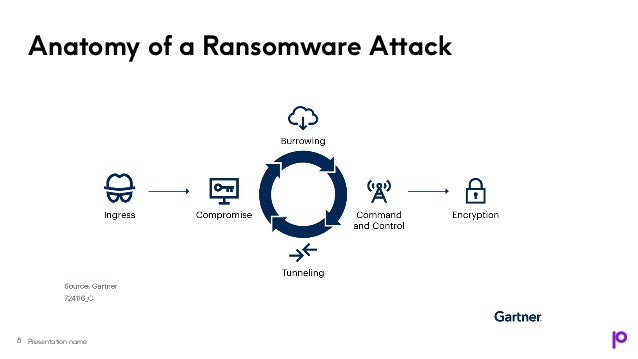
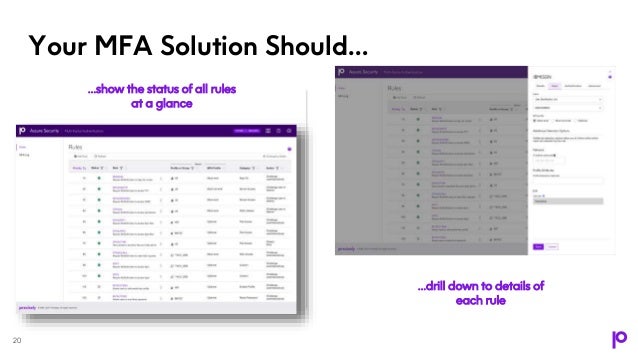
The document discusses the security measures necessary for IBM i systems, with a focus on the importance of multi-factor authentication (MFA) as a defense against increasing ransomware threats. It highlights the vulnerabilities present in IBM i systems and emphasizes that MFA can significantly enhance security by requiring multiple forms of verification. The document also outlines various authentication options, regulatory requirements, and implementation tips to safeguard organizational data effectively.