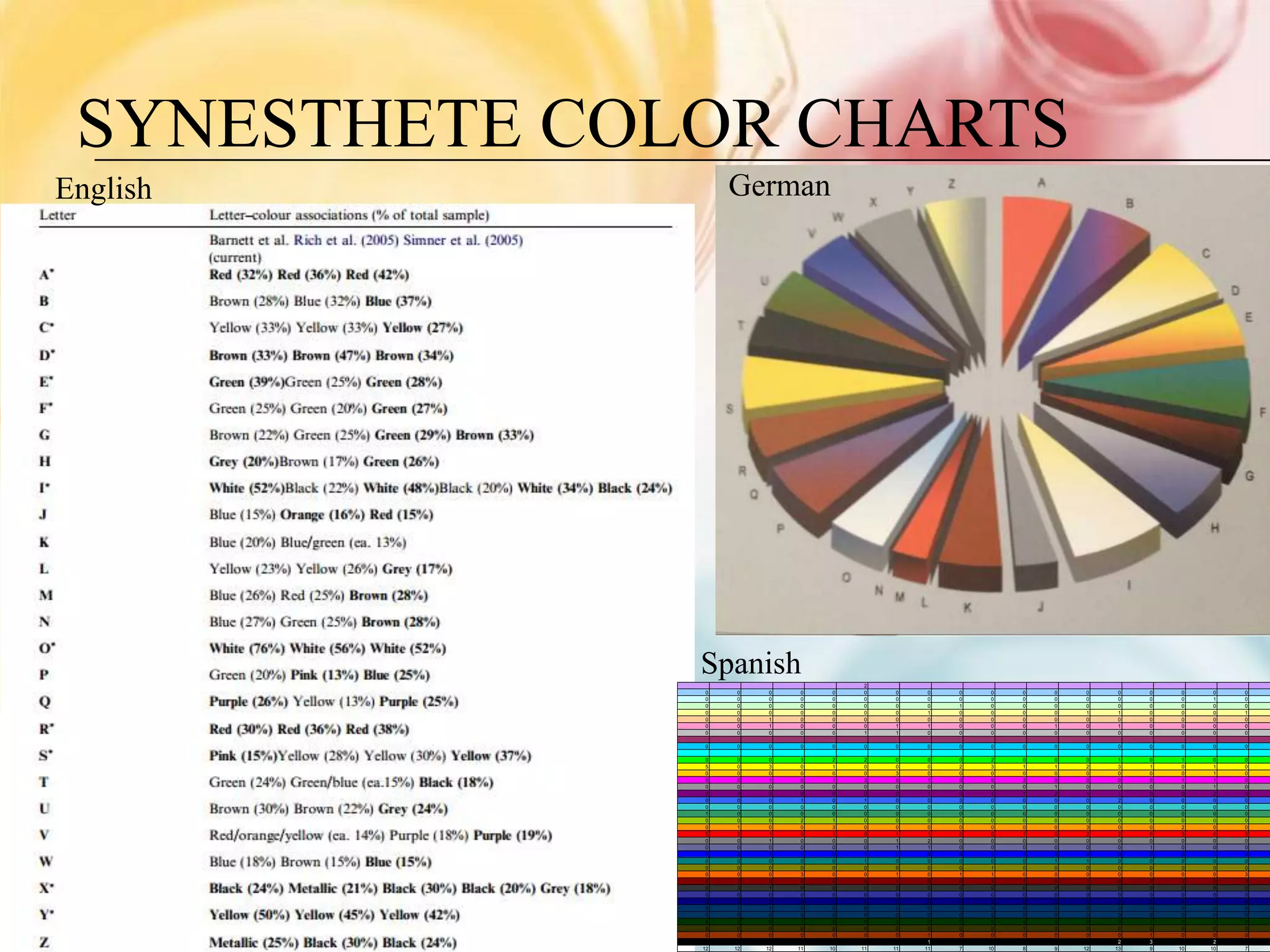
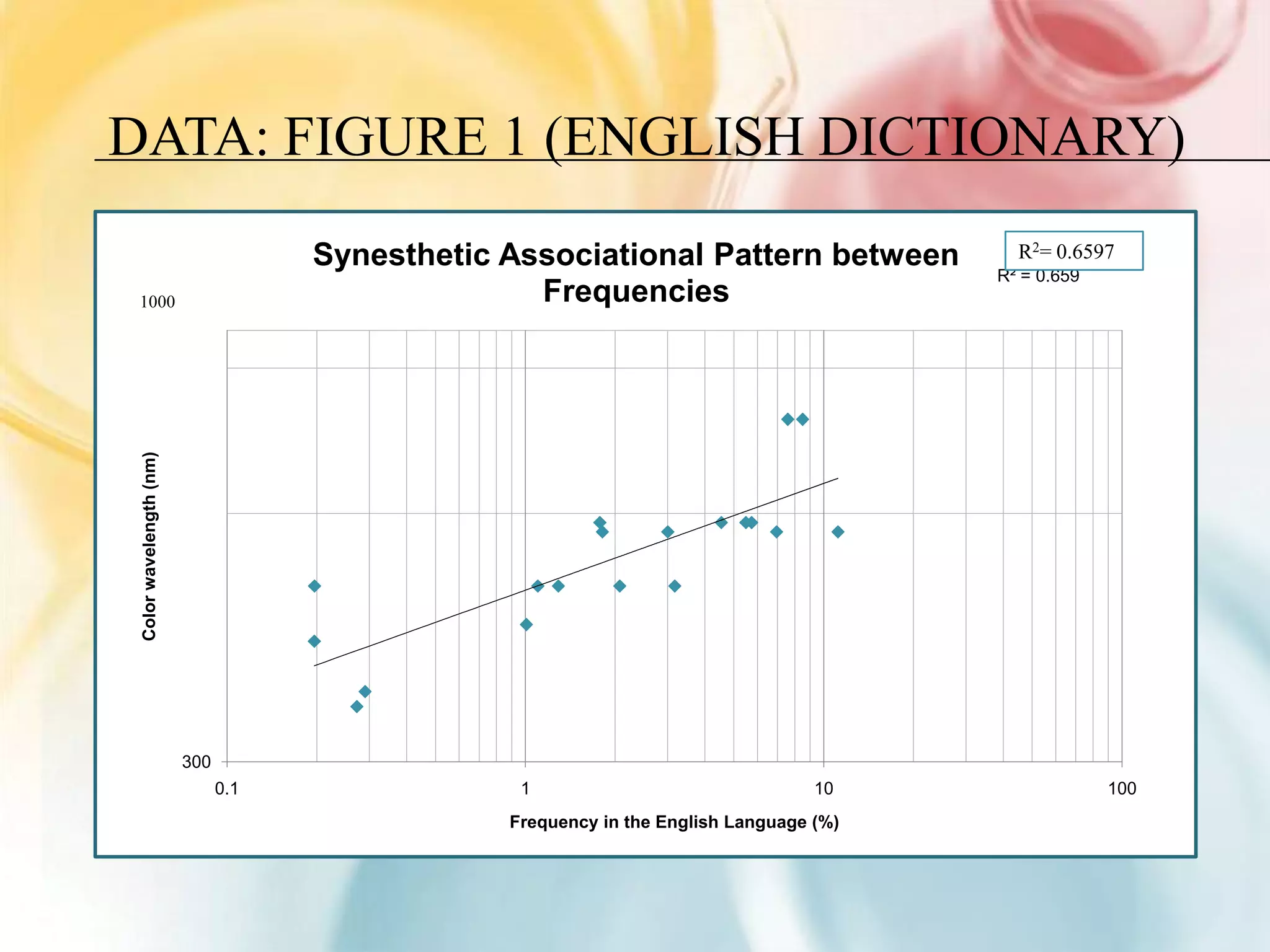
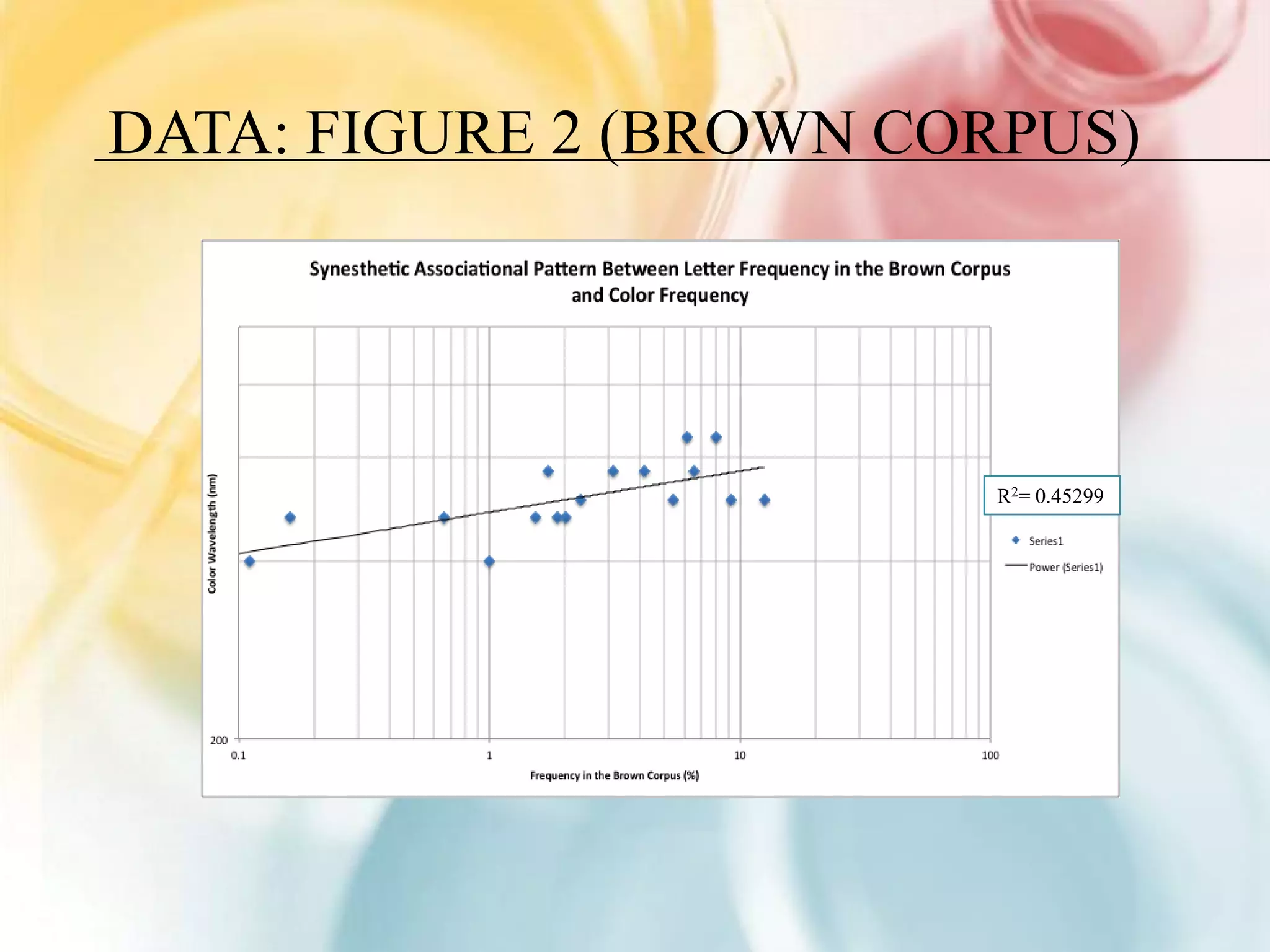
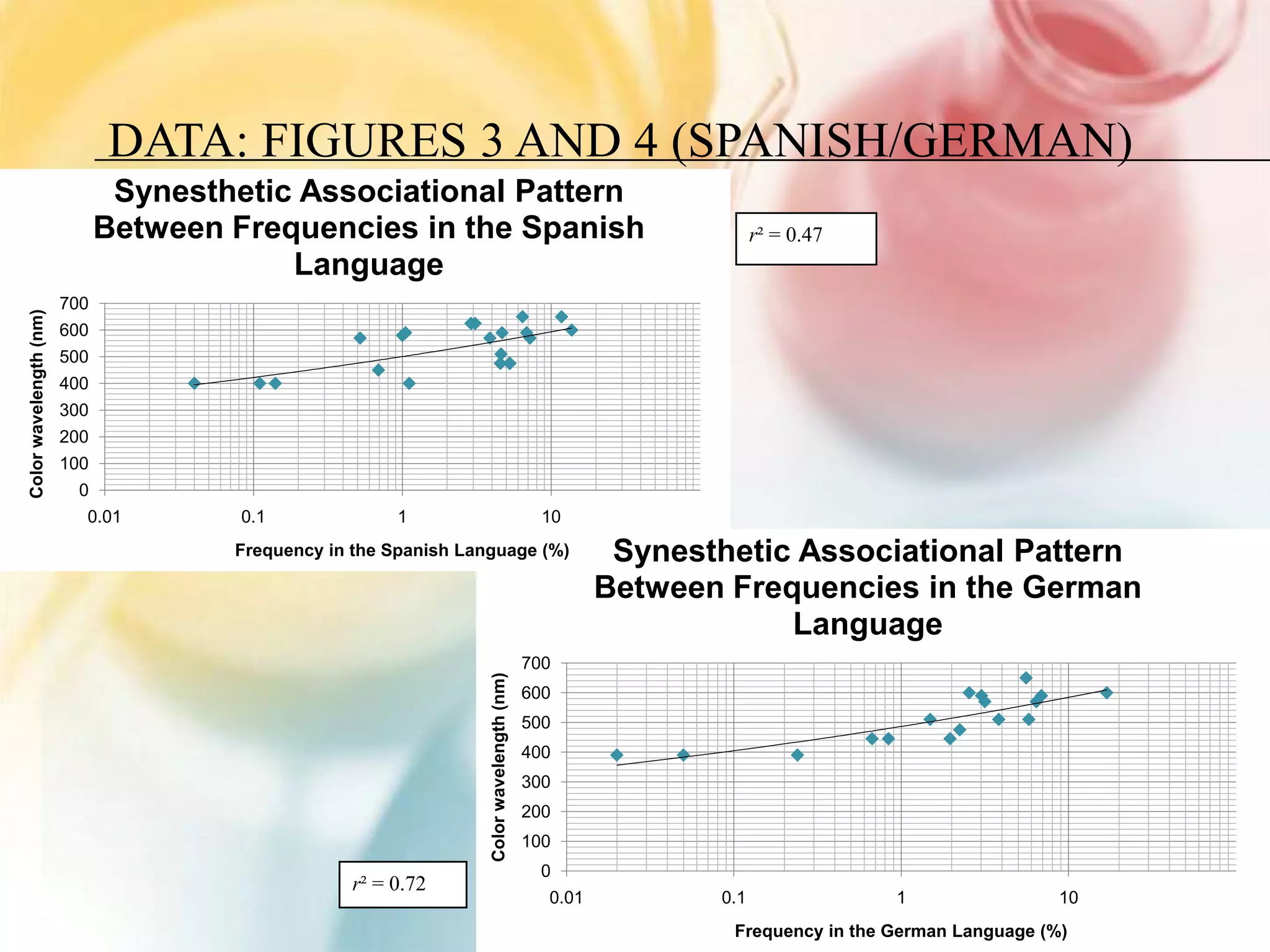
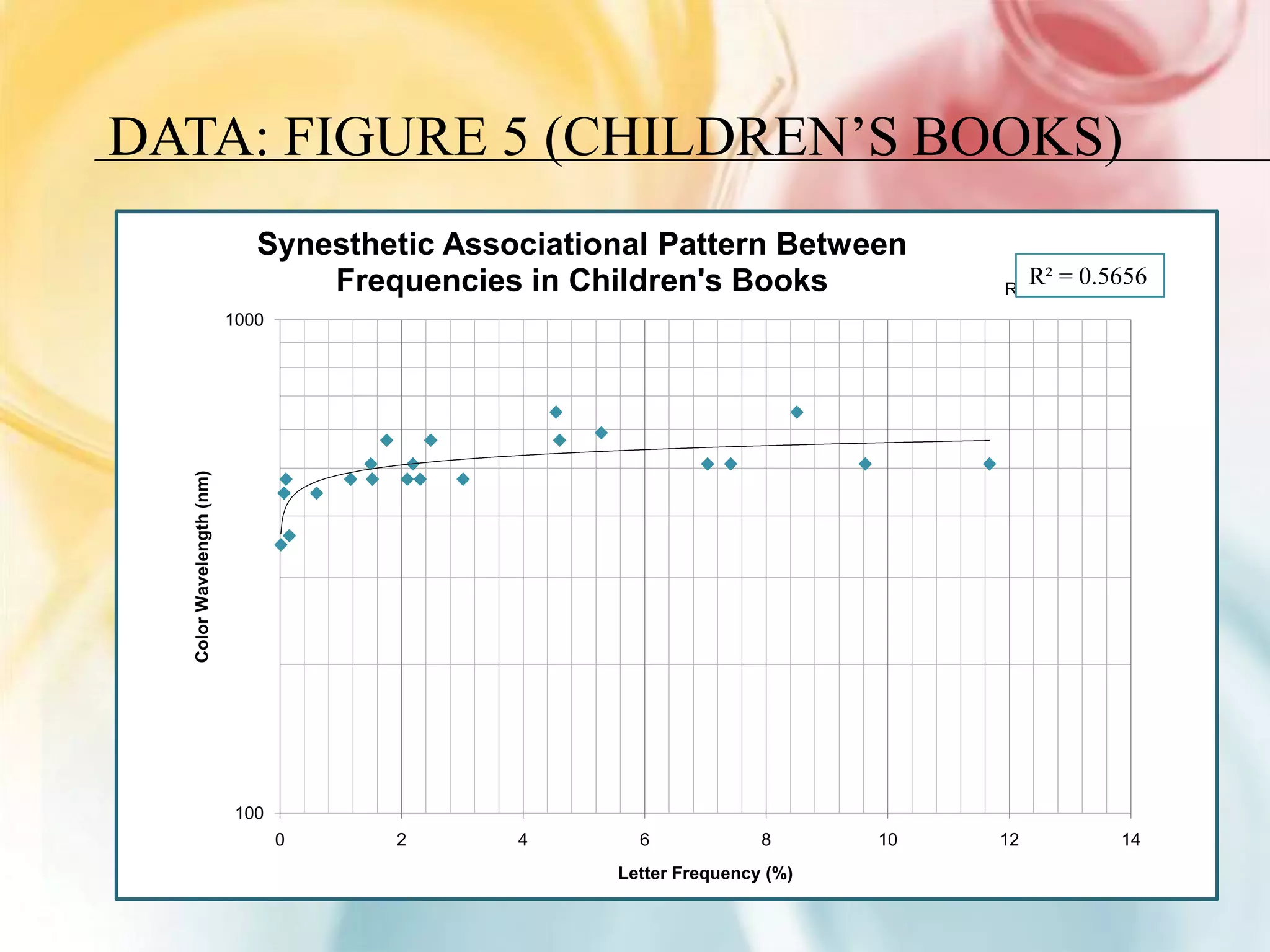
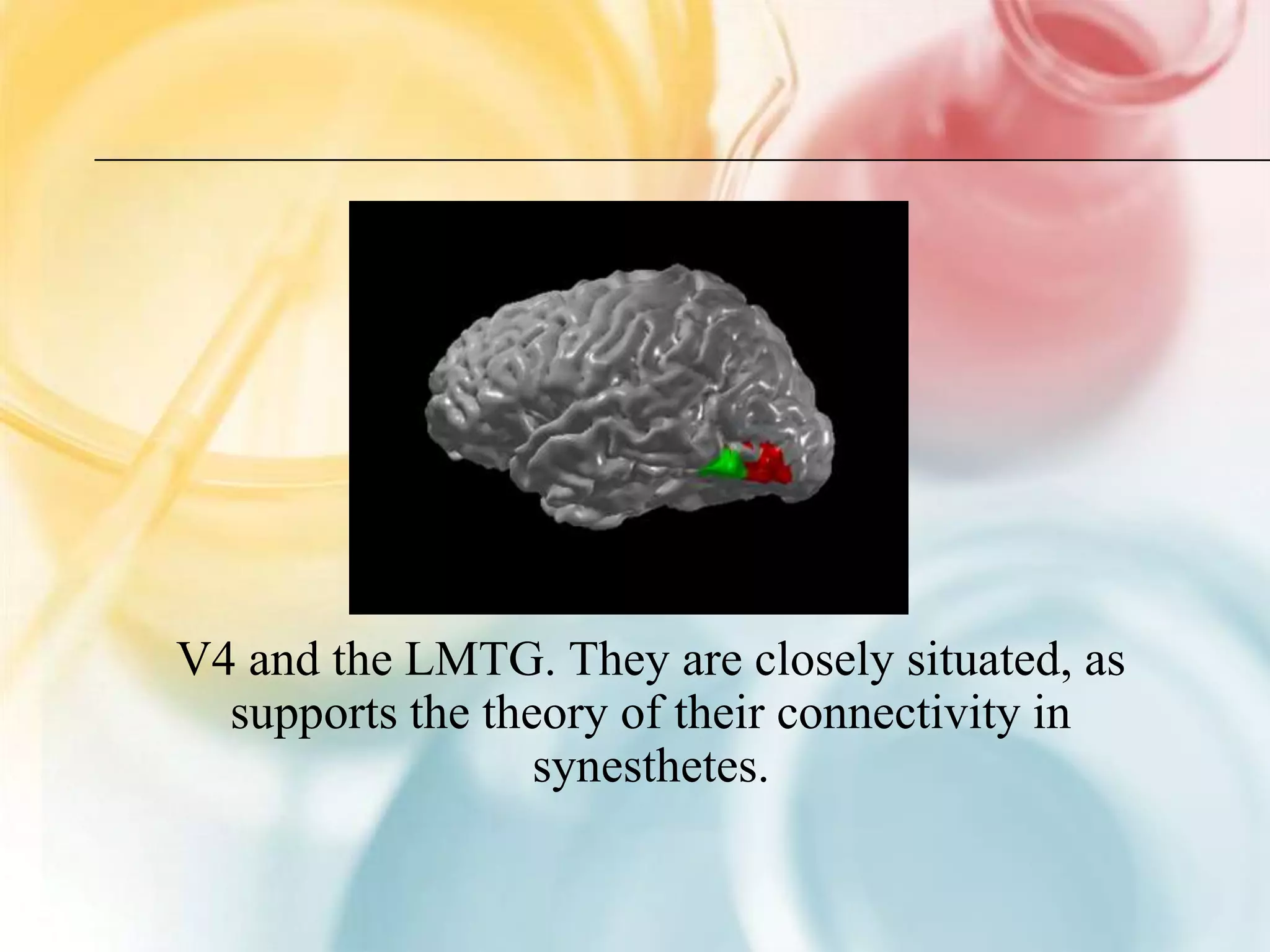
This document summarizes research on grapheme-color synesthesia, where letters or numbers elicit color associations. The researcher analyzed patterns between letter frequencies in different languages and typical color wavelengths associated with those letters by synesthetes. Charts of collective synesthetic color associations for letters in English, Spanish and German were presented. Statistical analyses found correlations between letter frequency and average associated color wavelength. This supported the theory that synesthetic associations form as individuals learn the alphabet and remain stable. The study hypothesized that synesthetic perceptions result from excess connections between the color center V4 and left middle temporal gyrus involved in semantic processing.