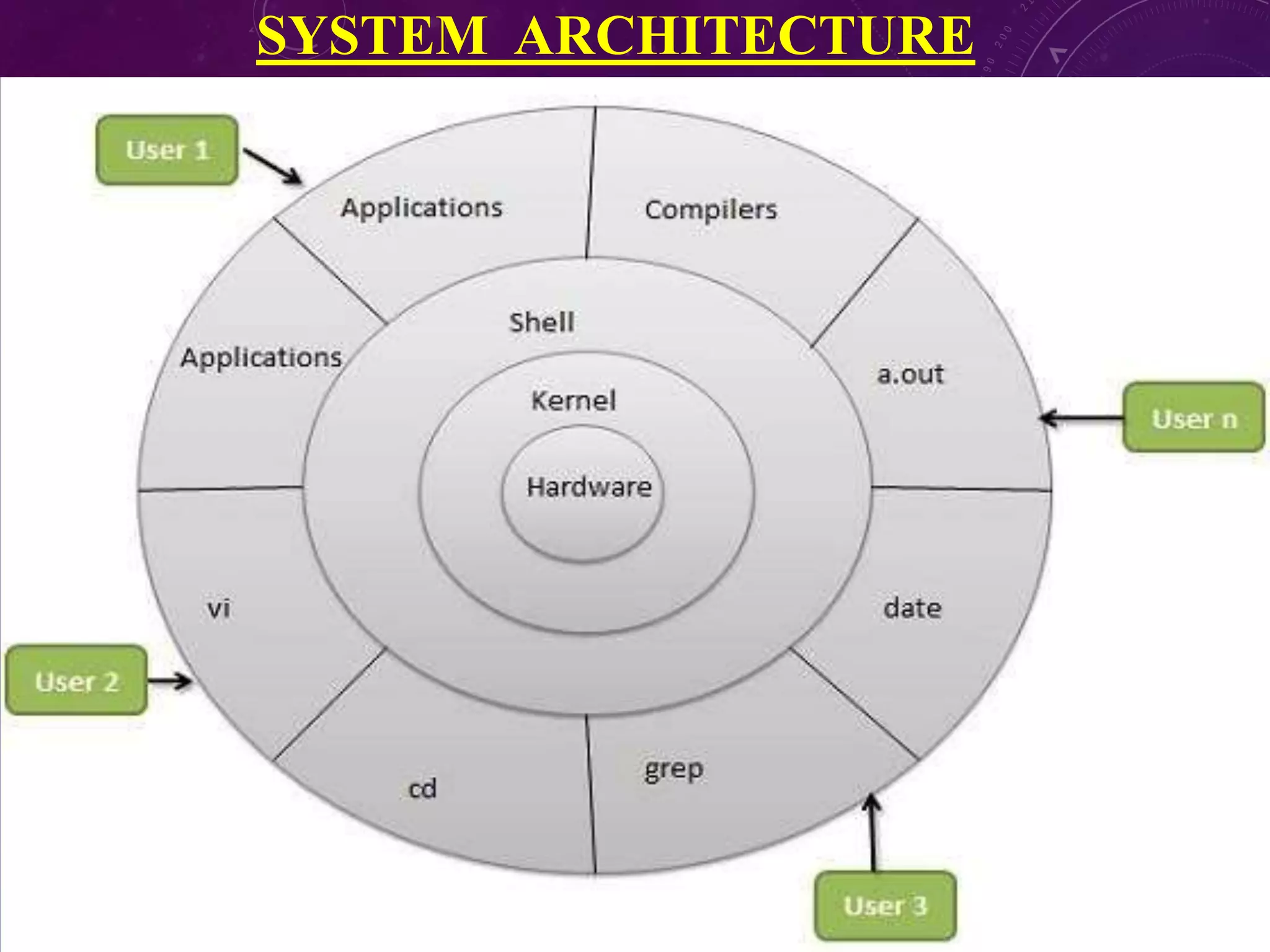
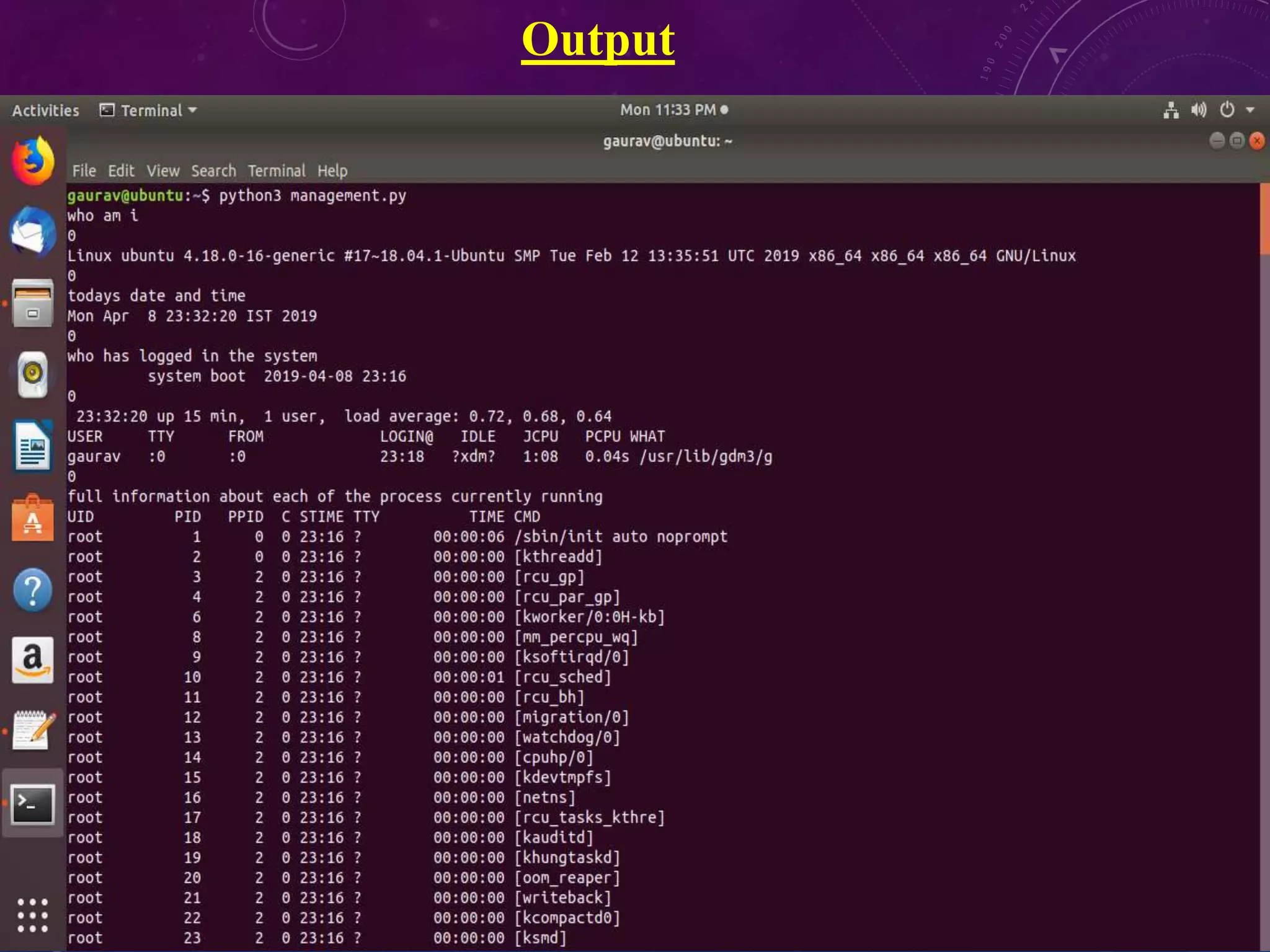
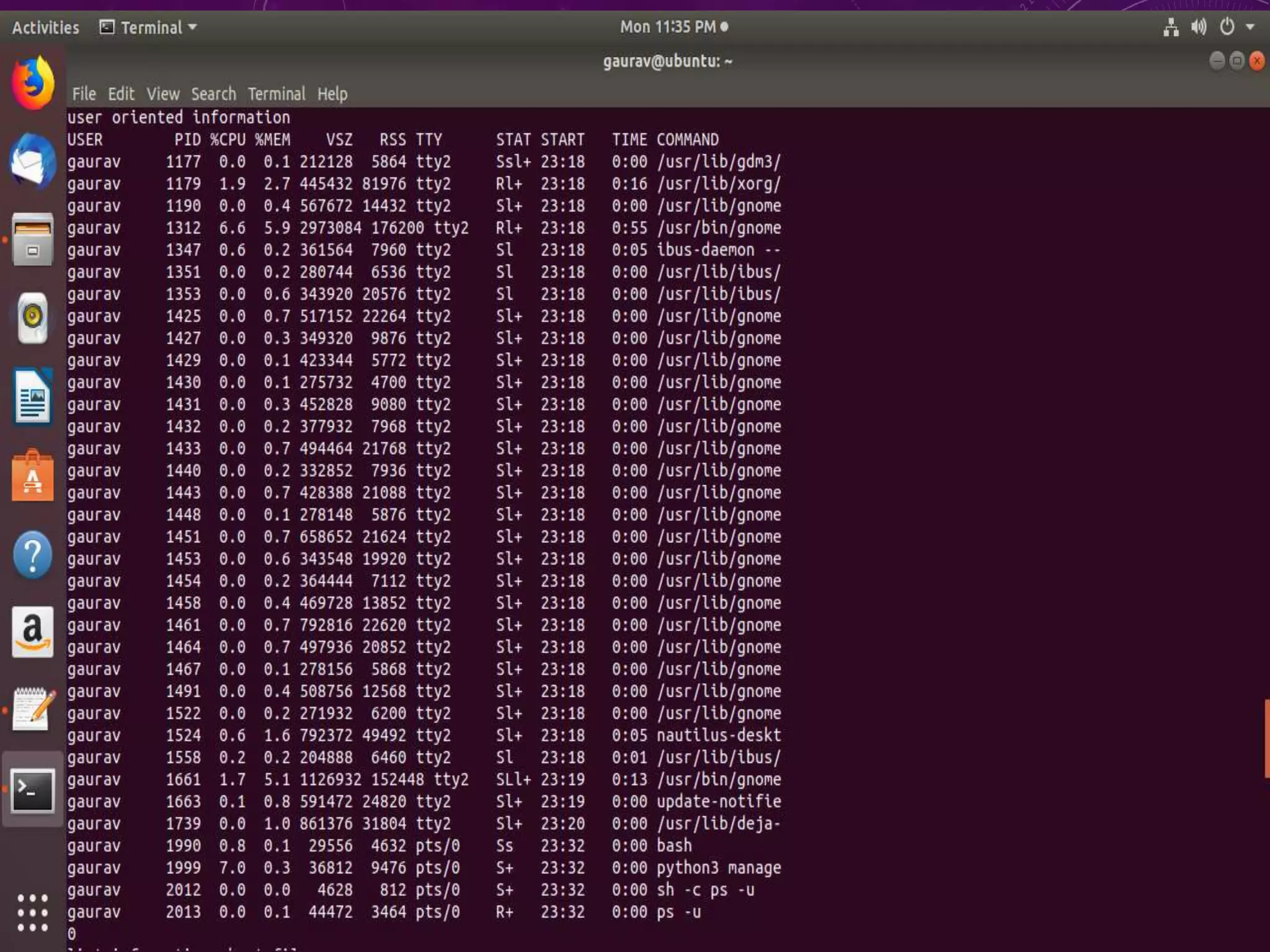
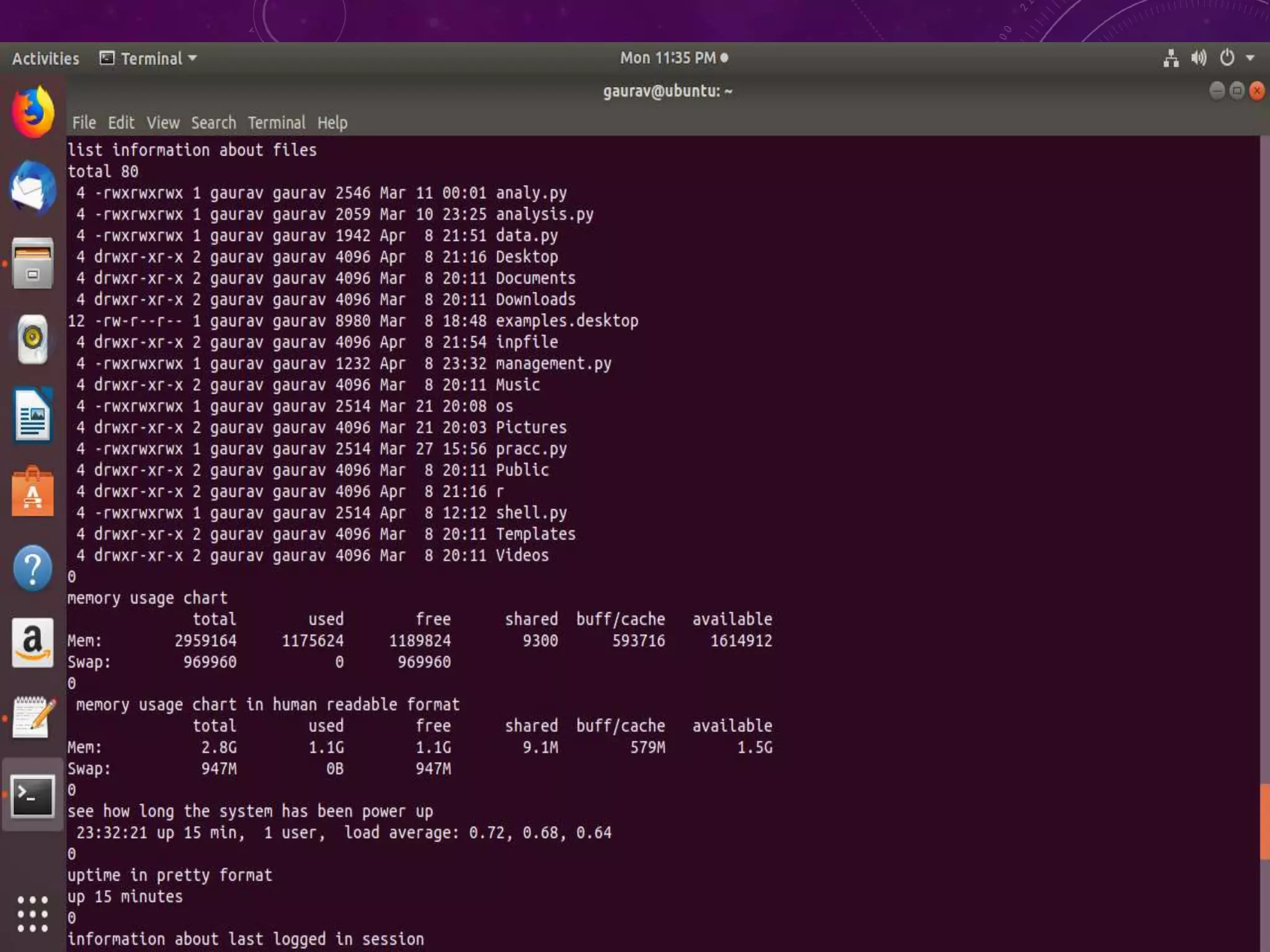
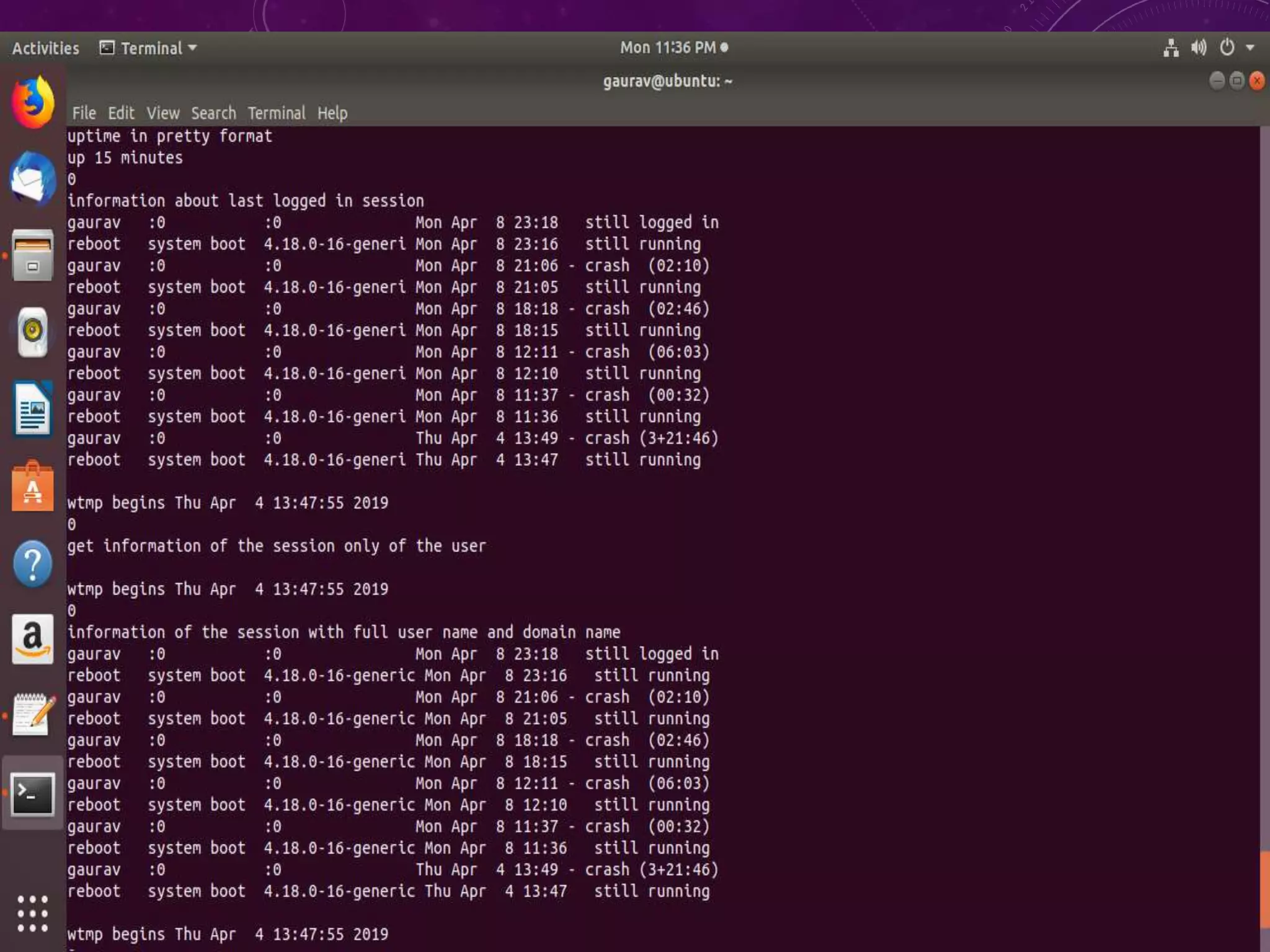
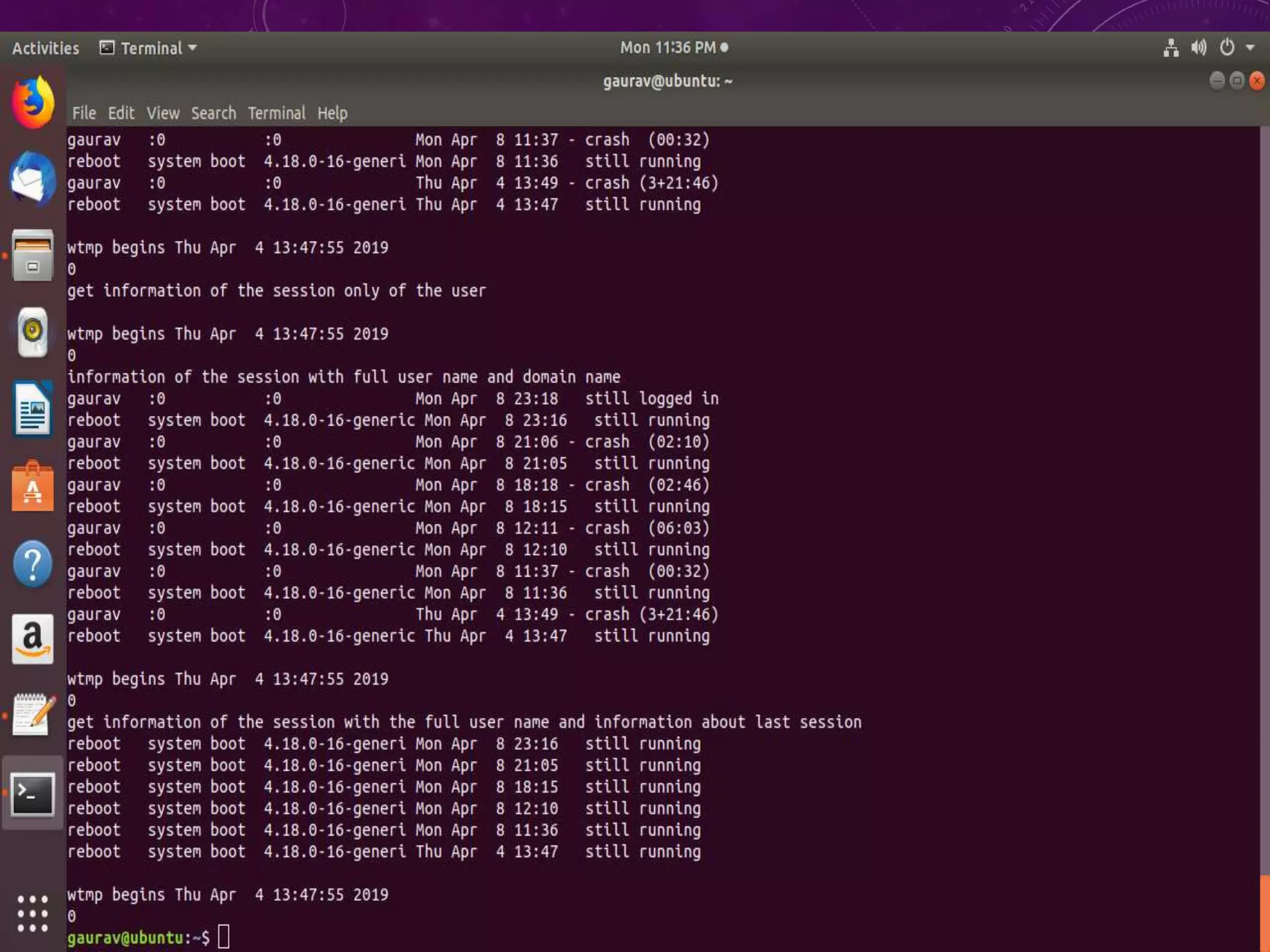
This document discusses shell programming and system administration. It provides an overview of shell scripts, their purpose, and common operations. It also describes the system architecture including hardware, kernel, shell, and utilities. Details are given on VMware, Fedora OS, Python, and various file system commands for system administration tasks.