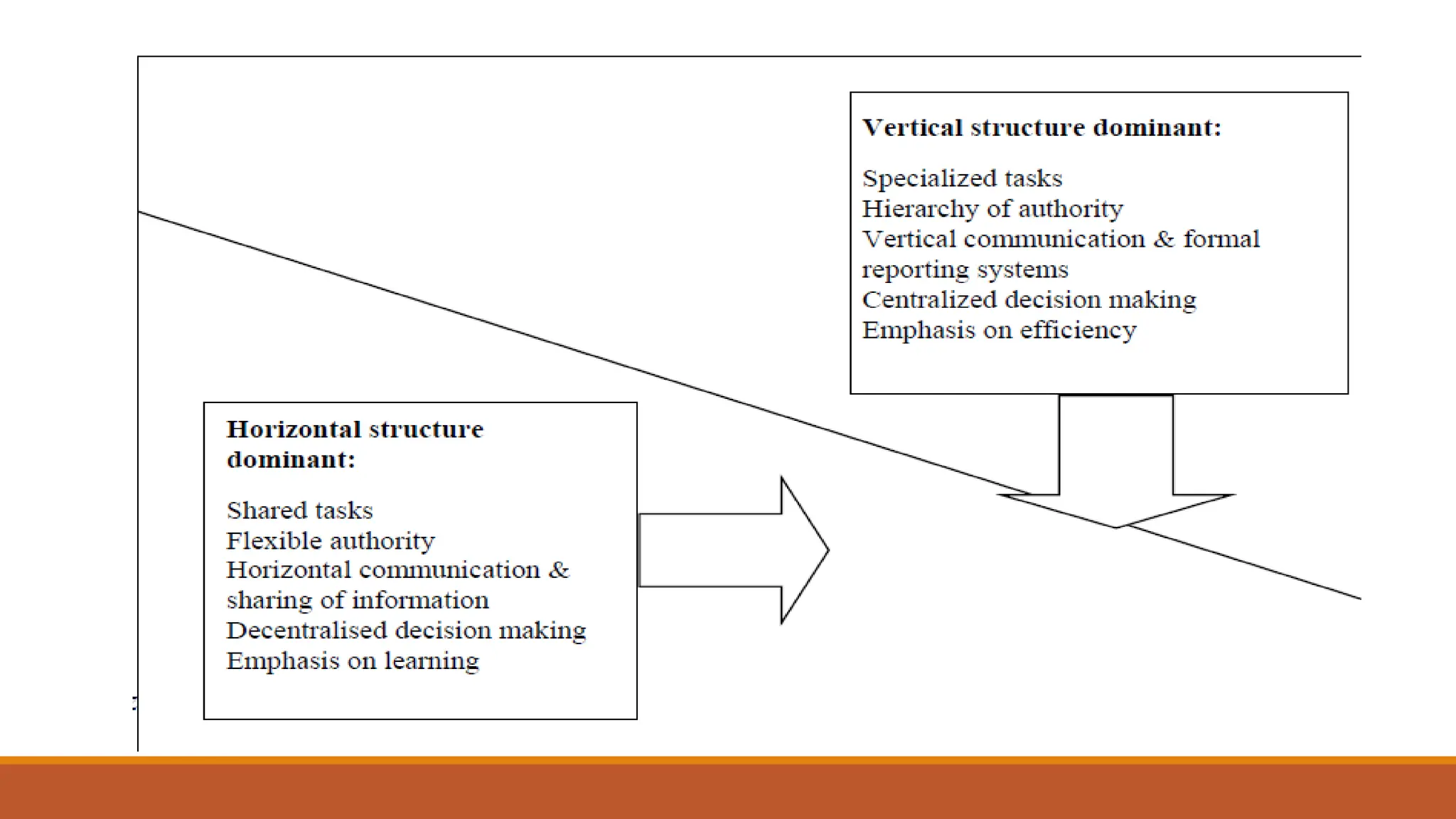
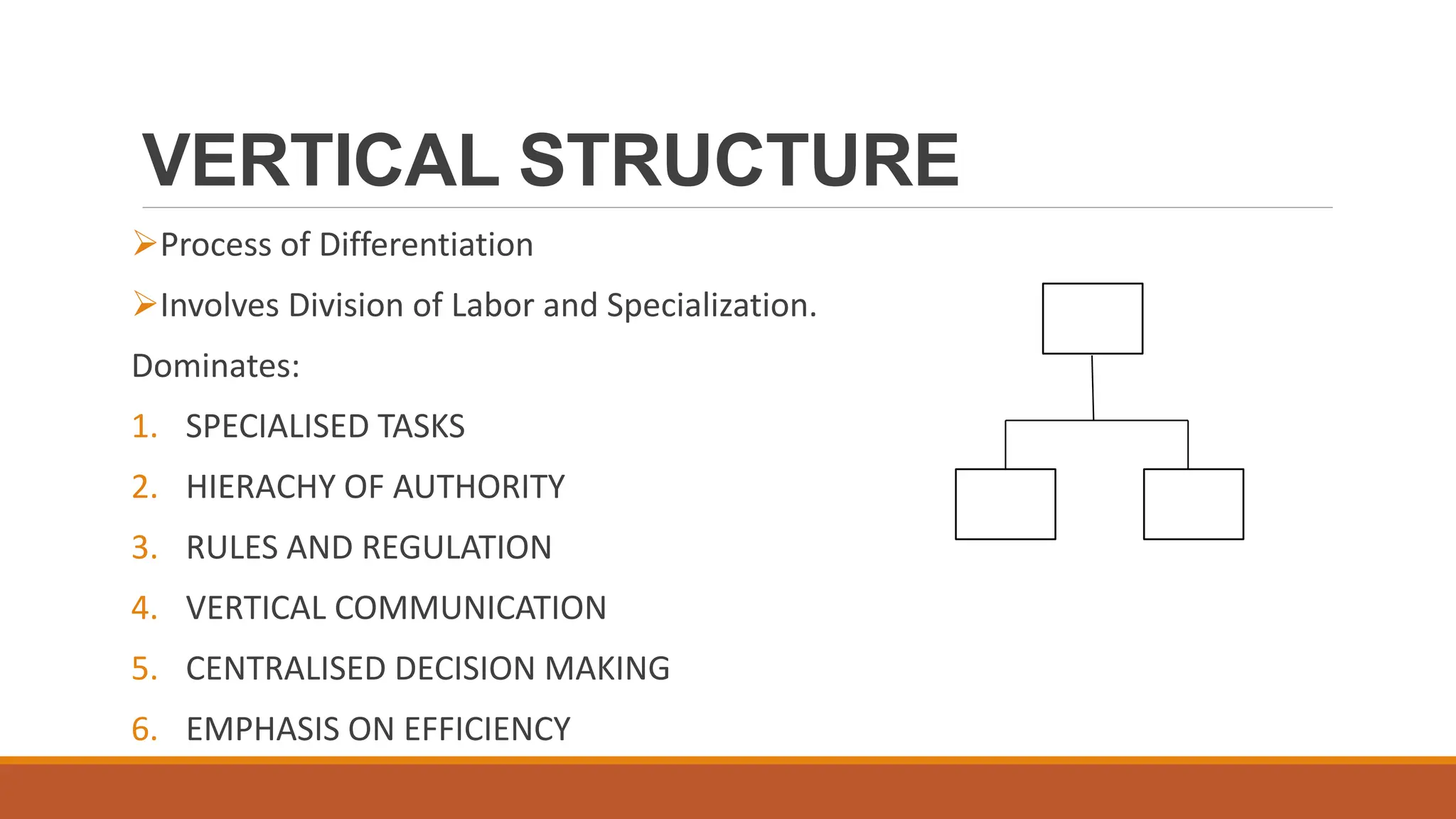
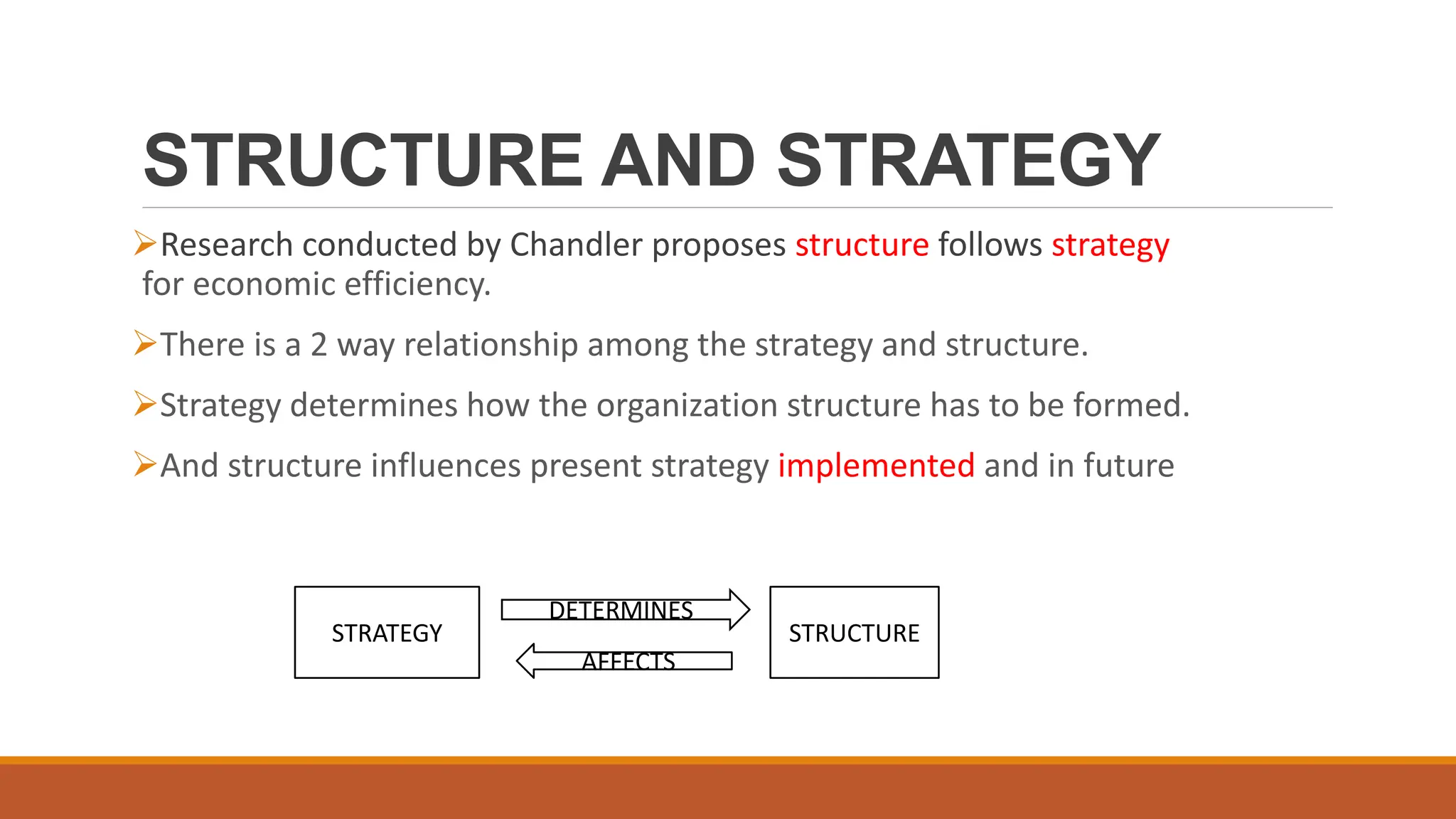
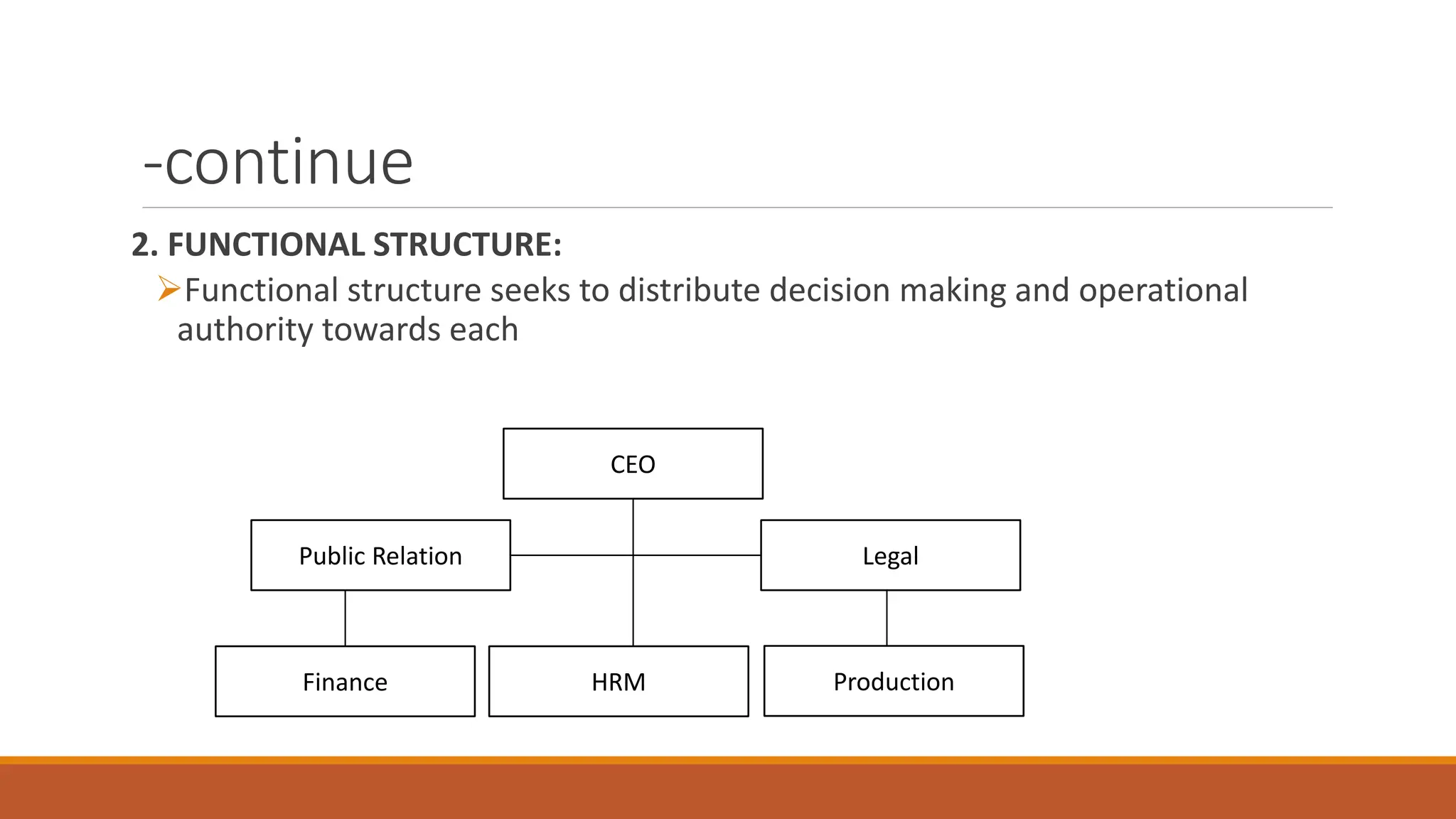
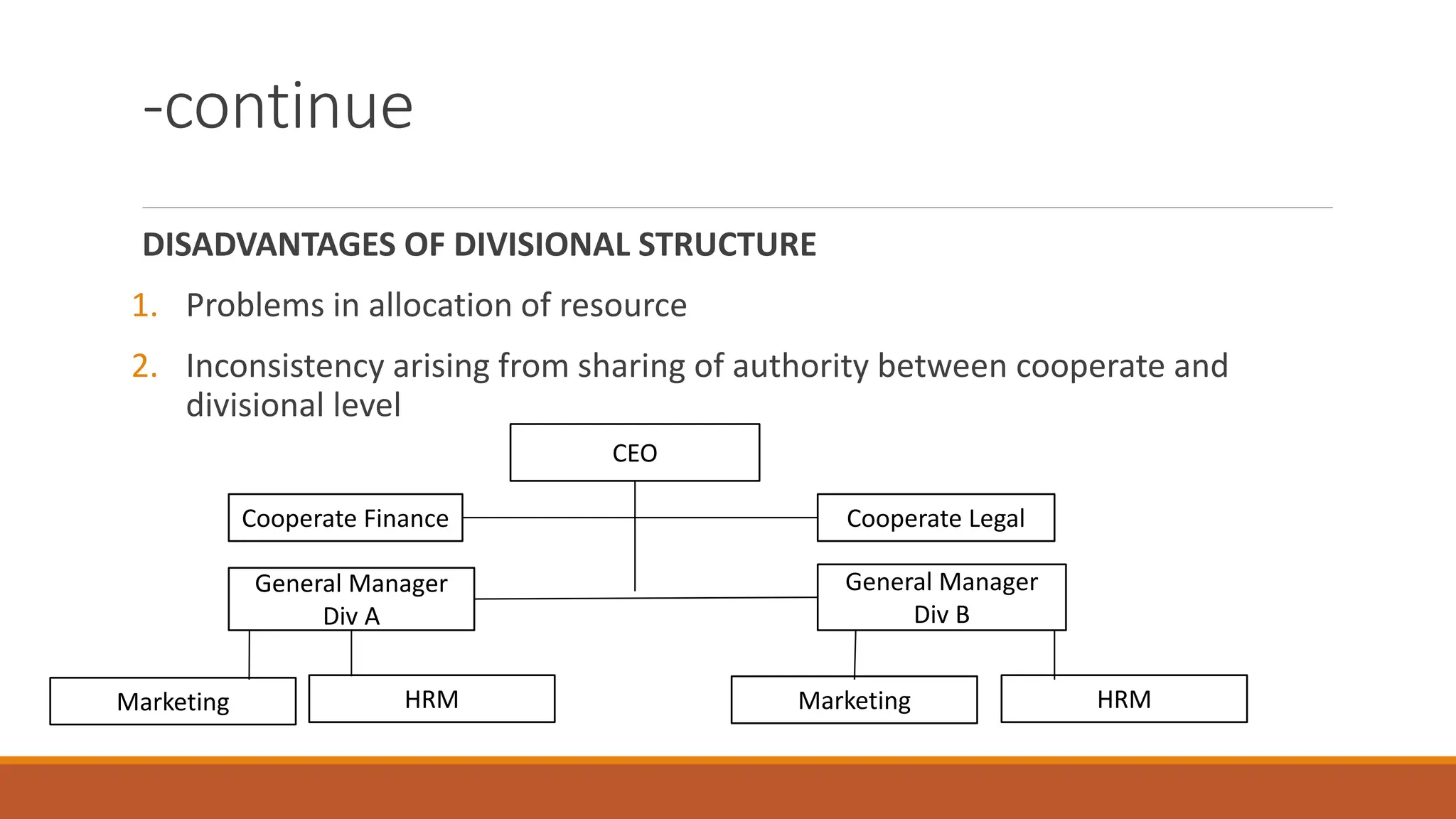
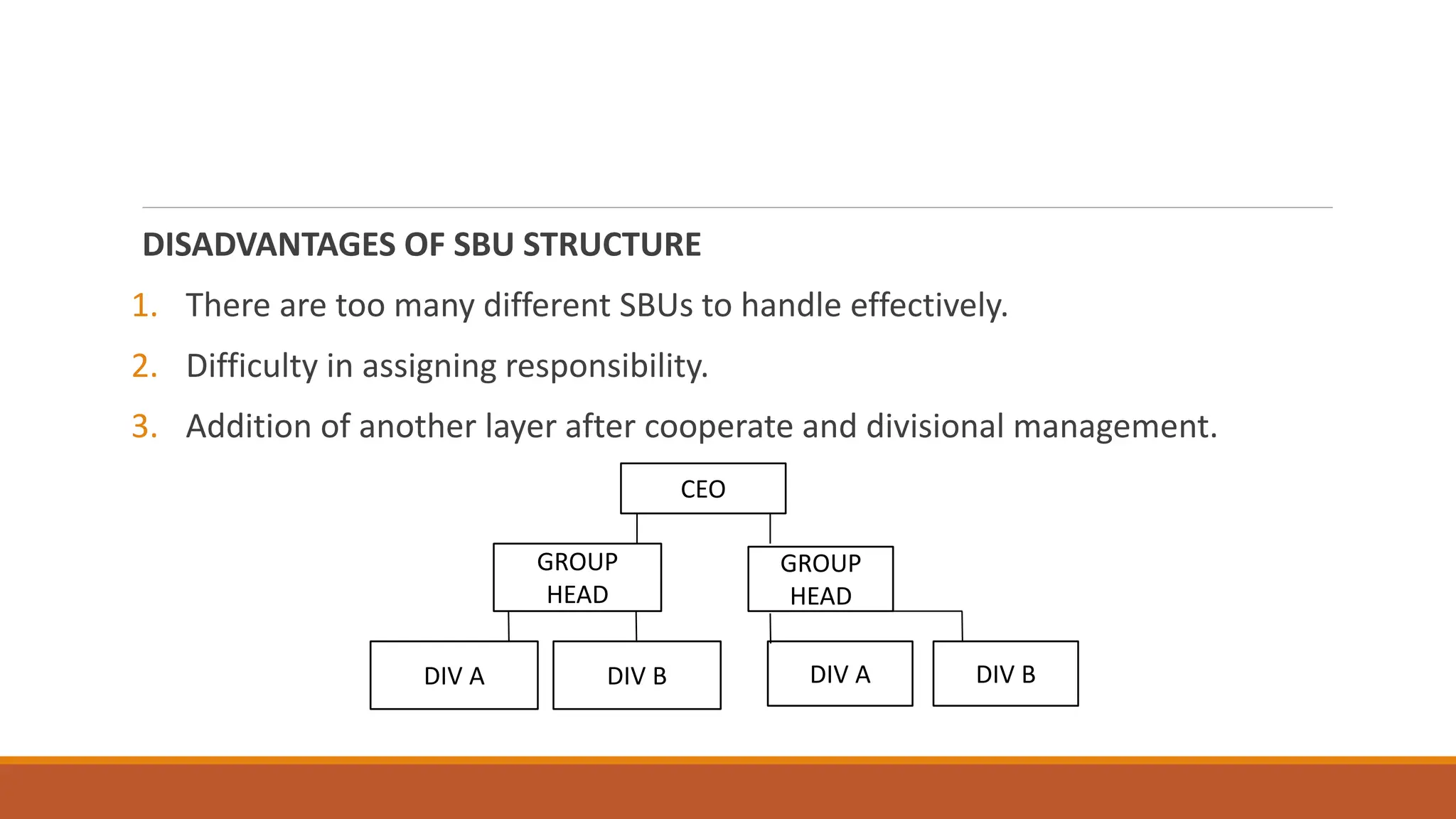
The document outlines different organizational structures, such as vertical, horizontal, functional, divisional, and matrix structures, along with their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. It emphasizes the relationship between structure and strategy, detailing how organizational goals influence the design of structures across various development stages. Additionally, it covers specialized structures such as strategic business units and network structures, highlighting their flexibility and adaptability to environmental changes.