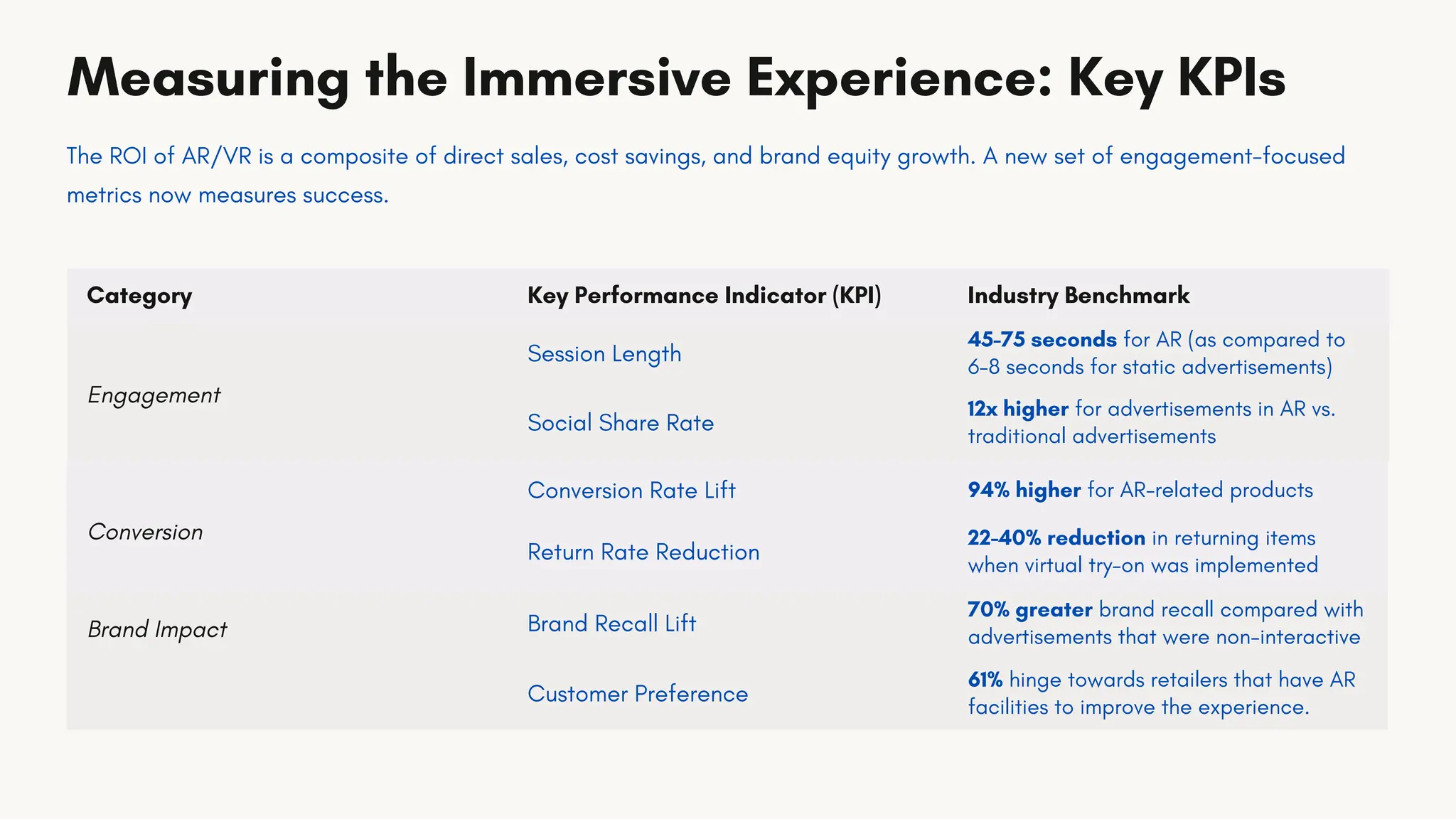
This slide shows how AR and VR capabilities have been leveraged by various industries like fashion, FMCG, cosmetics, automobiles, etc. to provide a fabulous customer experience and increase sales of various products via Case Studies and Theoretical Concepts.