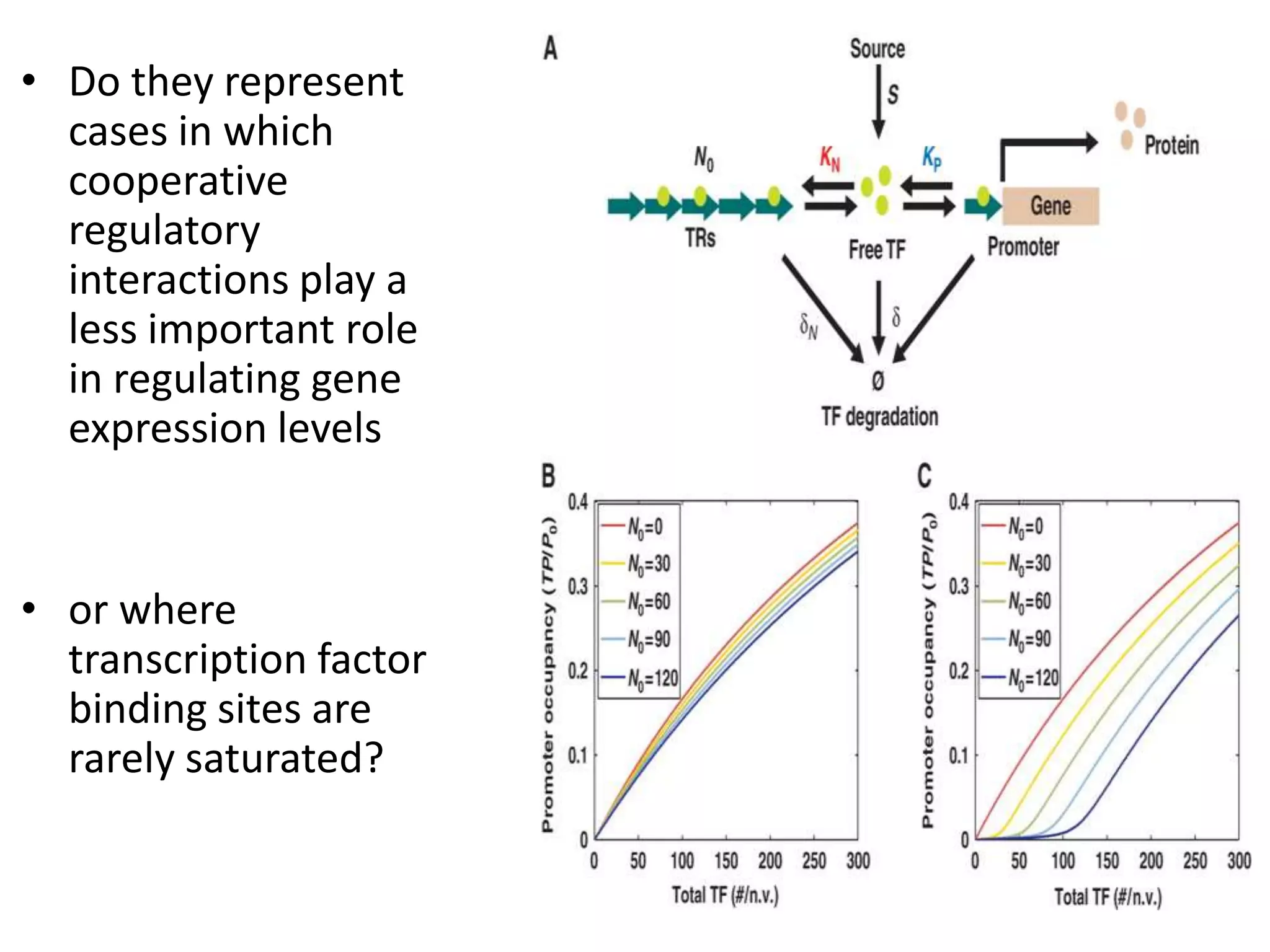
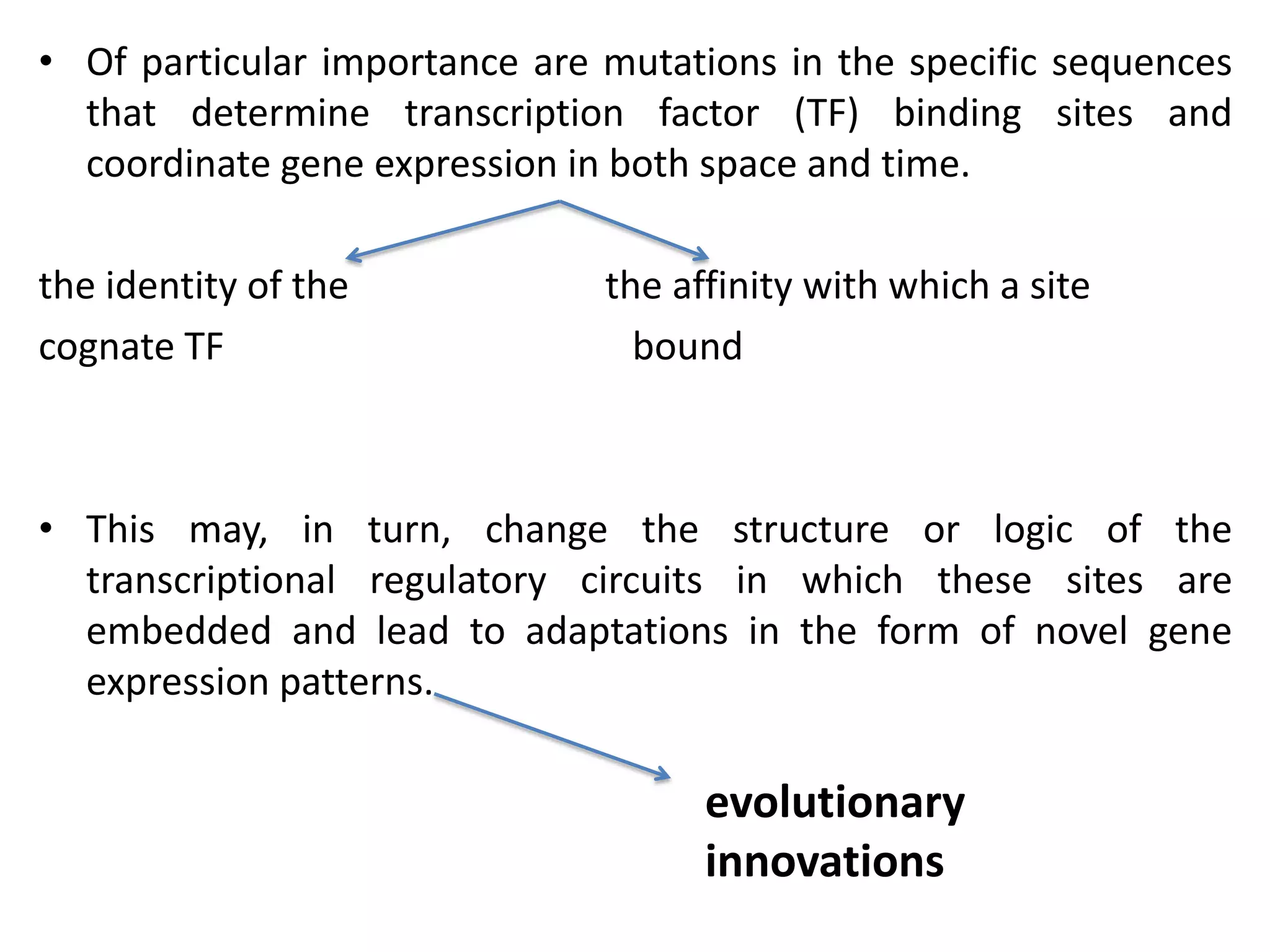
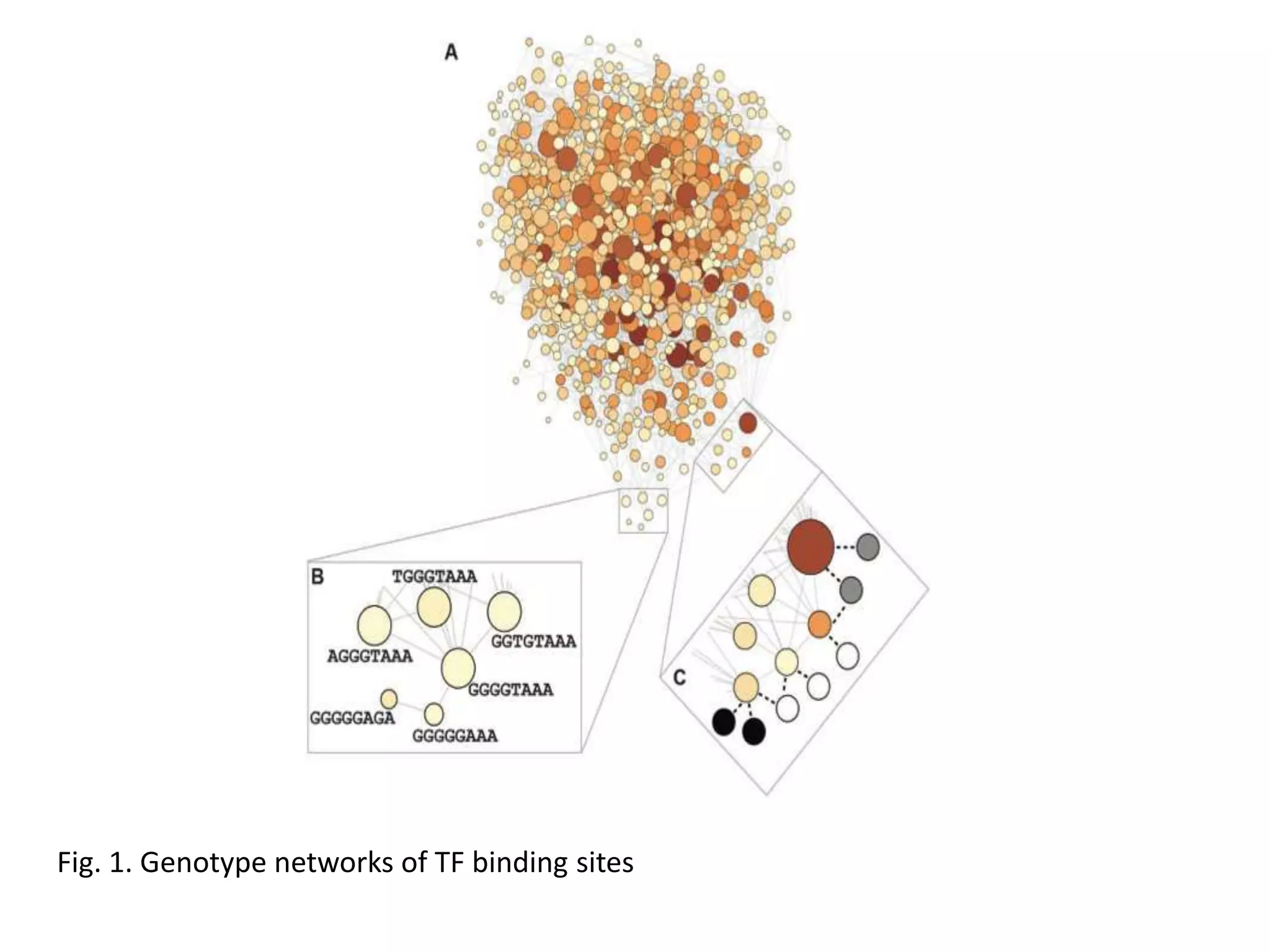
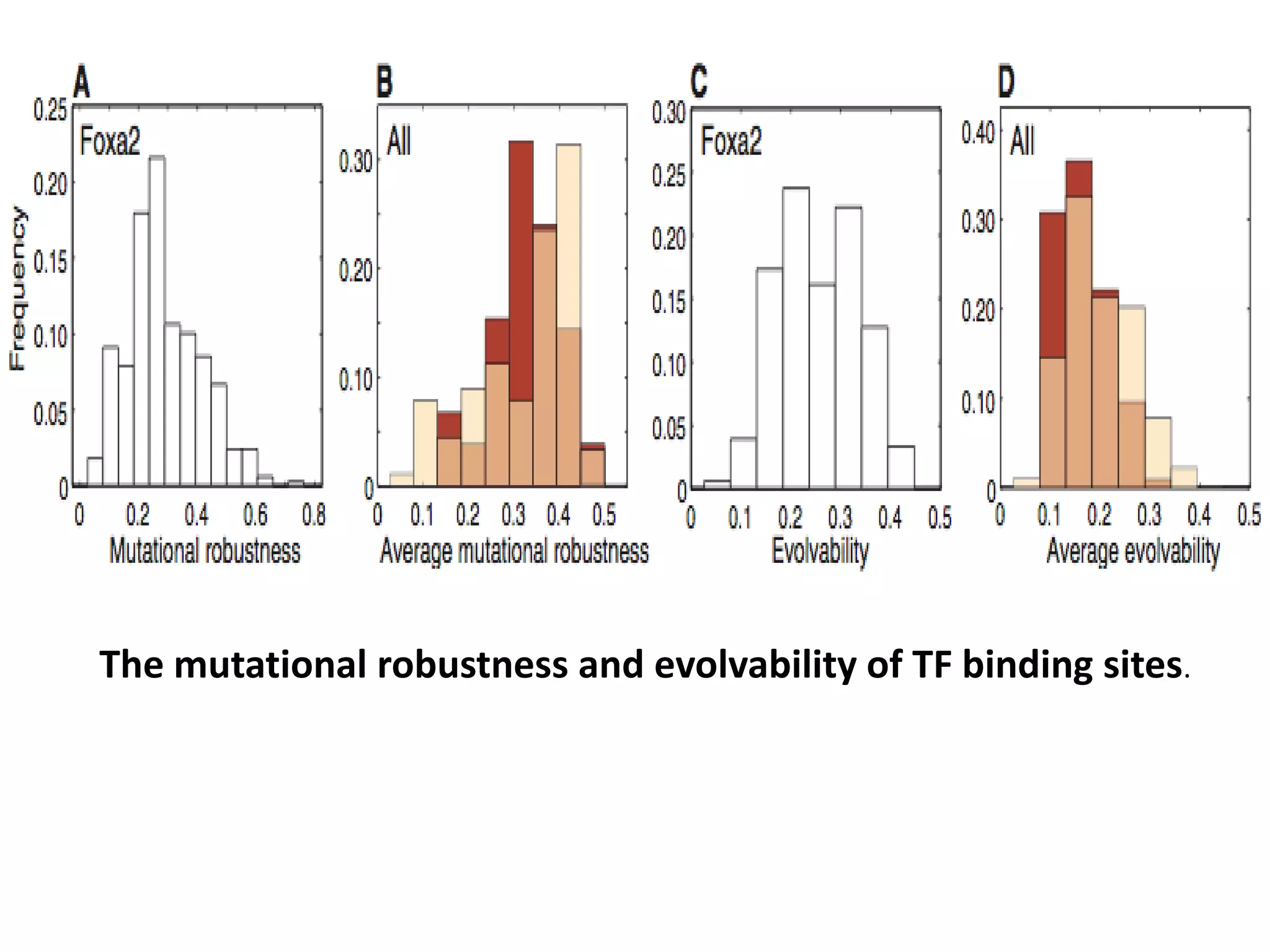
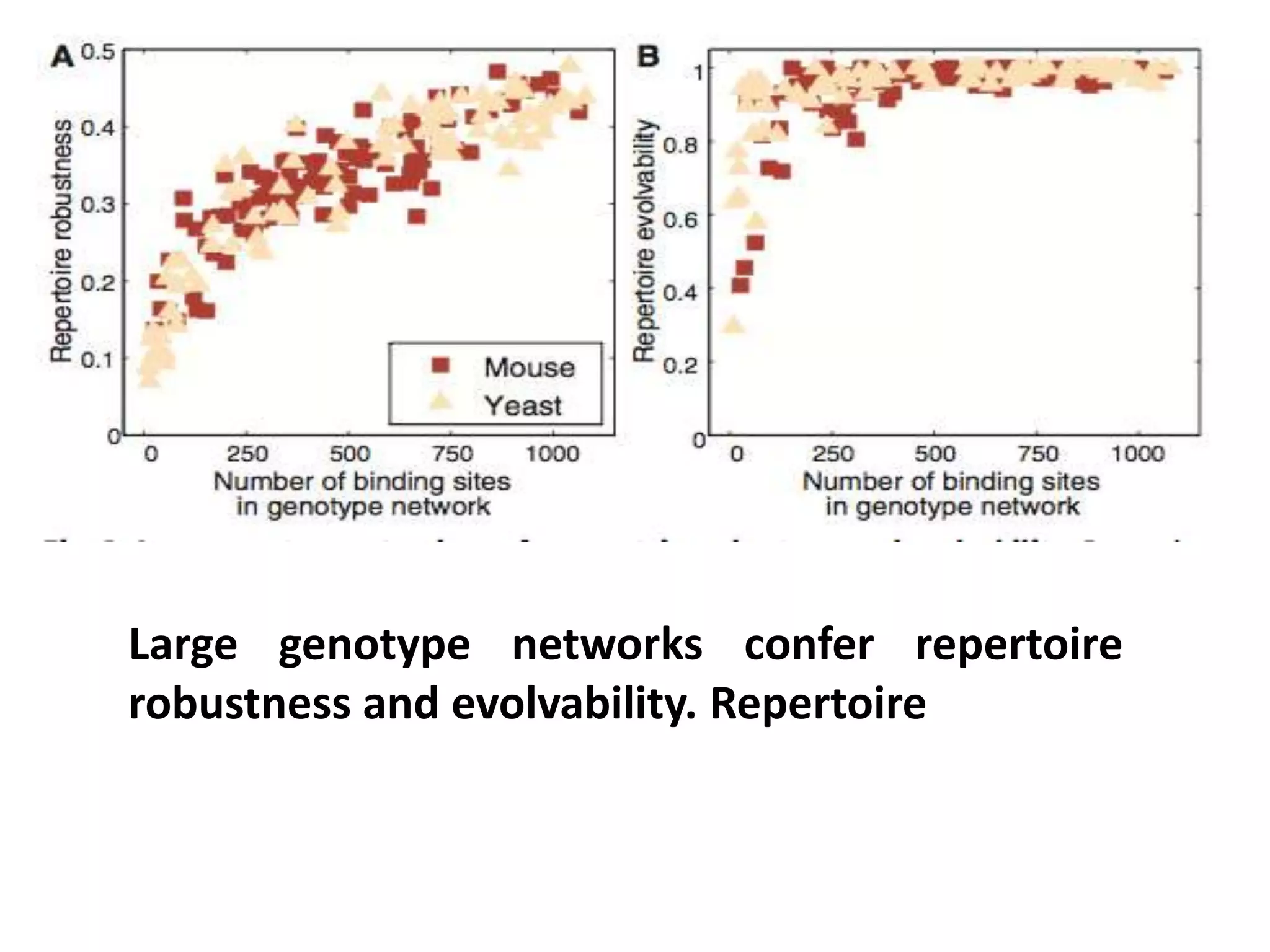
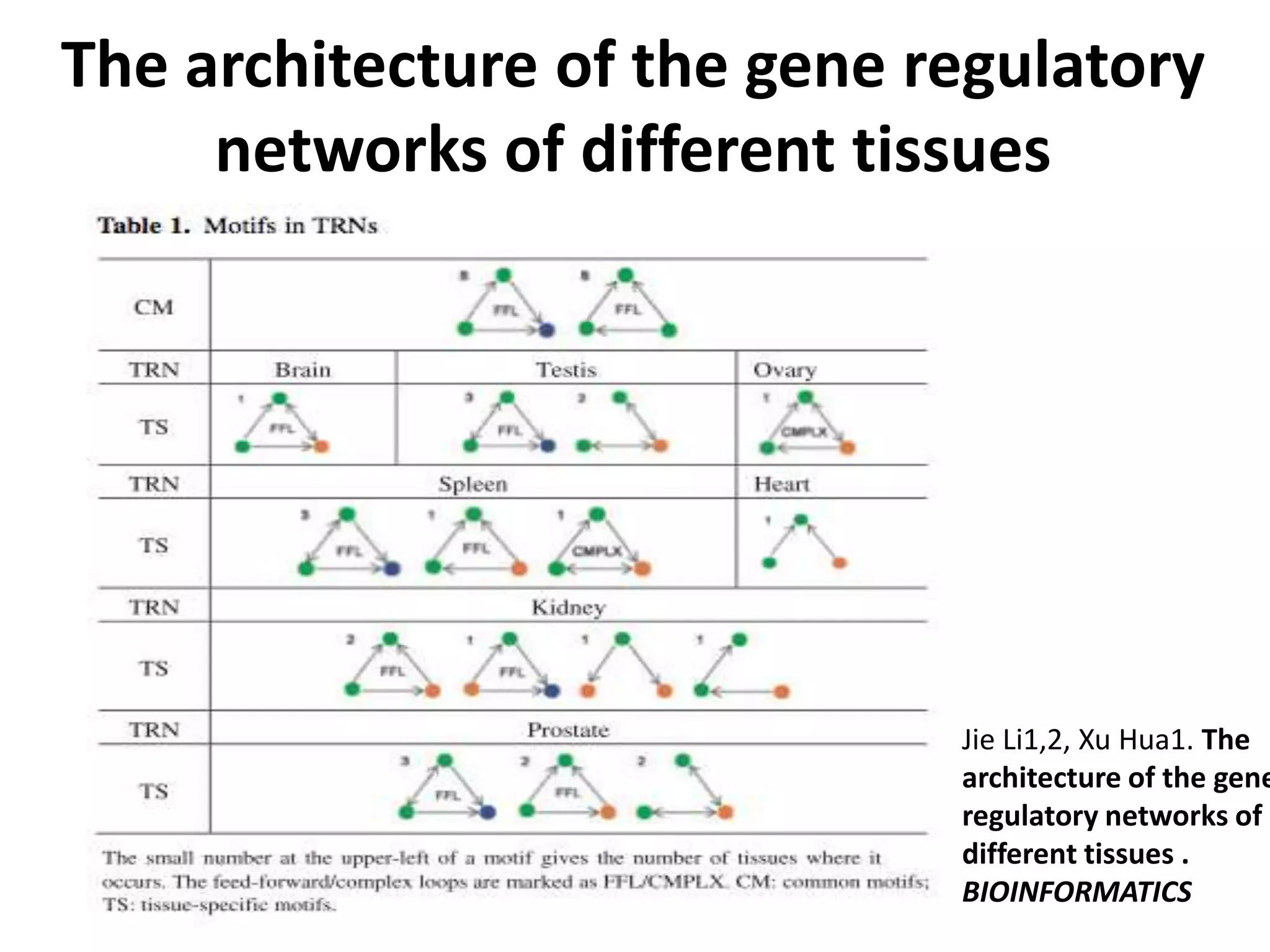
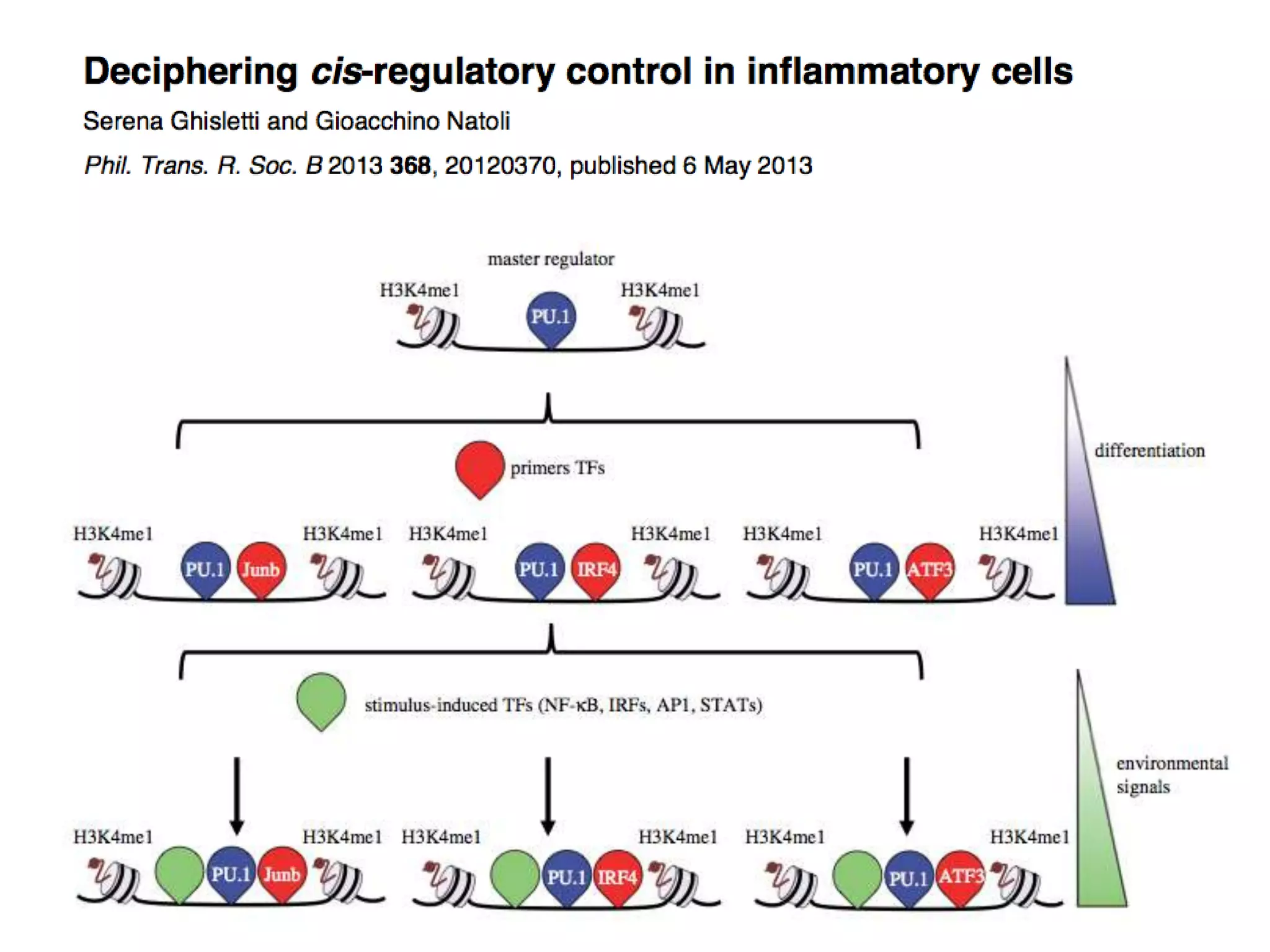
This document discusses the robustness and evolvability of transcription factor (TF) binding sites. It notes that TF binding sites are typically 6-10 nucleotides long and can be degenerate, binding different sequences. This degeneracy contributes to mutational robustness and evolvability by allowing binding of different TFs after mutation. Large genotype networks confer both robustness by maintaining phenotypes despite mutations, and evolvability by connecting genotypes with different phenotypes and allowing novel adaptations. The identity and affinity of the cognate TF bound can change regulatory circuits and lead to novel gene expression patterns and evolutionary innovations.