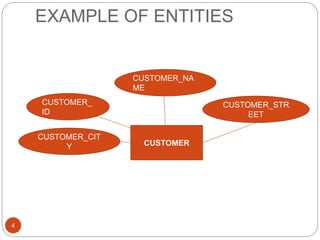
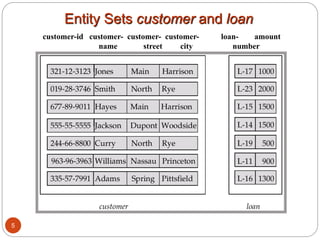
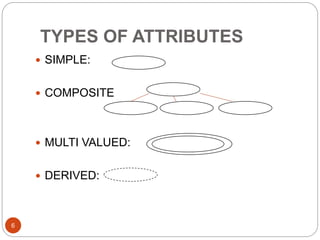
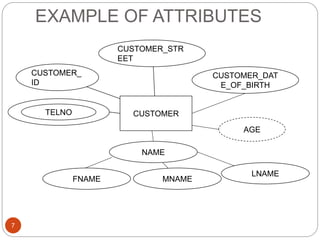
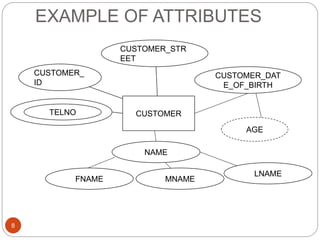
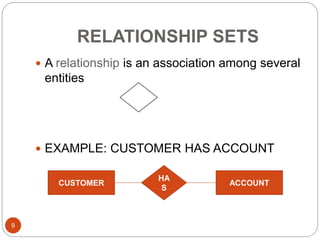
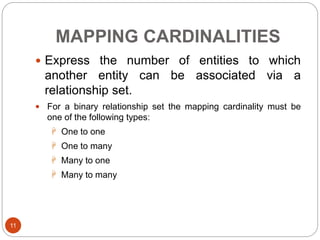
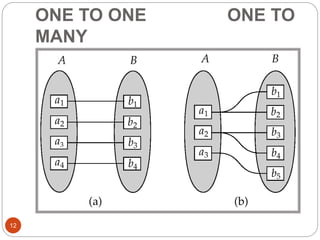
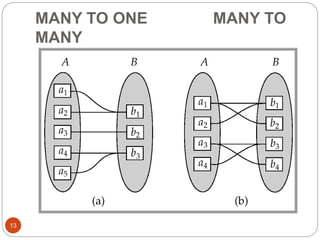
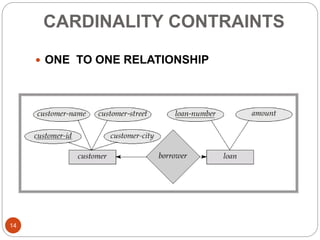
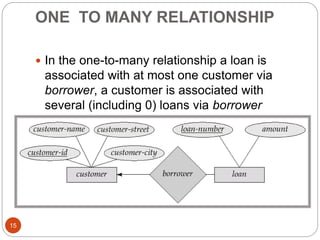
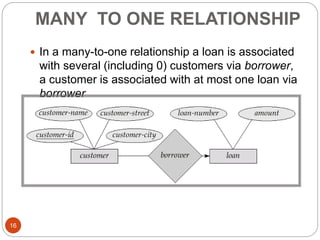
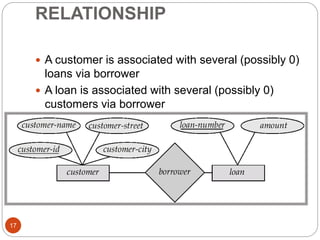
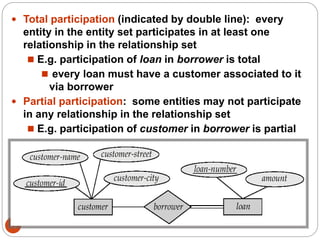
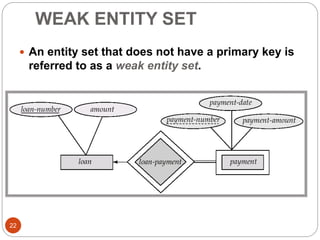
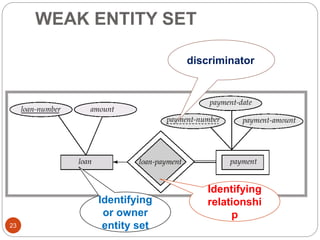
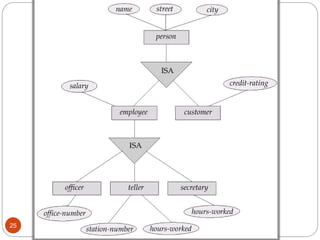
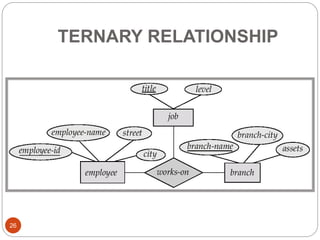
The document discusses the entity-relationship model, which includes concepts such as entity sets, attributes, relationship sets, and cardinalities. It explains how entities represent objects with specific properties and how relationships between entities can be defined using various cardinality constraints. Additionally, it touches on specialized topics like weak entity sets and the process of specialization within entity sets.