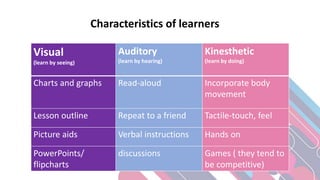
Teaching English to Young Learners (TEYL) focuses on children ages 6-12 in their first years of formal education. Key language development theorists discussed are Piaget, Vygotsky, and Bruner. Piaget's theory is that learning occurs through problem-solving interactions with the environment. Vygotsky emphasized social learning and the Zone of Proximal Development. Bruner stressed language as a tool for cognitive growth and using scaffolding techniques like simplifying tasks and demonstrating examples. Effective teaching requires understanding visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learning styles as well as developing motor skills through activities incorporating movement. Challenges for both young learners and their teachers include short attention spans, a wide