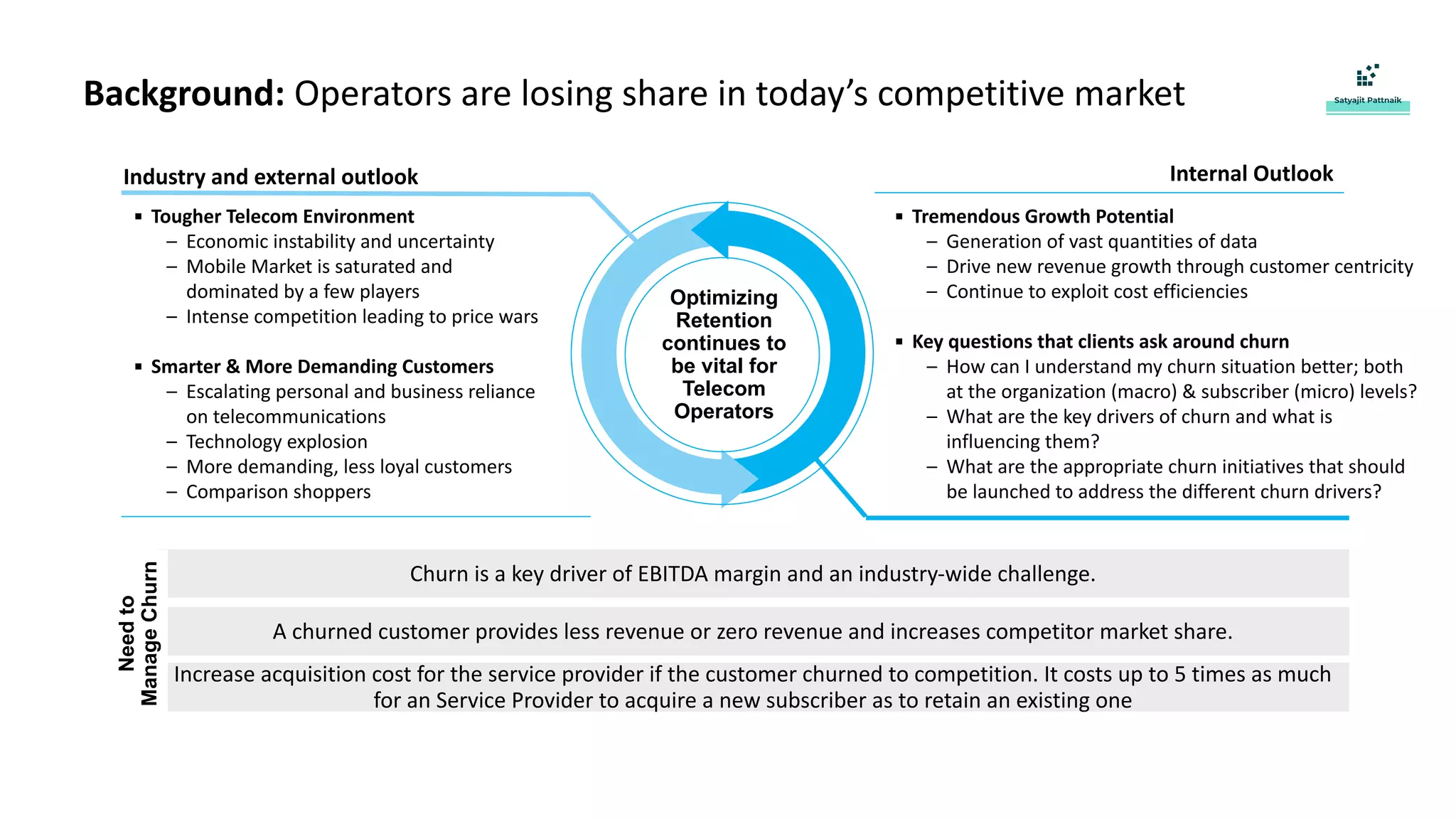
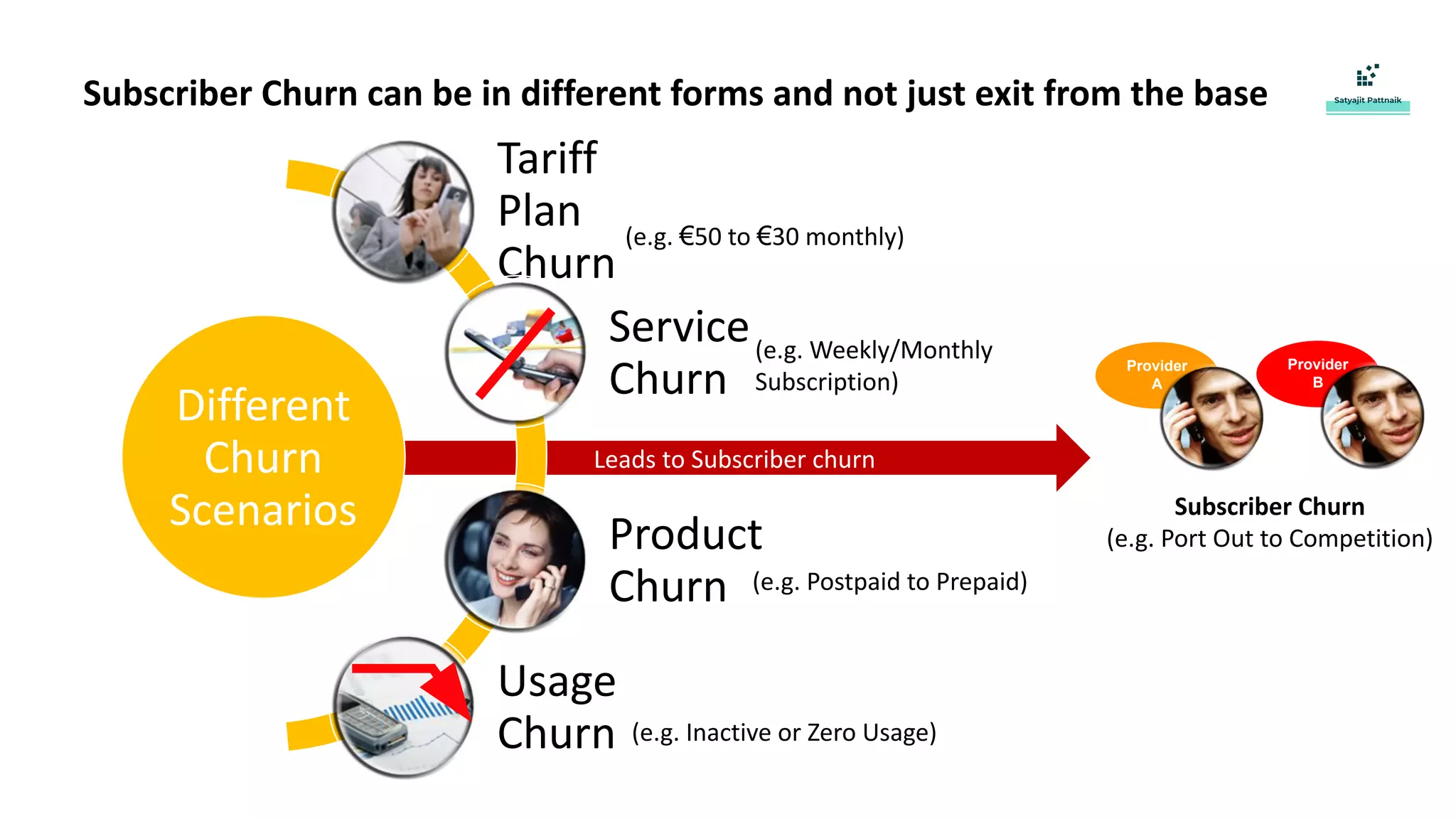
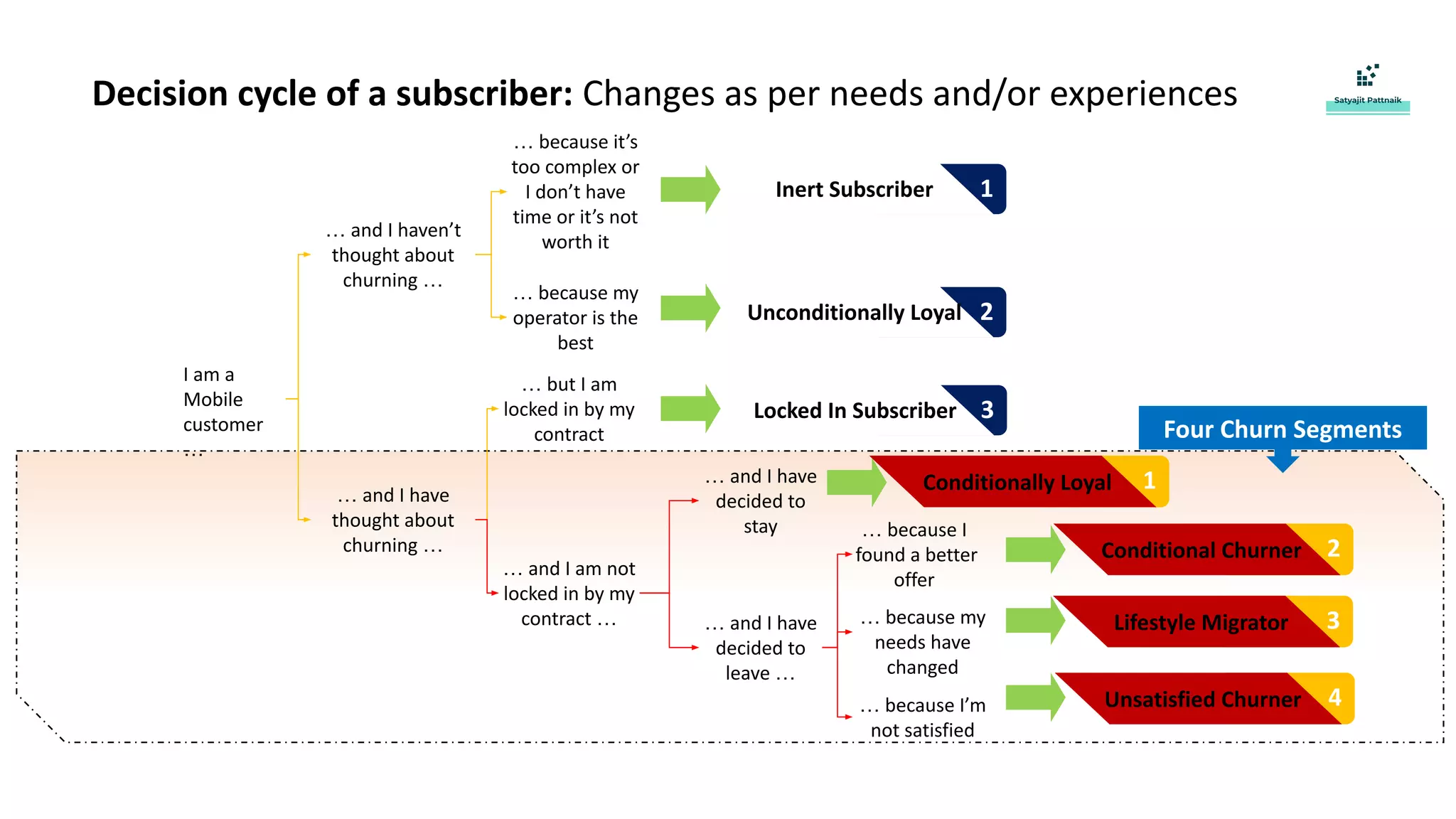
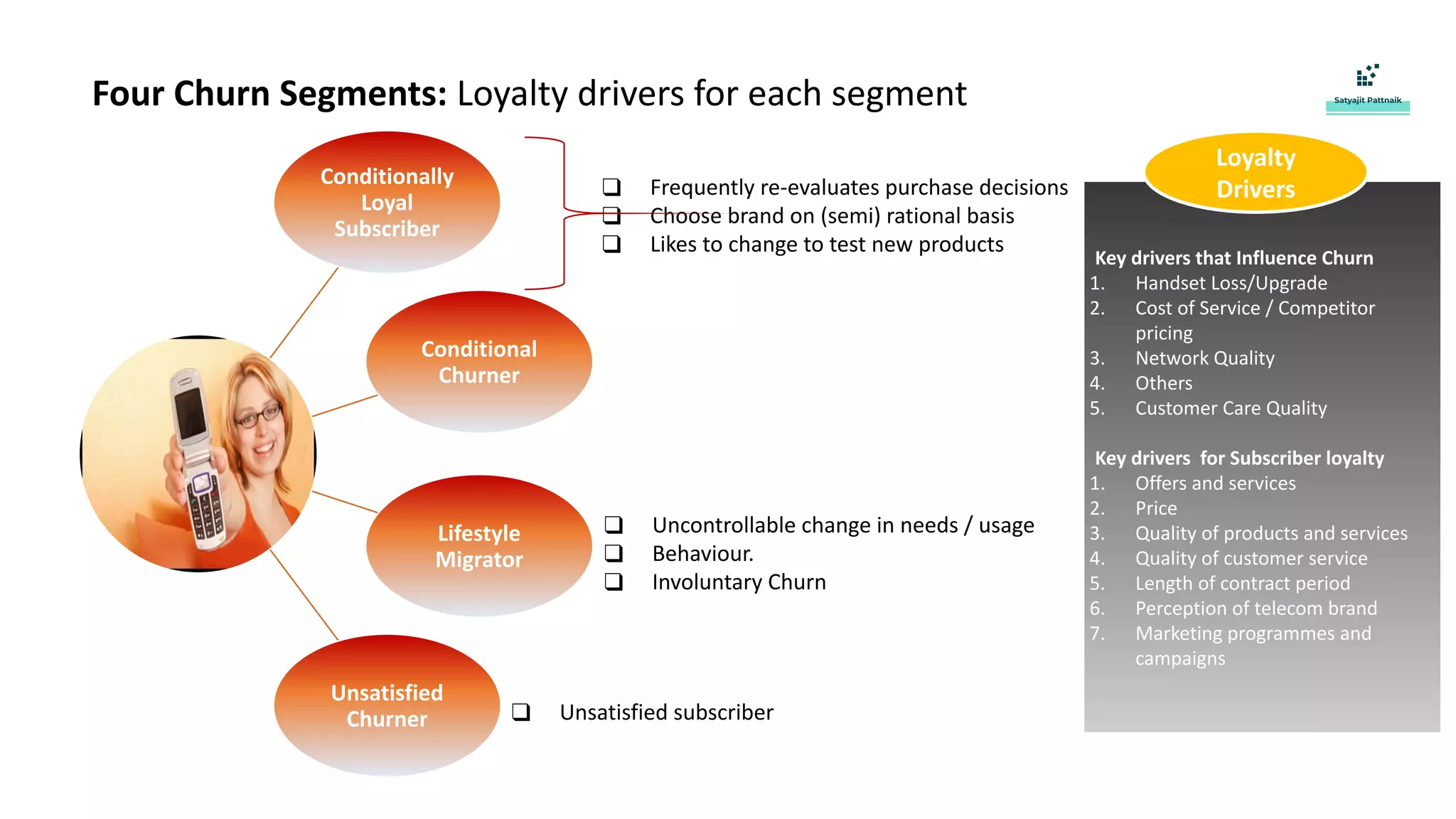
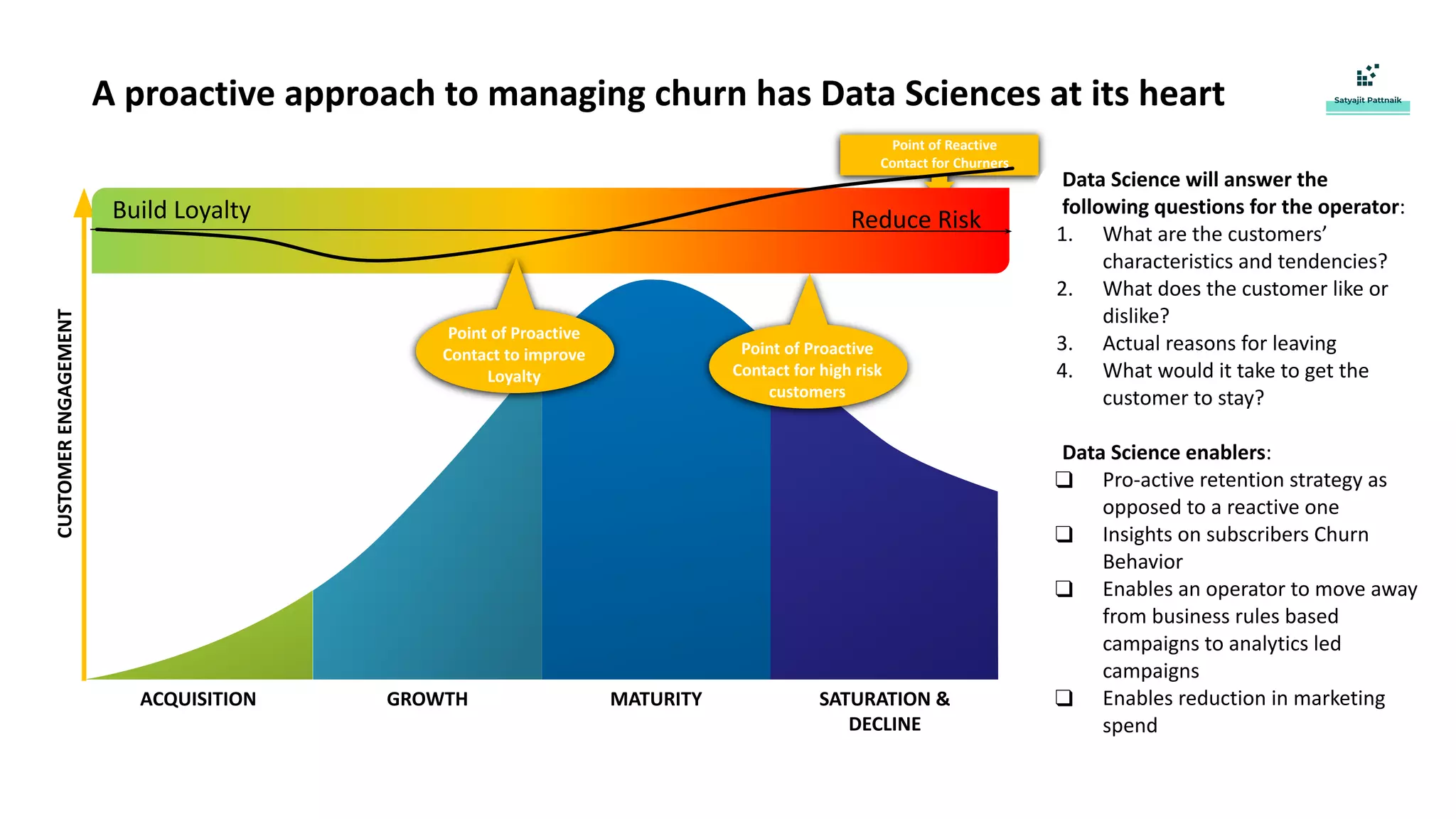
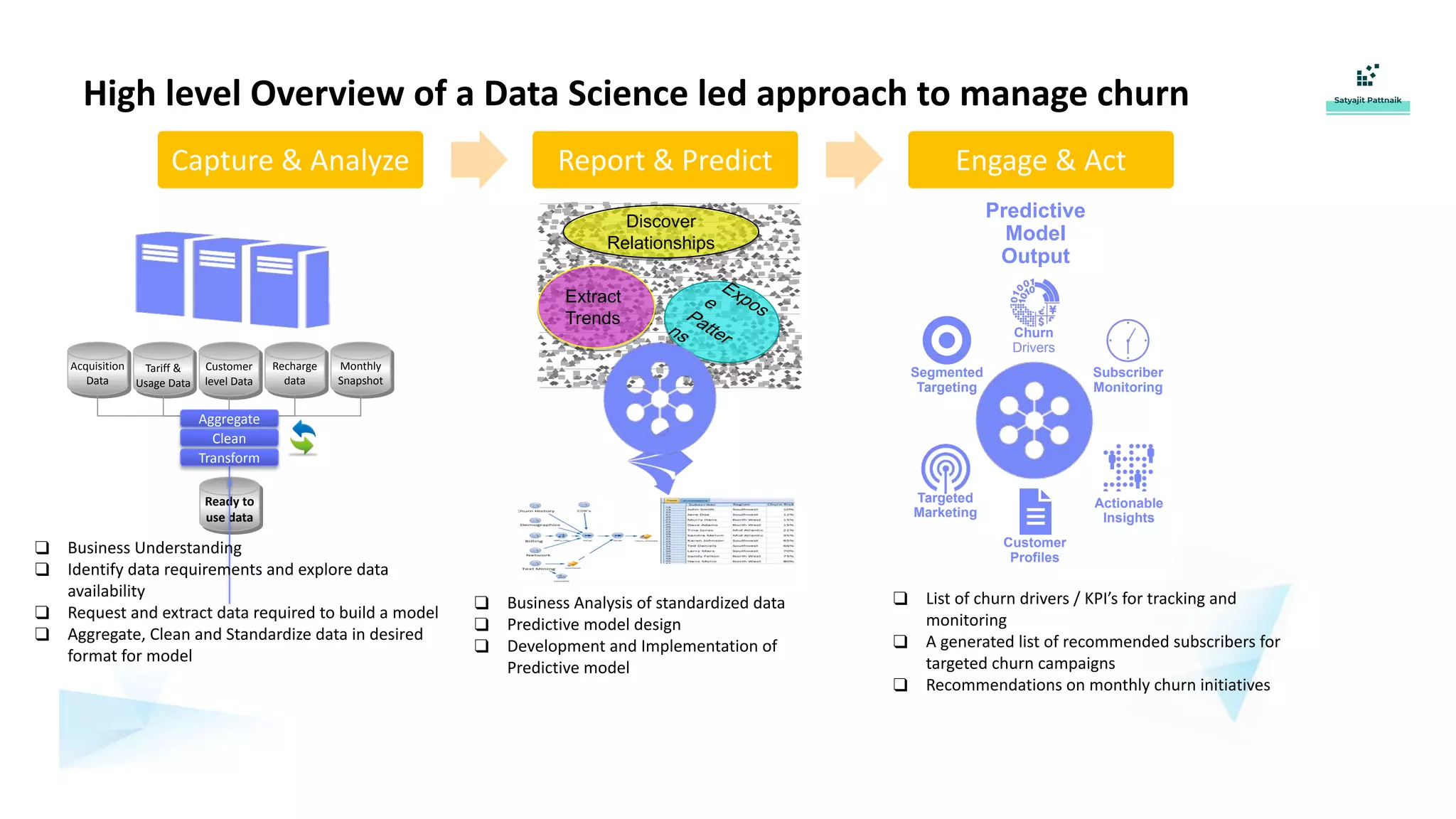
The document discusses strategies for customer retention in the telecom industry, highlighting the importance of addressing customer churn through data science. It outlines the key drivers of churn, different churn scenarios, and the necessity for proactive management using analytics to understand and address customer needs. Through a structured data science approach, telecom operators can derive insights to enhance customer loyalty and effectively reduce churn rates.