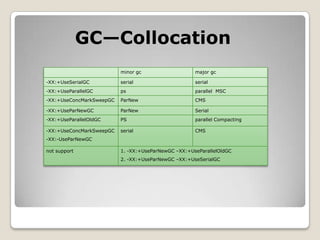
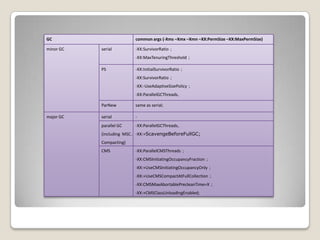
The document discusses the garbage collection (GC) mechanisms in the Sun JDK 1.6, explaining the concepts of memory allocation, different types of GC including minor and major collections, and how to tune and monitor GC performance. It details the generational garbage collection strategy, including the roles of new and old generations, and provides code examples to illustrate how different GC types operate in practice. The document serves as a guide for understanding GC's functionality and practical application in Java programming.












![Minor GC—Serialmostly allocate on TLABor eden,only two situations below will allocate on old:1、need allocate space > eden space;2、when add PretenureSizeThreshold,need allocate space > PretenureSizeThreshold. public class SerialGCDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ byte[] bytes=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes2=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes3=new byte[1024*1024*2];Thread.sleep(3000); byte[] bytes4=new byte[1024*1024*4];Thread.sleep(3000); }}-Xms20M –Xmx20M –Xmn10M –XX:+UseSerialGC-Xms20M –Xmx20M –Xmn10M -XX:PretenureSizeThreshold=3145728 –XX:+UseSerialGC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-16-320.jpg)
![Minor GC—Serialgc occurs when eden space is not enough.public class SerialGCDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ byte[] bytes=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes2=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes3=new byte[1024*1024*2];System.out.println(“step 1"); byte[] bytes4=new byte[1024*1024*2];Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println(“step 2"); byte[] bytes5=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes6=new byte[1024*1024*2];System.out.println(“step 3"); byte[] bytes7=new byte[1024*1024*2];Thread.sleep(3000); }}-Xms20M –Xmx20M –Xmn10M –XX:+UseSerialGC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-17-320.jpg)

![Minor GC—Serial public class SerialGCDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ byte[] bytes=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes2=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes3=new byte[1024*1024*2];System.out.println("step 1"); bytes=null; byte[] bytes4=new byte[1024*1024*2];Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println("step 2"); byte[] bytes5=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes6=new byte[1024*1024*2]; bytes4=null; bytes5=null; bytes6=null;System.out.println("step 3"); byte[] bytes7=new byte[1024*1024*2];Thread.sleep(3000); }}-Xms20M –Xmx20M –Xmn10M –XX:+UseSerialGC-Xms20M –Xmx20M –Xmn10M -XX:-HandlePromotionFailure –XX:+UseSerialGC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-19-320.jpg)


![Minor GC—Serialpublic class SerialGCThreshold{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{SerialGCMemoryObject object1=new SerialGCMemoryObject(1);SerialGCMemoryObject object2=new SerialGCMemoryObject(8);SerialGCMemoryObject object3=new SerialGCMemoryObject(8);SerialGCMemoryObject object4=new SerialGCMemoryObject(8); object2=null; object3=null;SerialGCMemoryObject object5=new SerialGCMemoryObject(8);Thread.sleep(4000); object2=new SerialGCMemoryObject(8); object3=new SerialGCMemoryObject(8); object2=null; object3=null; object5=null;SerialGCMemoryObject object6=new SerialGCMemoryObject(8);Thread.sleep(5000); }}class SerialGCMemoryObject{ private byte[] bytes=null; public SerialGCMemoryObject(int multi){ bytes=new byte[1024*256*multi]; }}-Xms20M –Xmx20M –Xmn10M –XX:+UseSerialGC-Xms20M –Xmx20M –Xmn10M –XX:+UseSerialGC-XX:MaxTenuringThreshold=1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-22-320.jpg)


![Minor GC—Serial [GC [DefNew: 11509K->1138K(14336K), 0.0110060 secs] 11509K->1138K(38912K), 0.0112610 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.01, real=0.01 secs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-25-320.jpg)

![Minor GC—ParNew [GC [ParNew: 11509K->1152K(14336K), 0.0129150 secs] 11509K->1152K(38912K), 0.0131890 secs] [Times: user=0.05 sys=0.02, real=0.02 secs]if add -XX:+UseAdaptiveSizePolicy to startup args,then output: [GC [ASParNew: 7495K->120K(9216K), 0.0403410 secs] 7495K->7294K(19456K), 0.0406480 secs] [Times: user=0.06 sys=0.15, real=0.04 secs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-27-320.jpg)

![Minor GC—PSmostly allocate on TLAB or eden. public class PSGCDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ byte[] bytes=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes2=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes3=new byte[1024*1024*2];Thread.sleep(3000); byte[] bytes4=new byte[1024*1024*4];Thread.sleep(3000); }}-Xms20M –Xmx20M –Xmn10M –XX:SurvivorRatio=8 –XX:+UseParallelGC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-29-320.jpg)

![Minor GC—PSwhen eden space is not enough,and not allocate on old,thengc occurs.public class PSGCDemo{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ byte[] bytes=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes2=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes3=new byte[1024*1024*2];System.out.println(“step 1"); byte[] bytes4=new byte[1024*1024*2];Thread.sleep(3000);System.out.println(“step 2"); byte[] bytes5=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes6=new byte[1024*1024*2];System.out.println(“step 3"); byte[] bytes7=new byte[1024*1024*2];Thread.sleep(3000); }}-Xms20M –Xmx20M –Xmn10M –XX:SurvivorRatio=8 –XX:+UseParallelGC-XX:+PrintGCDetails –XX:verbose:gc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-31-320.jpg)
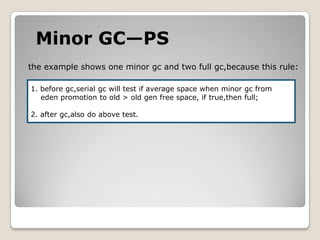

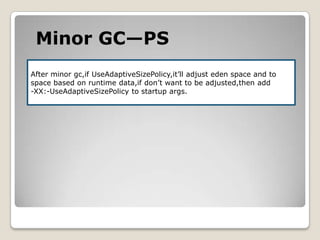
![Minor GC—PS[GC [PSYoungGen: 11509K->1184K(14336K)] 11509K->1184K(38912K), 0.0113360 secs] [Times: user=0.03 sys=0.01, real=0.01 secs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-35-320.jpg)



![Major GC—Serial[Full GC [Tenured: 9216K->4210K(10240K), 0.0066570 secs] 16584K->4210K(19456K), [Perm : 1692K->1692K(16384K)], 0.0067070 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.01 secs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-39-320.jpg)


![Major GC—Parallel MSC[Full GC [PSYoungGen: 1208K->0K(8960K)] [PSOldGen: 6144K->7282K(10240K)] 7352K->7282K(19200K) [PSPermGen: 1686K->1686K(16384K)], 0.0165880 secs] [Times: user=0.01 sys=0.01, real=0.02 secs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-42-320.jpg)


![Major GC—Parallel Compacting[Full GC [PSYoungGen: 1224K->0K(8960K)] [ParOldGen: 6144K->7282K(10240K)] 7368K->7282K(19200K) [PSPermGen: 1686K->1685K(16384K)], 0.0223510 secs] [Times: user=0.02 sys=0.06, real=0.03 secs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-45-320.jpg)

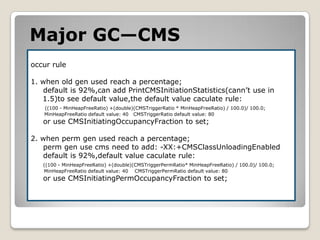
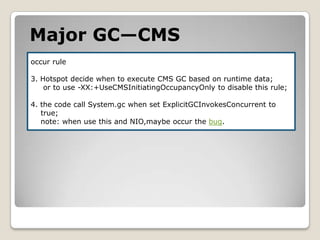
![Major GC—CMSpublic class CMSGCOccur{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ byte[] bytes=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes1=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes2=new byte[1024*1024*2]; byte[] bytes3=new byte[1024*1024*1]; byte[] bytes4=new byte[1024*1024*2];Thread.sleep(5000); }}-Xms20M –Xmx20M –Xmn10M -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -XX:+UseCMSInitiatingOccupancyOnly -XX:+PrintGCDetails-Xms20M –Xmx20M –Xmn10M -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -XX:+PrintGCDetails](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-49-320.jpg)

![Major GC—CMS[GC [1 CMS-initial-mark: 13433K(20480K)] 14465K(29696K), 0.0001830 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs][CMS-concurrent-mark: 0.004/0.004 secs] [Times: user=0.01 sys=0.00, real=0.01 secs] [CMS-concurrent-preclean: 0.000/0.000 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] CMS: abort preclean due to time [CMS-concurrent-abortable-preclean: 0.007/5.042 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=5.04 secs] [GC[YG occupancy: 3300 K (9216 K)][Rescan (parallel) , 0.0002740 secs][weak refs processing, 0.0000090 secs] [1 CMS-remark: 13433K(20480K)] 16734K(29696K), 0.0003710 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [CMS-concurrent-sweep: 0.000/0.000 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] [CMS-concurrent-reset: 0.000/0.000 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs]when add -XX:+UseAdaptiveSizePolicy,then output CMS will change to ASCMSCMS GC Log](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-51-320.jpg)


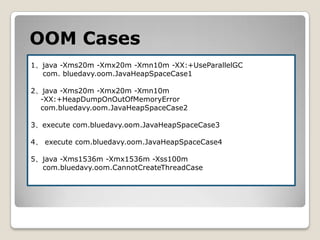
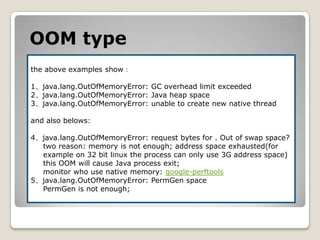

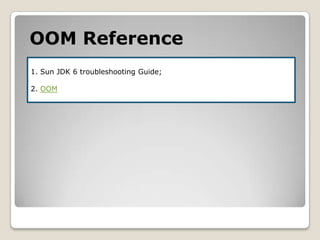
![GCMonitor1. jstat–gcutil [pid] [intervel] [count]2. -verbose:gc -XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCApplicationStoppedTime -XX:+PrintGCDateStamps -XX:+PrintHeapAtGC -Xloggc:[file]gclog can be analised by GCLogVieweror gchisto.3. if support GUI,then can use visualvm.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-62-320.jpg)


![tuning case4 cpu,os: linux 2.6.18 32 bitstartup args-server -Xms1536m -Xmx1536m –Xmn700mgc log:67919.817: [GC [PSYoungGen: 588706K->70592K(616832K)] 1408209K->906379K(1472896K), 0.0197090 secs] [Times: user=0.06 sys=0.00, real=0.02 secs]67919.837: [Full GC [PSYoungGen: 70592K->0K(616832K)] [PSOldGen: 835787K->375316K(856064K)] 906379K->375316K(1472896K) [PSPermGen: 64826K->64826K(98304K)], 0.5478600 secs] [Times: user=0.55 sys=0.00, real=0.55 secs]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-65-320.jpg)

![tuning casegc log:68132.862: [GC [PSYoungGen: 594736K->63715K(609920K)] 1401225K->891090K(1465984K), 0.0309810 secs] [Times: user=0.06 sys=0.01, real=0.04 secs] 68132.893: [Full GC [PSYoungGen: 63715K->0K(609920K)] [PSOldGen: 827375K->368026K(856064K)] 891090K->368026K(1465984K) [PSPermGen: 64869K->64690K(98304K)], 0.5341070 secs] [Times: user=0.53 sys=0.00, real=0.53 secs]then repeat.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sunjdk1-6gcenglishversion-100906023454-phpapp01/85/Sun-jdk-1-6-gc-english-version-67-320.jpg)