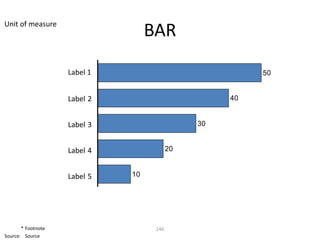
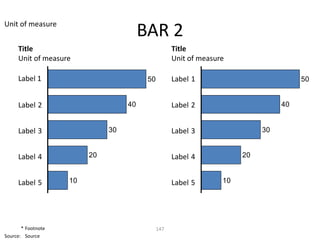
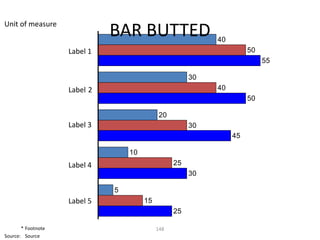
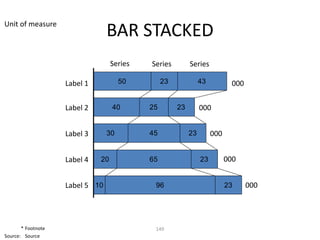
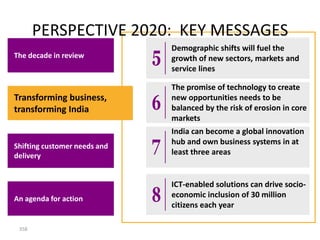
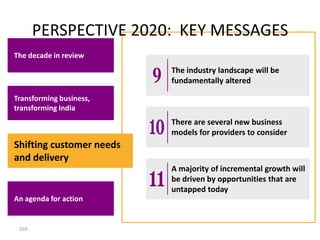
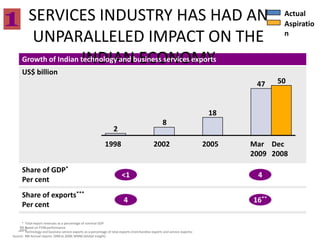
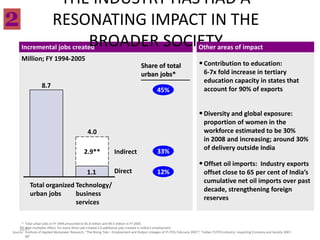
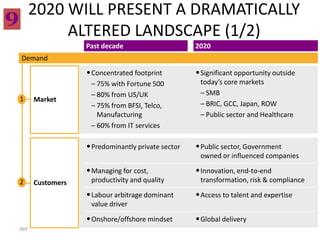
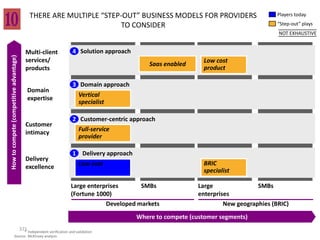
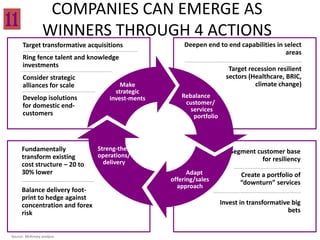
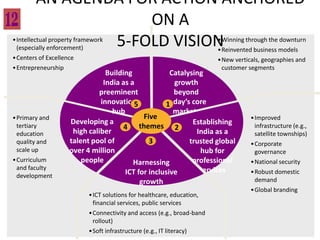
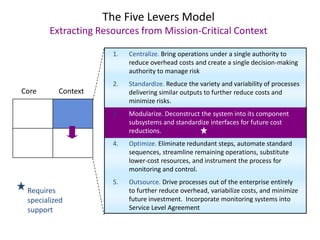
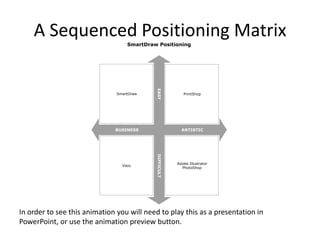
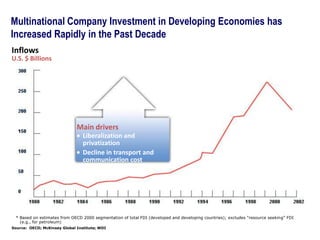
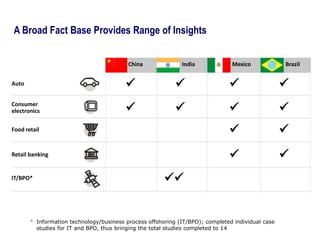
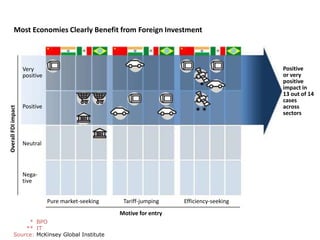
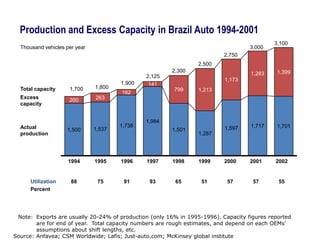
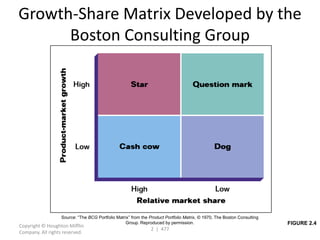
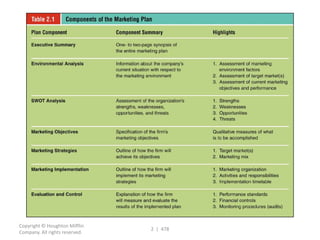
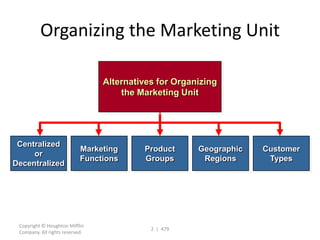
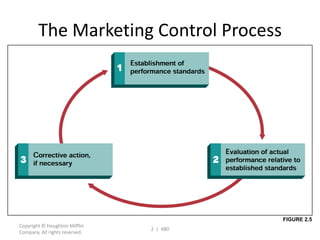
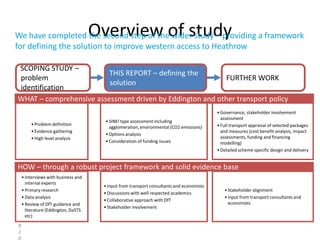
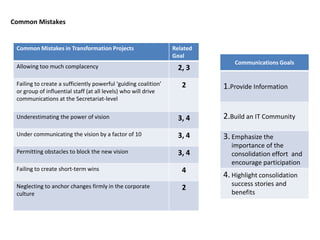
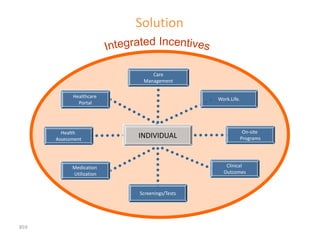
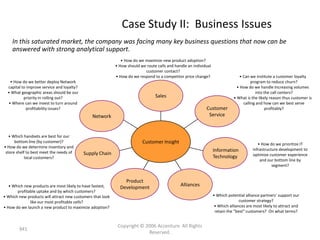
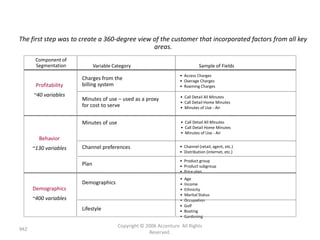
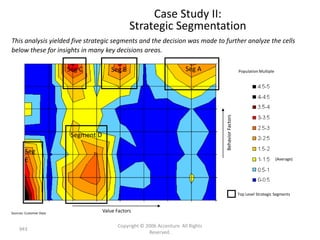
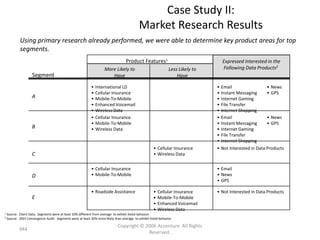
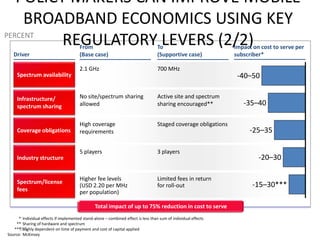
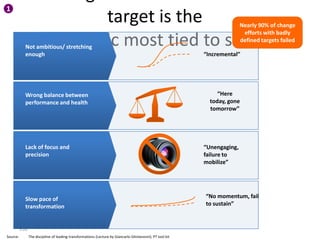
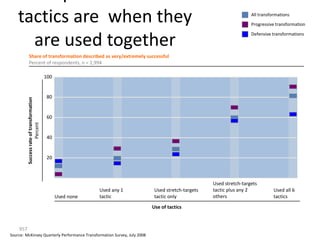
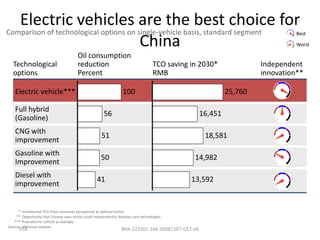
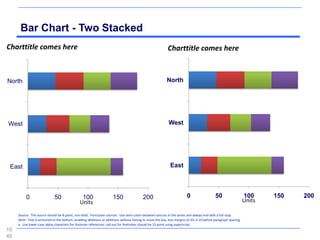
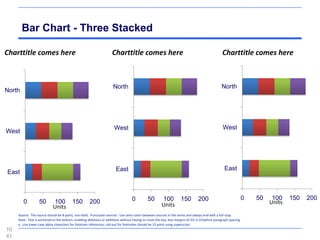
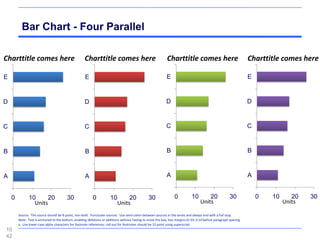
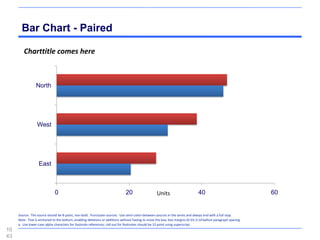
This document contains a presentation template with the following:
1. Instructions for adding a logo that will apply to all slides.
2. Several slides containing diagrams, charts, images and text examples that can be used in a presentation.
3. Footnotes and sources for images and content.
The template provides a variety of visual elements and examples that can be customized for a business presentation.



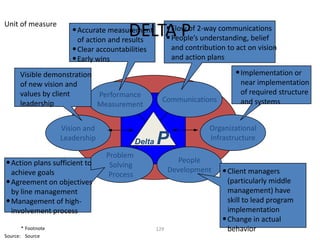
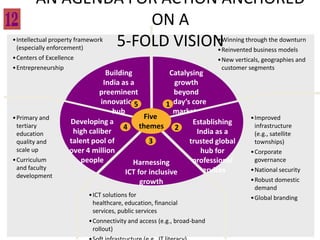
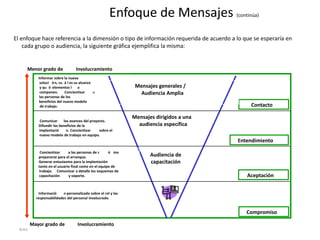
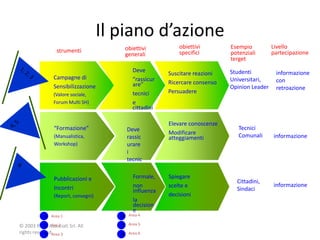
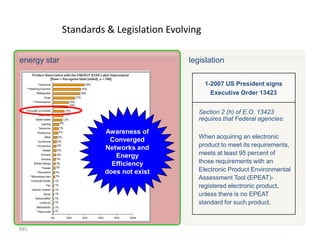
![Introduction
How do I incorporate my logo to a slide
that will apply to all the other slides?
- On the [View] menu, point to [Master], and then click
[Slide Master] or Notes Master. Change images to the
one you like, then it will apply to all the other slides.
[ Image information in product ]
- Image : mowolf
- Note to customers : This image has been licensed to be used within PowerPoint template only.
- You may not extract the image for any other use.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/templatesforwork-090823175031-phpapp02/85/Templates-For-Work-4-320.jpg)
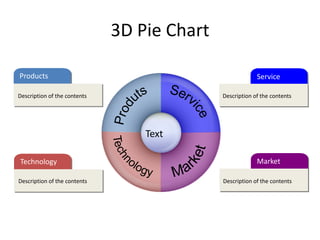


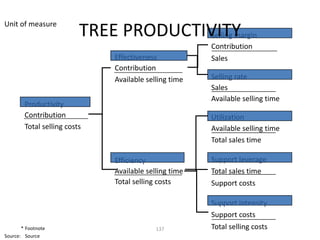

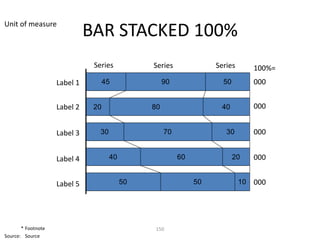
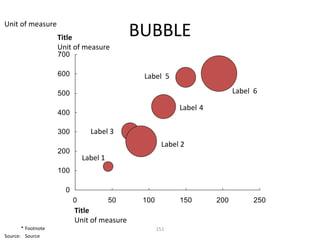
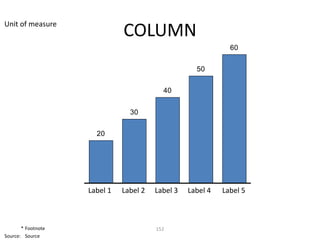
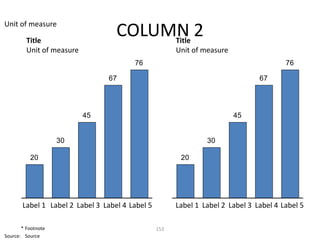
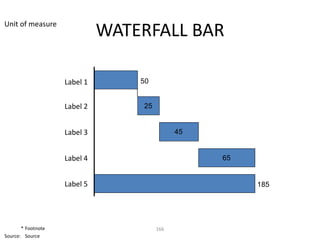
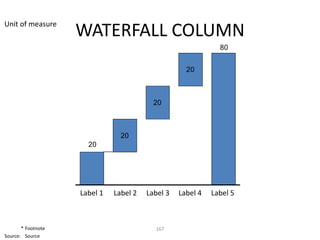

















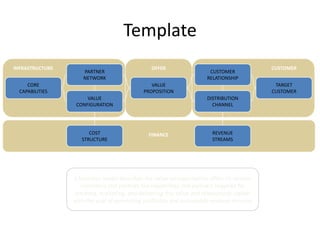
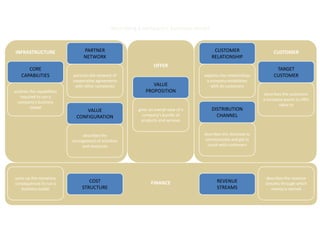
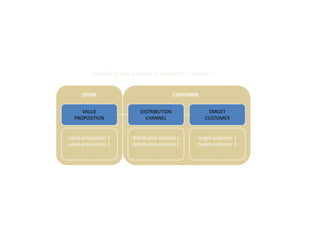
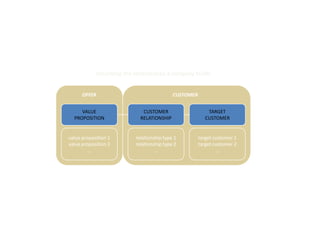
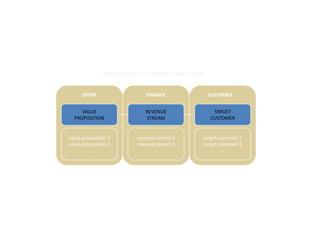
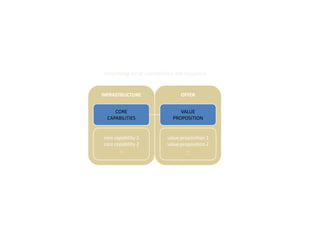
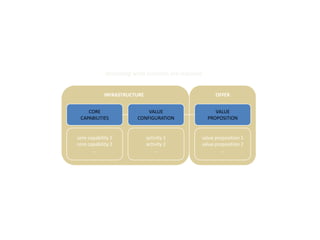


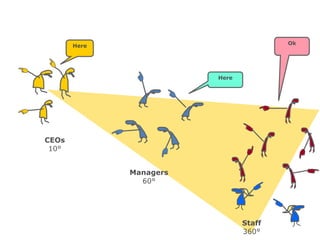



















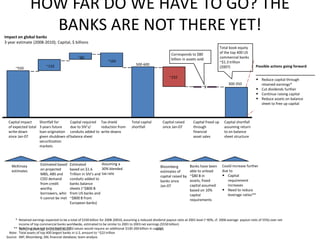





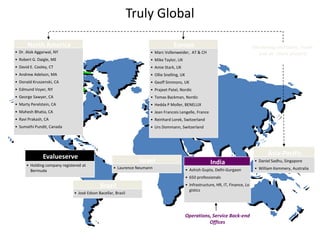



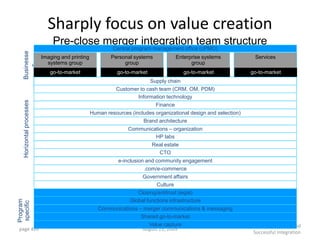
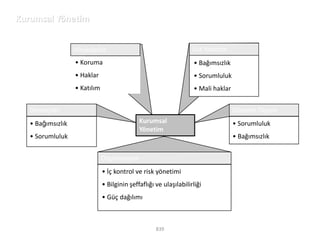
![Morgan Stanley
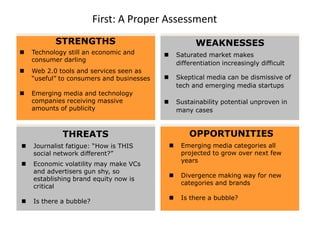
Requirements for Success
Importance of Culture
“Despite leaner times, Morgan Stanley has been one of the most successful
European banks and was the first major tenant at Canary Wharf, helping to build
the area‟s success.”
“After September 11, hotlines and counselling sessions were used heavily. As
one employee wrote: “Morgan Stanley showed its true character and strength
during the tragedy.”
The Sunday Times, 100 Best Companies to Work for 2002 (March, 2002)
“By general consensus in the investment banking community, there is something
special about Morgan Stanley's London office”
“…what keeps them here is a team culture, a sense that this is a meritocracy…”
Fortune, Best Companies to Work for – 10 Great Companies in Europe (February 4, 2002)
“…[Morgan Stanley‟s] recent success has been nothing short of sensational.”
“Several employees in our survey praise Morgan Stanley for being a
meritocracy.”
The Sunday Times, 50 Best Companies to Work for 2001 (February, 2001)
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/templatesforwork-090823175031-phpapp02/85/Templates-For-Work-475-320.jpg)

































































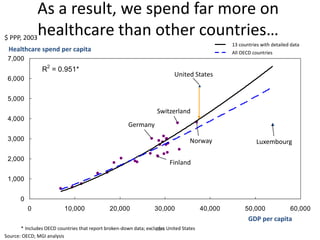
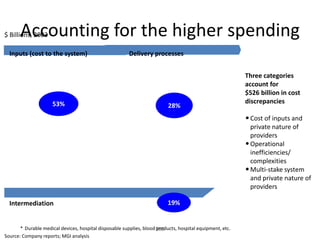
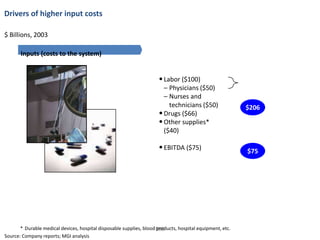
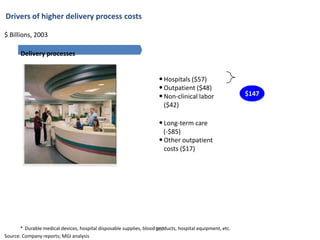

















![Hot Tip
• How do I incorporate my logo to a
slide that will apply to all the other
slides?
– On the [View] menu, point to [Master], and
then click [Slide Master] or [Notes Master].
Change images to the one you like, then it will
apply to all the other slides.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/templatesforwork-090823175031-phpapp02/85/Templates-For-Work-618-320.jpg)


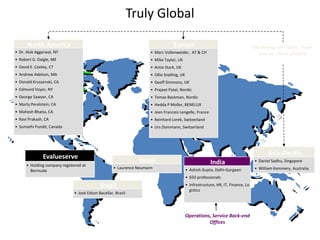
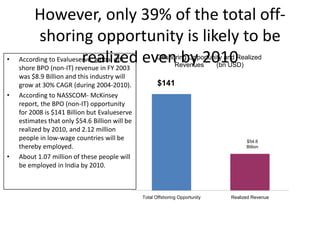
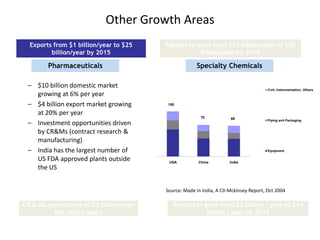


















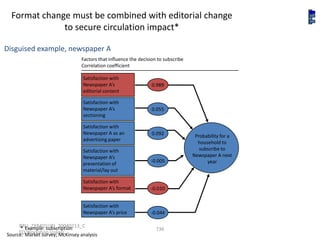



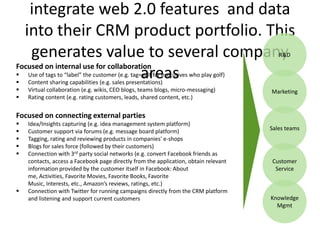






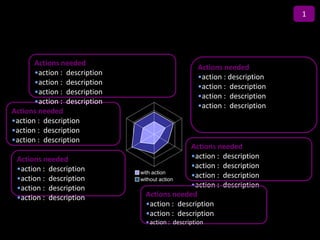
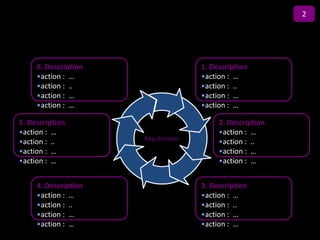
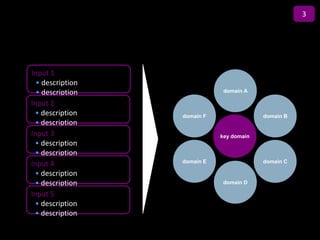
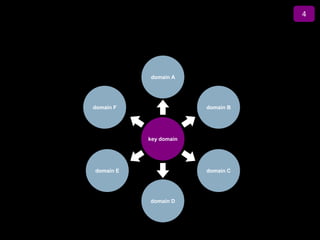
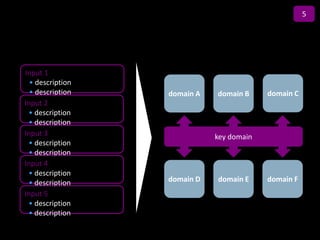




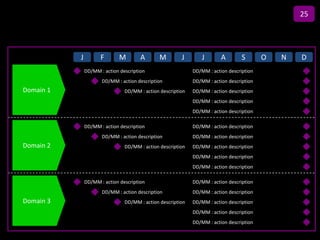
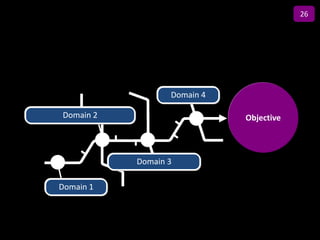
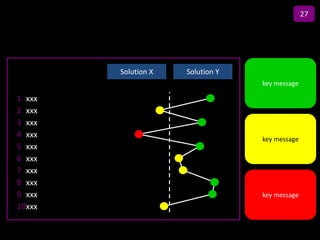
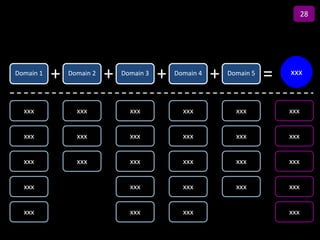









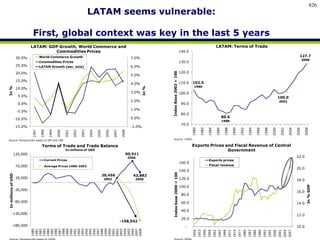
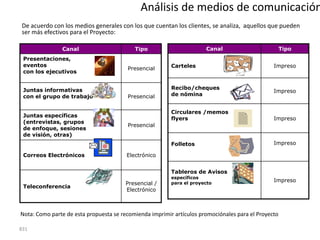
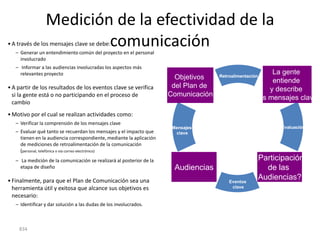

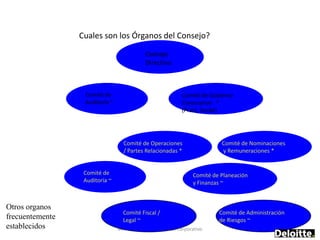



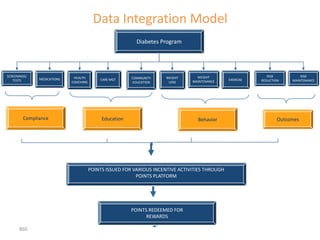















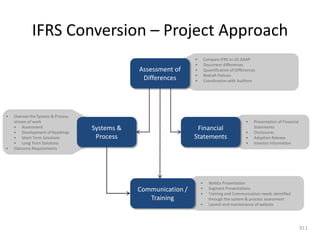
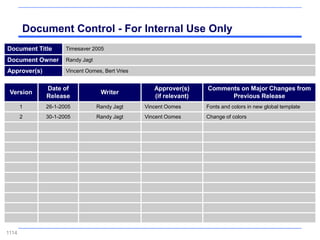
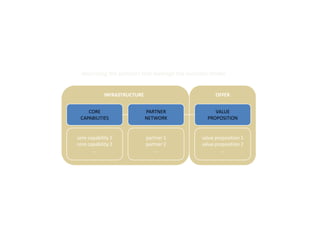
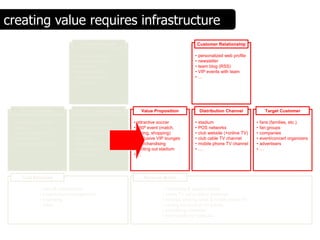
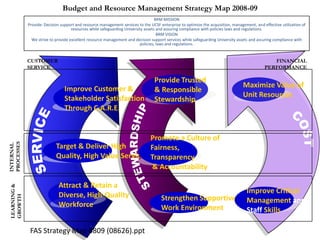
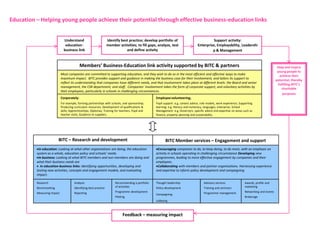
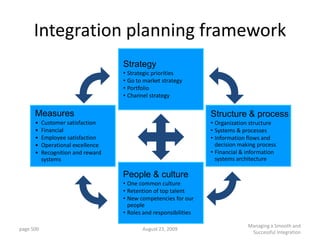
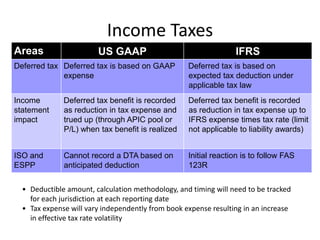
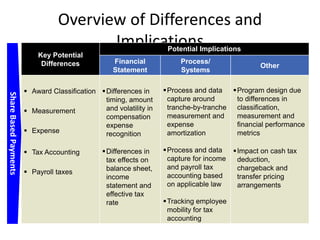
![Summary – Share Based Payments
Owner John Doe: Corporate Accounting
Business Business Unit: Corporate
Unit & Area Business Area: Share Based Payments
There are a number of accounting changes which impact the calculation of Share Based Payments (SBP). These changes impact
Stock Options, SARs, RSUs, PRSUs and PPRSUs. All of the changes for Share Based Payment impact at the corporate level, there
is not direct impact on the Business Units.
• Grade Vesting : This change has no implication on the process however [3rd Party Provider] will need to be informed of the
change for the Fair Value calculations. (There will be change in the process as company will have to now calculate expense on
accelerated method then straightl-ine method.)
• Fair Value / Intrinsic Liability: The templates used for the SAR calculations will need to be updated to reflect the accounting
change on conversion to IFRS. (not applicable to US company as USGAAP/IFRS has same treatment for liability plan)
• Forfeiture – Actual vs. Estimated : For Stock Options and SARs currently the Company does not accrue for forfeiture estimate
IFRS Process & and recognized as vested. Under IFRS, the Company will be required to estimate the number of equity instruments expected to
Systems Impact vest and then revised estimate as required. This will add an additional process to the current workflow. (no difference between
IFRS and US GAAP)
• DTA : All SBP types are affected by this change. This results in an additional process and journal entry for the accrual.
• Payroll Taxes : Currently payroll taxes are expensed as incurred, i.e. at the time of exercise. Under IFRS the Company should
accrue for Payroll tax during the award life. The accrual process is additional step to the current workflow.
912](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/templatesforwork-090823175031-phpapp02/85/Templates-For-Work-912-320.jpg)
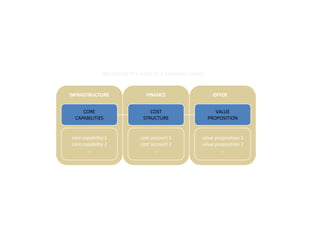
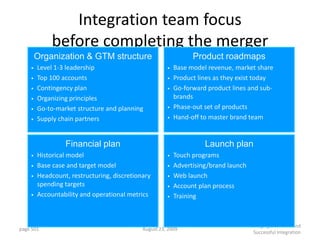
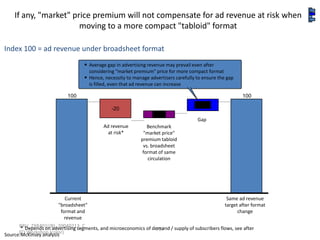
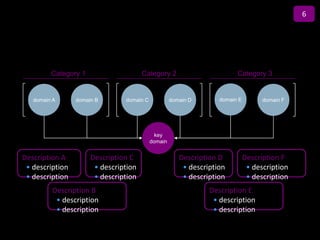
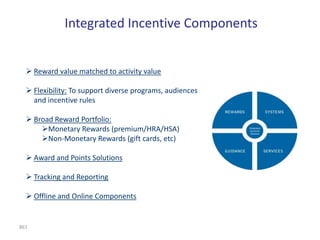
![Graded Vesting Example– Upward
Sloping Volatility
Inputs Volatility Term Structure
Number of Tranches 3
70%
Stock Price $10.00
Strike Price $10.00 60%
Dividend Yield (%) 0.00% 50%
Risk free rate (%) 3.33%
Volatility
40%
Volatility (%) 35.0%
Contractual Term (Years) 10.00 30%
20%
10%
Summary 0%
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
GAAP-123(R) Value $3.23
Expected Term (Years)
IFRS 2 Value [1] $3.07
Difference ($) -$0.16
Difference (%) -5.06%
Notes
[1] Under IFRS 2, the expected term for plain-vanilla options is estimated for each individual tranche. The IFRS
value shown is the weighted-average value of each of the individual tranches. The overall weighted-average expected
life is set equal to the expected life assumed under GAAP. We have assumed that the expected life of each tranche
is equal to a fixed amount of time plus the individual tranche's vesting period, such that the weighted-average
expected life of the tranches is equal to the expected life under GAAP.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/templatesforwork-090823175031-phpapp02/85/Templates-For-Work-914-320.jpg)








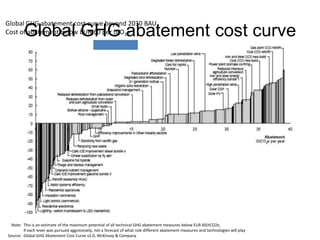

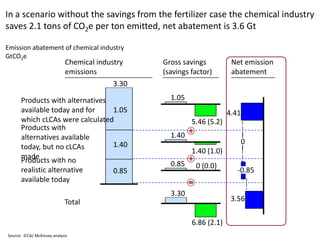
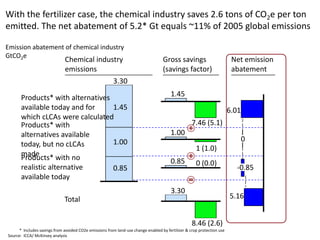

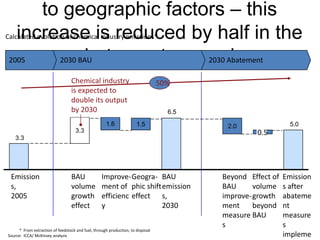
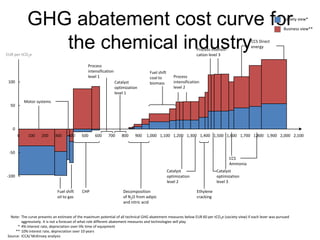
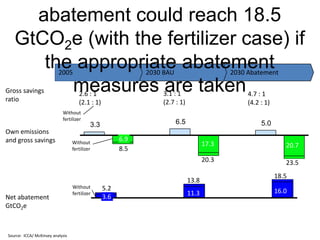
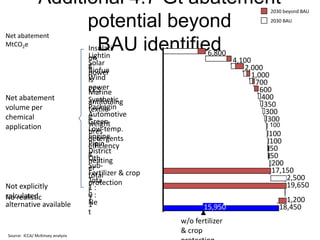
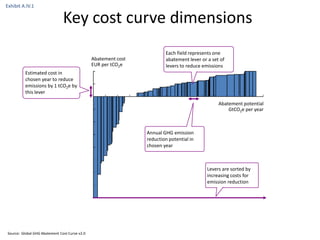
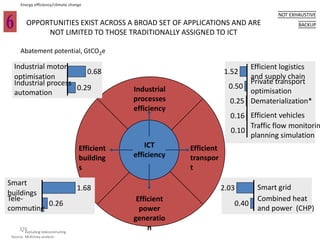
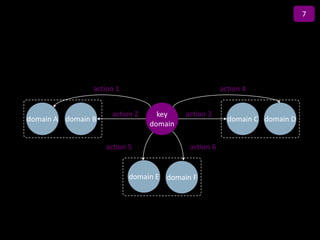
![Exhibit A.IV.2
Abatement cost formula
[Full cost of CO2e efficient alternative] cost of reference solution]
[Full
–
Abatement cost =
[CO2e emissions from reference solution] – [CO2e emissions from alternative]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/templatesforwork-090823175031-phpapp02/85/Templates-For-Work-982-320.jpg)










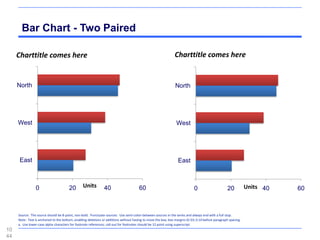
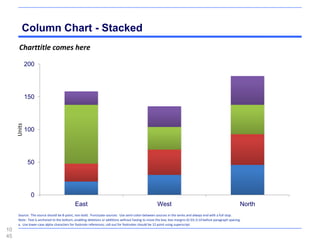
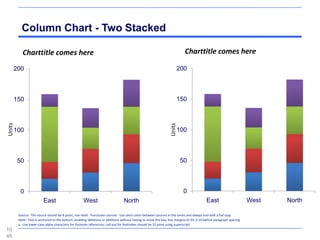
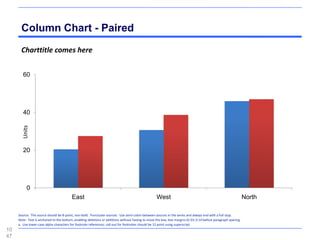



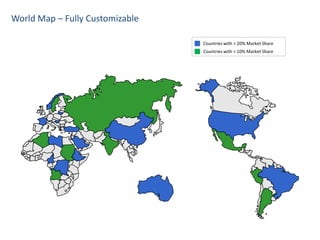
![Maps - Western Europe, The World
Subtitle comes here
[ ungroup to select countries ]
108
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/templatesforwork-090823175031-phpapp02/85/Templates-For-Work-1084-320.jpg)

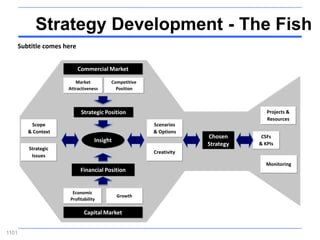
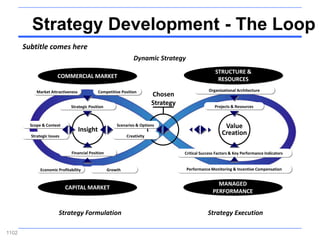
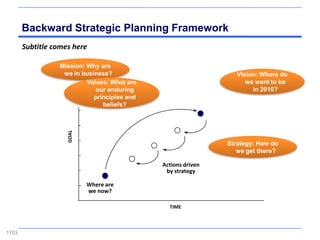
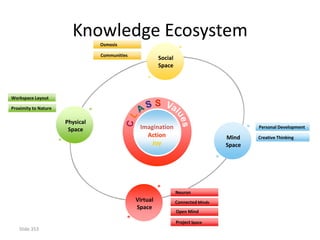
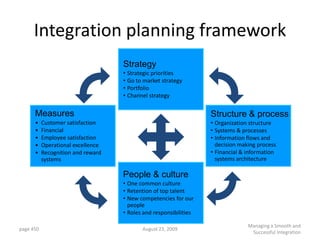
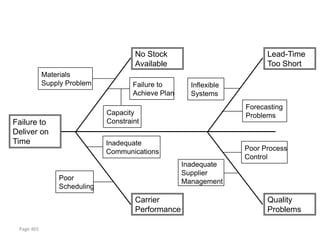
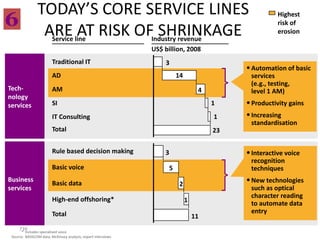
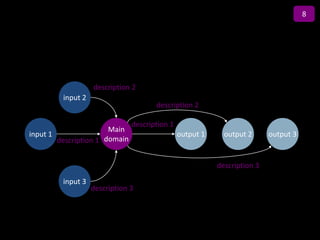
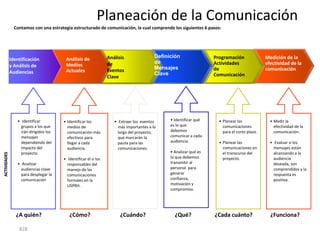
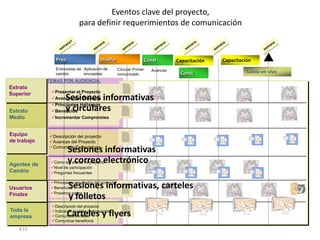
![Incremental versus Dynamic Strategic Planning
Framework
Incremental Planning Process Dynamic Strategic Planning Process
Vision of where we
need to be five years
from now
Where can we be
next year?
GOAL
GOAL
Versus
Actions driven by
Actions taken in strategy
Where we response to Where are
are now? circumstances we now?
TIME TIME
Incrementalism Focus
[One reason why companies stagnate] [One reason why companies grow]
1104](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/templatesforwork-090823175031-phpapp02/85/Templates-For-Work-1104-320.jpg)