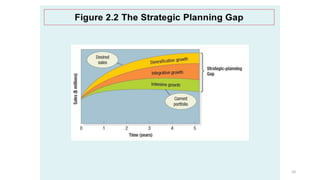
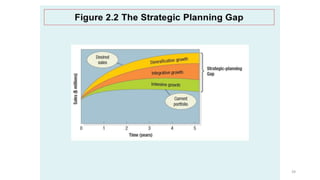
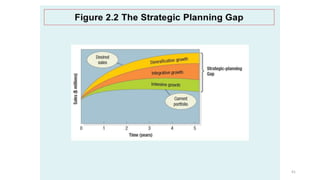
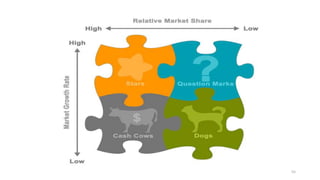
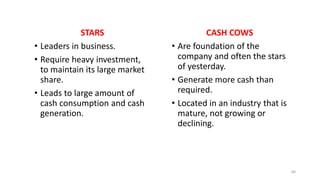
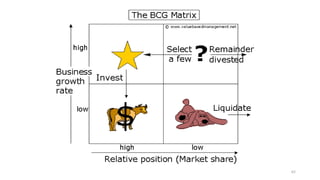
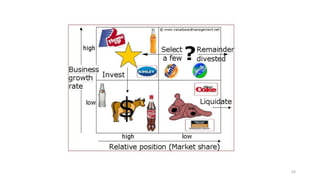
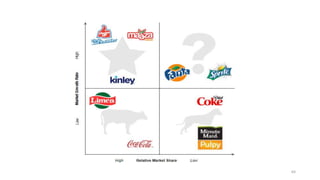
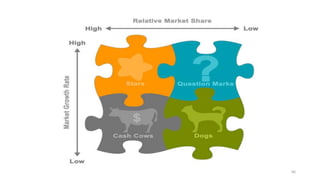
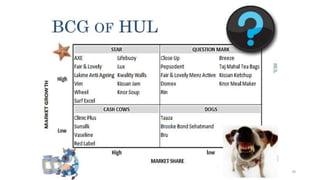
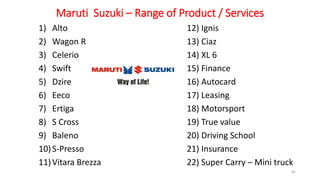
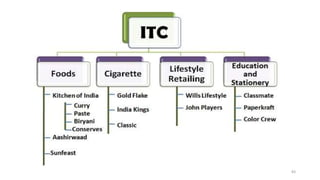
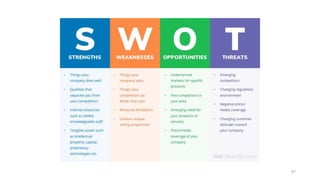
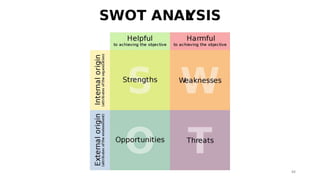
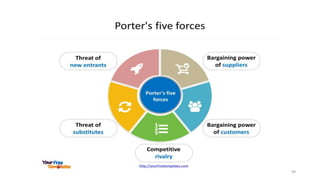
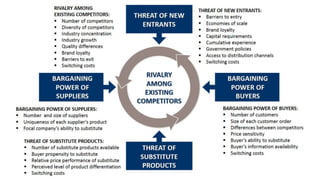
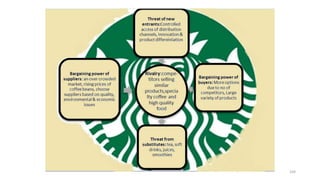
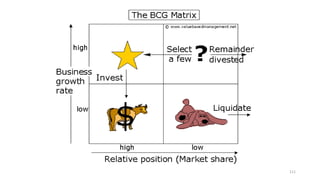
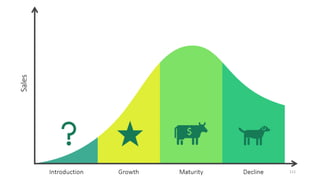
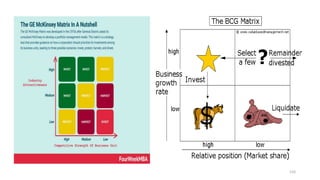
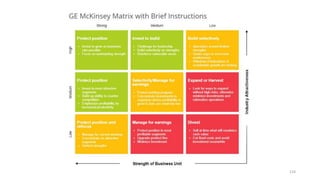
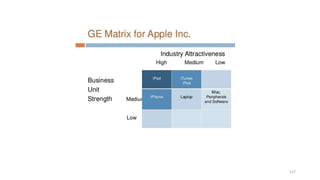
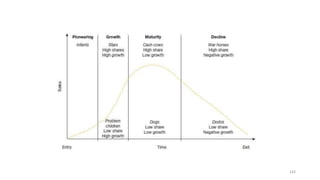
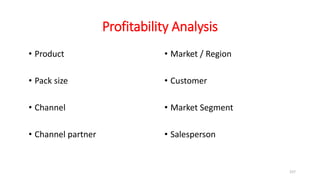
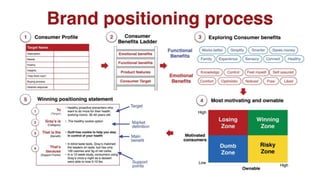
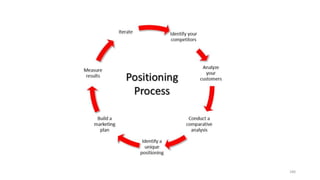
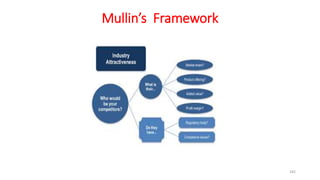
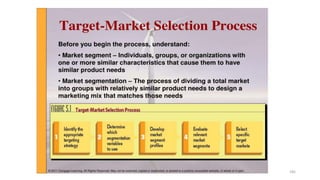
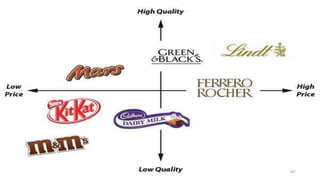
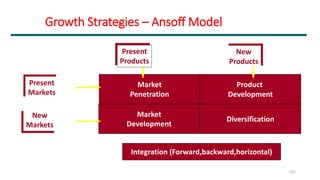
The document discusses various marketing metrics and tools used for evaluating marketing performance, including gap identification and bridging tools like the BCG matrix and Ansoff matrix. It explains how to conduct a gap analysis to identify differences between a company's current and desired performance. Strategies like market penetration, development, product development, and diversification are presented to close performance gaps through intensive, integrative, or diversification growth. Key metrics mentioned include sales, profit, market share, customer satisfaction, and reputation.