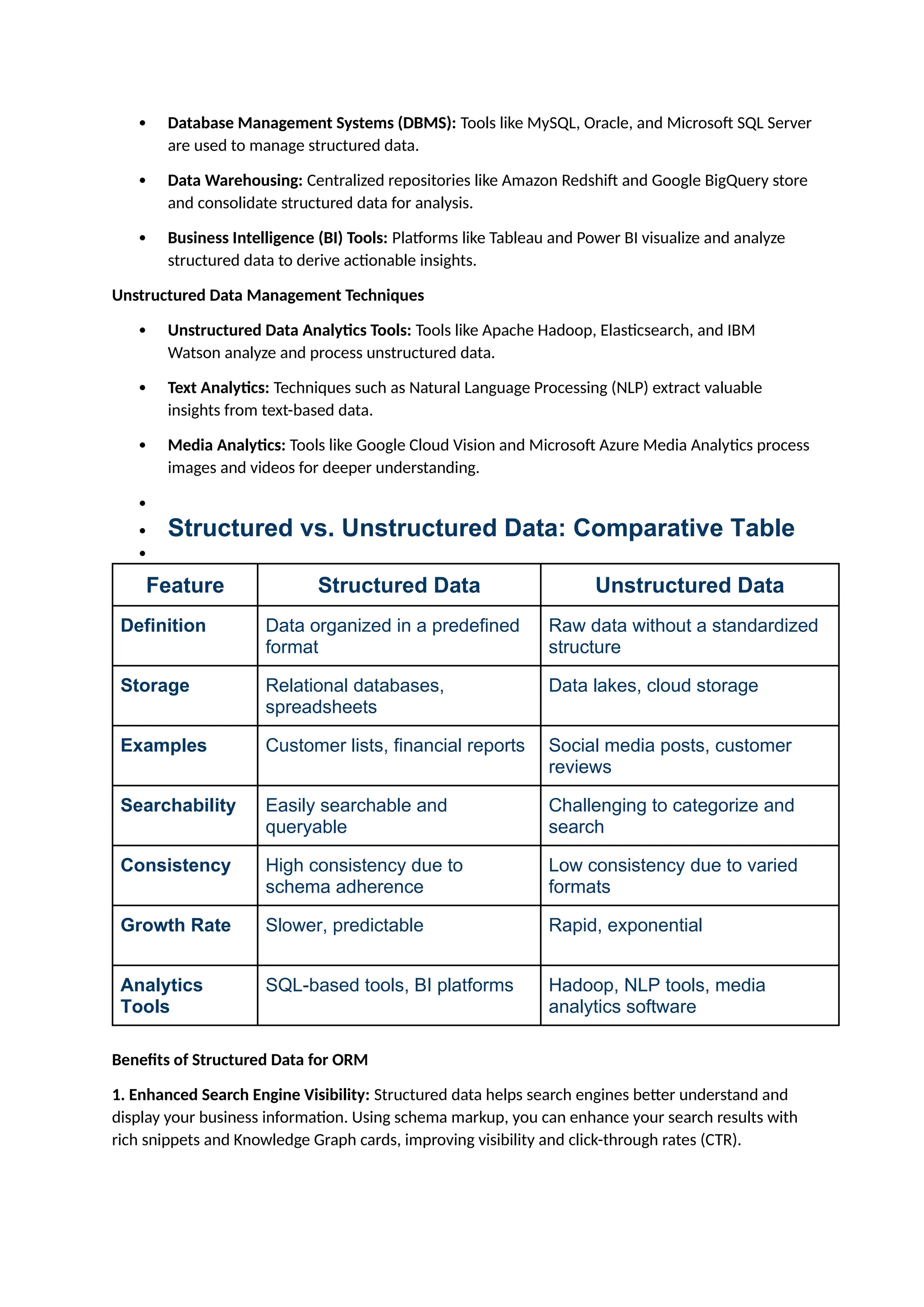
The document discusses the importance of balancing structured and unstructured data for business success, noting that structured data comprises about 20% and unstructured data 80% of total data generated. It highlights the benefits of both data types in enhancing decision-making and online reputation management, while outlining effective management techniques for each. By integrating structured and unstructured data, businesses can improve customer engagement and drive long-term success.