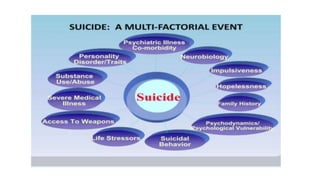
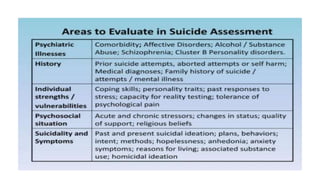
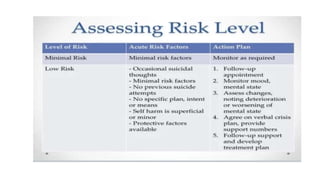
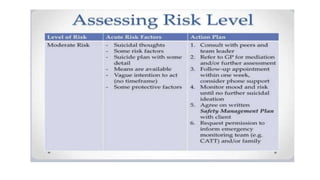
This document discusses suicide risk assessment. It defines key terms like suicide, suicide attempts, and suicidal ideation. It also outlines theories of suicide and lists factors that can increase or decrease risk. Components of a suicide assessment include identifying risk factors, conducting a psychiatric exam, directly asking about suicide, determining the level of risk, and creating a treatment plan. Evidence-based warning signs and rating scales used in assessments are also provided. Treatment options mentioned include medication, counseling, CBT, and DBT.