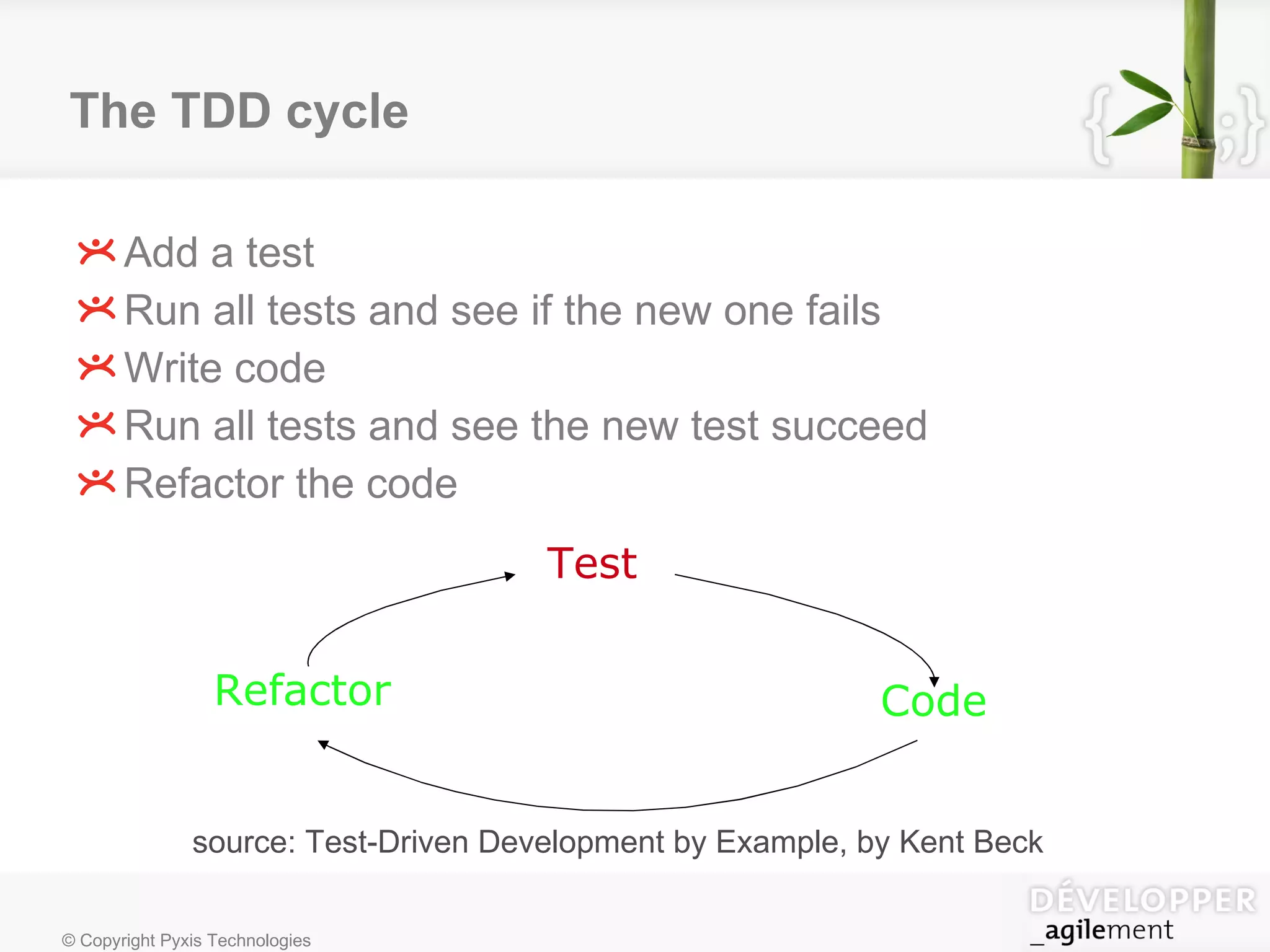
Test-driven development (TDD) is a software development technique where unit tests are written before code to define desired functionality. Writing tests first helps produce code with better design, lower maintenance costs, and fewer bugs. Key principles of TDD include writing code only to pass failing tests and eliminating duplication. Benefits include better test coverage, easier refactoring, and preventing regressions. TDD helps developers act as users to define behavior through interactions between system components.