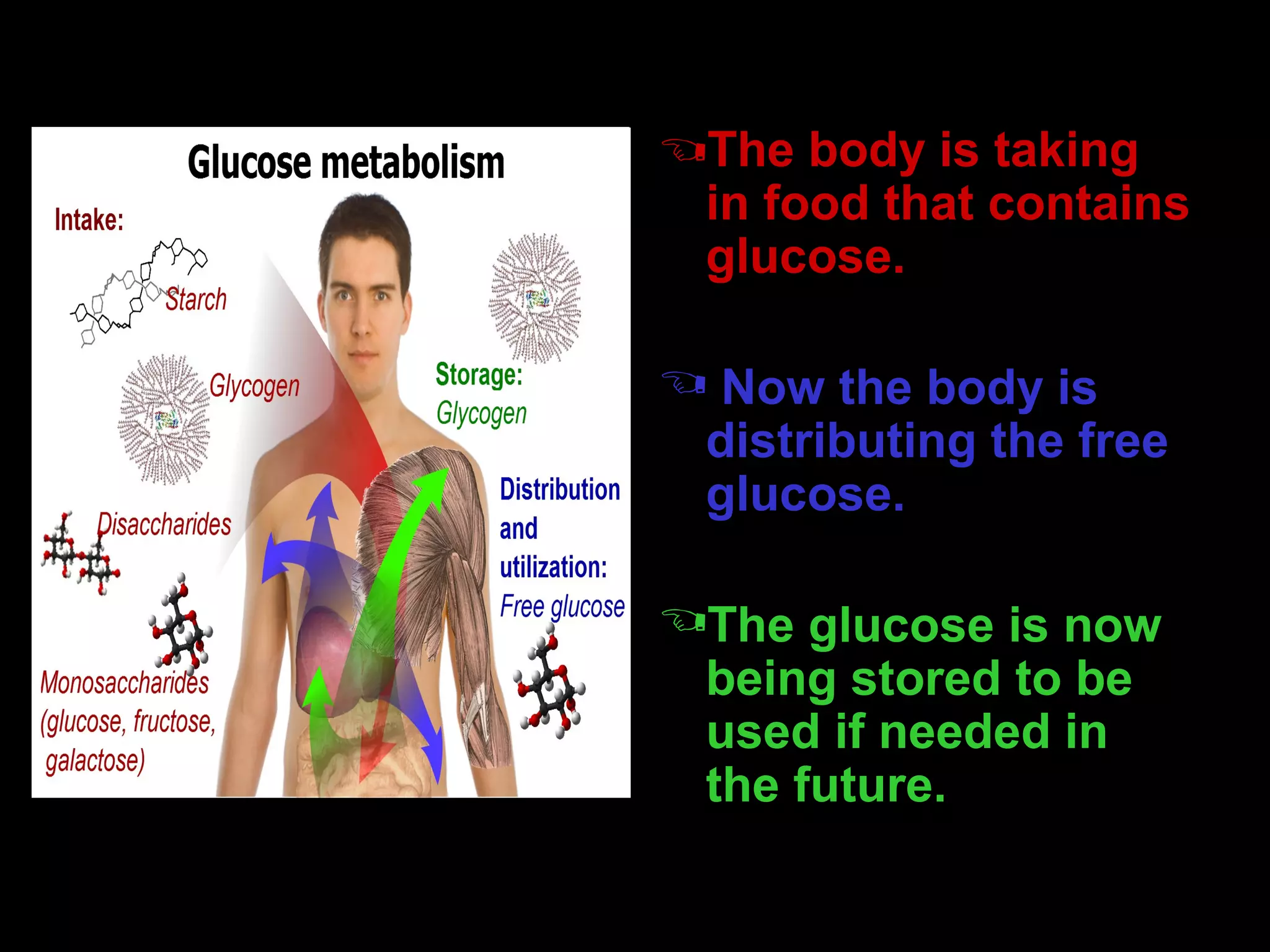
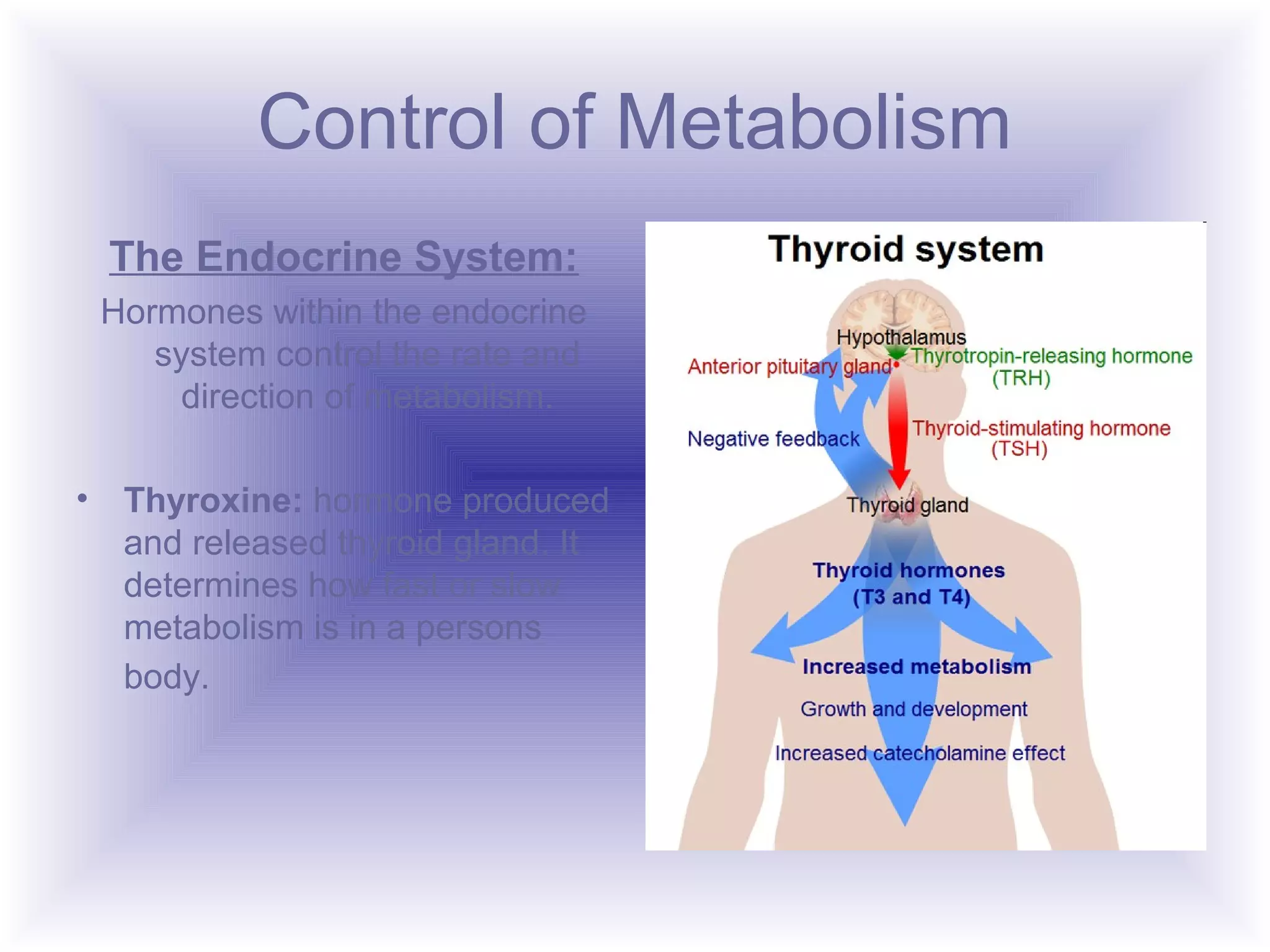
The process of metabolism involves three main steps:
1) Plants undergo photosynthesis to produce glucose which humans then consume through eating plants.
2) The body breaks down food into simple sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids through digestion.
3) The glucose is either stored for future use through anabolic metabolism or used immediately for energy through catabolic metabolism. The endocrine system, through hormones like thyroxine, controls the rate and direction of metabolism.