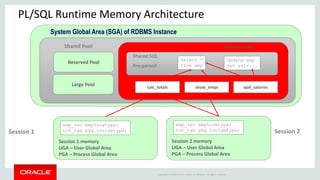
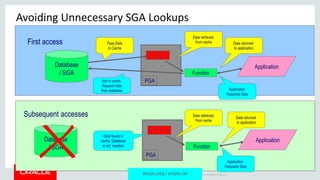
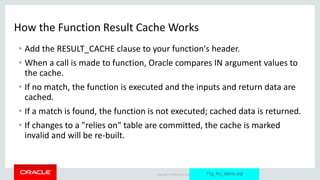
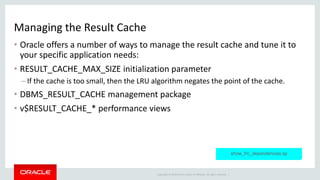
The document discusses PL/SQL performance features, focusing primarily on data caching techniques including deterministic functions, PGA caching, and the function result cache introduced in Oracle Database 11g. The function result cache is presented as the most effective caching mechanism, allowing for improved performance by storing frequently accessed data in the SGA across sessions. Key considerations for implementing these caching techniques are also highlighted, including their limitations and best practices for optimal use.