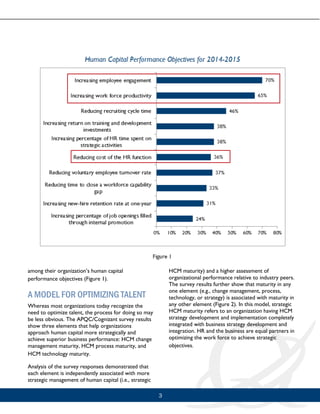
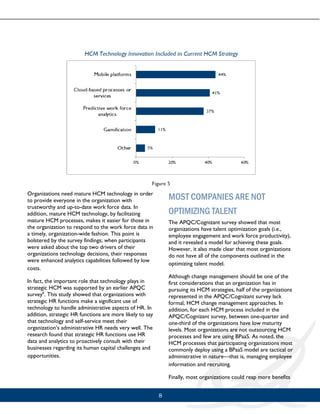
This document discusses how organizations can optimize their talent through talent optimization. It presents a model for talent optimization that includes achieving maturity in human capital management (HCM) change management, processes, and technology. The model is based on a survey that found these three elements are independently associated with more strategic HCM and better organizational performance. However, the survey also found that most organizations have not fully developed all three elements. It concludes that organizations that can achieve maturity across change management, processes, and technology will gain a competitive advantage through optimizing talent.