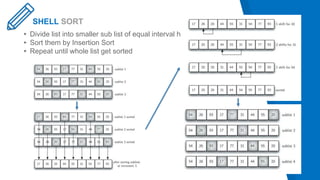
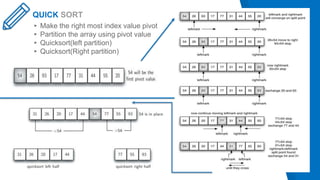
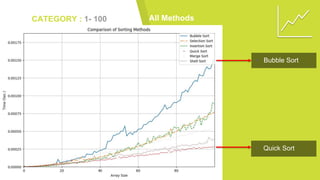
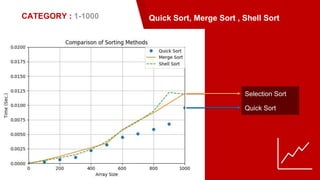
This document analyzes and compares sorting algorithms including bubble sort, insertion sort, selection sort, shell sort, merge sort, and quick sort. It describes the time complexity of each algorithm using asymptotic analysis and experimental results. Testing was done on different sized data sets from 1-100 values, 1-1000 values, and 1-10000 values. Quick sort performed the best overall, having an average time complexity of O(n log n), while bubble sort performed the worst with O(n^2) time complexity. In conclusion, quick sort is the most efficient sorting method, while bubble sort is the least efficient.