Strategies for Managing White Spot Lesions in Orthodontic Patients and A Suggested Protocol.pdf
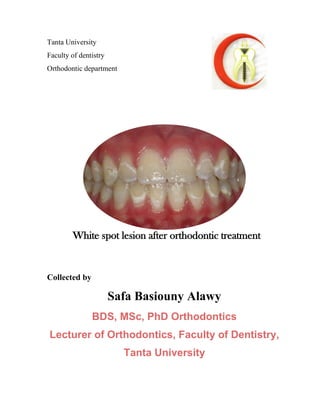
- 1. Tanta University Faculty of dentistry Orthodontic department Collected by Safa Basiouny Alawy BDS, MSc, PhD Orthodontics Lecturer of Orthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Tanta University White spot lesion after orthodontic treatment
- 2. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 2 Contents • Definition of WSL • Etiology • Incidence • Classification of white spot lesions • Methods of diagnosis o Visual inspection and radiography o Trans-illumination methods o Florescence methods o Electrical conductivity o Ultrasonic methods o Optical coherence tomography and polarization sensitive optical coherence Tomography o Frequency-domain laser-induced infrared photothermal radiometry and modulated luminescence • Prevention of WSL o Oral hygiene o Fluoride (toothpaste, mouthrinse, gel, varnish, luting cement, adhesives, elastomeric chains) o Calcium-phosphate-based delivery systems o Lasers o Nanoparticles (nanocoating of brackets, bioactive glass) • Treatment of WSL o Oral hygiene o Topical Fluoride application o Calcium-phosphate-based delivery systems o Lasers o Tooth bleaching agents o Microabrasion o Ozone o Resin infiltration (ICON)
- 3. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 3 Definition: “white opacity,” occur as a result of subsurface enamel demineralization that is located on smooth surfaces of teeth. Or “subsurface enamel porosity from carious demineralization” that presents itself as “a milky white opacity when located on smooth surfaces Etiology: 1. prolonged “undisturbed” plaque accumulation on the affected teeth surface, commonly due to inadequate oral hygiene. Under these conditions, acids diffuse into the enamel and the demineralization continues in the subsurface enamel, then the intact enamel surface collapses and becomes cavitated. 2. The presence of fixed orthodontic appliances causes an increasing number of plaque retention sites as a result of the presence of brackets, bands, wires, and other applications, which makes the cleaning of teeth more difficult. furthermore, excess bonding, long etching time (>15 s), decayed/treated molars, and the duration of treatment are considered other risk factors 3. The other important factors that impact this process are the patient’s modifying factors, including medical history, dental history, medication history, diet, levels of calcium, phosphate, and bicarbonate in saliva, fluoride levels, and genetic susceptibility. Incidence: • Orthodontic treatment has been reported as the most frequent factor for this situation, and equal susceptibility has been reported whether teeth are banded or bonded. • The prevalence of WSLs varies widely in the literature. It ranges from 23 to 95%. The reported prevalence of WSLs is quite variable, depending on the sample size, method of detection, the use of a fluoride regimen during treatment, inclusion of pre-existing developmental enamel defects, and selected patients' groups. • WSLs developed more frequently in the maxillary arch than they did in the mandibular. Ceren Deveci, Çağdaş Çınar and Resmiye Ebru Tirali. Management of White Spot Lesions in Dental Caries - Diagnosis, Prevention and Management book. 2018. Page 130-165
- 4. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 4 • The researchers identified other risk factors during the treatment such as treatment time exceeded 36 months, patients with poor oral hygiene, and patients whose oral hygiene declined during treatment and pre-existing WSLs. • They observed that the lesions are often symmetrical. • WSLs are often seen under loose bands, around the periphery of the bracket base and in areas that are difficult to be detected by the patient and not easily accessed by the toothbrush • More frequently on the maxillary laterals, maxillary canines, and mandibular molars. In other studies, different results were obtained. According to these studies, the most inclined teeth to demineralization are the first permanent molars, the maxillary incisors, the mandibular lateral incisors, and canines. Classification of white spot lesions White-spot lesions were first classified in orthodontics according to their visual size. This classification made according to the width of opacity formed on enamel surface was as follows: o Class 0: None or less than 1 mm opacity o Class 1: Opacity covers 1/3 of tooth surface o Class 2: Opacity covers 1/3 to 2/3 of tooth surface o Class 3: Opacity covers wider than 2/3 of tooth surface Another classification made by Gorelick, et al., which considers both size and intensity of lesions is as follows: o Class 1: No white spot lesion formation o Class 2: Mild white spot lesion present o Class 3: Severe white spot lesion present o Class 4: Cavitation is present in addition to white spot lesion Temel SS, Kaya B (2019) Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment of White Spot Lesions Related to Orthodontics. Int J Oral Dent Health 5:085.
- 5. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 5 In general, white discolorations of enamel can be classified as dental fluorosis, opacities or WSLs. Russell has developed a set of criteria to differentiate between fluorosis and opacities. Fluorosis Non-fluoride opacities or WSLs white/yellowish lesions Milky white opacity Not well defined, blending with normal enamel have a more defined shape, well differentiated from surrounding enamel. often located in the middle of the tooth -frequently seen on teeth which calcify slowly (cuspids, bicuspids, second and third molars), -rare in lower incisors -any tooth may be affected, -frequently seen on labial surfaces of lower incisors usually seen on six or eight homologous teeth. may occur singly but usually one to three teeth affected Russell. A . L. the Differential Diagnosis of Fluoride and Nonfluoride Enamel Opacities. J Public Health Dent. 1961;21(4):143–6.
- 6. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 6 • Diagnosis: 1. Visual inspection and radiography: The simplest method of detecting WSLs is the mirror-sound application and visual inspection. The demineralization of the enamel and microporosity affects the transmission of light within the enamel. Thus, the enamel layer loses its bright color and appears opaque-white due to optical refraction. 2. Trans-illumination methods: -Fiber optic trans-illumination (FOTI) and digital imaging fiber optic trans-illumination (DIFOTI) -The use of fiber optic light makes it possible to see smaller superficial white lesions; it undergoes optical refraction by passing an intense light beam through the tooth. - In the DIFOTI method, focused images can be taken with the help of a CCD camera installed in the system. The images can be analyzed by a computer and the diagnosis of approximal, occlusal, and soft surface caries can be done simultaneously. The DIFOTI method can detect demineralization as early as 2 weeks, but DIFOTI fails to measure the depth of the lesion Ceren Deveci, Çağdaş Çınar and Resmiye Ebru Tirali. Management of White Spot Lesions in Dental Caries - Diagnosis, Prevention and Management book. 2018. Page 130-165
- 7. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 7 3. Florescence methods -laser fluorescence (DIAGNOdent—KaVo, Germany). The fluorescence of the laser beam is less in demineralized enamel than normal enamel. a red diode laser beam of 650 nm is applied to the occlusal surface of the tooth. It is collected using an optical fiber located at the same end, filtered by high frequency light wavelengths, and counted by a photodiode. - Only low-frequency fluorescence that passes through the caries lesion is measured and quantified. Thus, the name “quantifiable laser fluorescence” is used as a value of the measurement scale, and when it increases, the likelihood of decay increases. -A value of 5–25 indicates early lesions, 26–35 indicates early dentin caries, and over 35 indicates deep dentin caries. - disadvantage: it can give false positive results in the presence of painted fissures, plaque and calculus, pit and fissures sealant, and in the presence of restorative material Therefore, it is important to clean the tooth surface when using DIAGNOdent. 4. Electrical conductivity Difference arises in the electrical transmission of solid and demineralized enamel surfaces due to porosity. Saliva penetrates the enamel and increases the electrical permeability of the tooth 5. Ultrasonic methods high-frequency pulse-echo ultrasound waves (18 MHz) produce different echoes in sound and demineralized enamel. Studies have shown that ultrasound is a successful method in deep dentin lesions, but it is even more useful in evaluating remineralization 6. Optical coherence tomography and polarization sensitive optical coherence Tomography uses infrared light to obtain high-resolution images of approximately 10–20 microns with confocal microscopy. The accuracy of OCT is quite high and it can show early mineral changes
- 8. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 8 7. Frequency-domain laser-induced infrared photothermal radiometry and modulated luminescence (PTR/LUM) In this method, the thermal energy conversion of the optical energy provides better evaluation of tissue density and lesion depth than visual techniques.
- 9. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 9 Prevention of WSL -The structure of hydroxyapatite crystals is under the influence of a natural cycle between demineralization and remineralization. This cycle works in the favor of either demineralization or remineralization, depending on environmental factors. -The aim of modern dentistry is to manage initial caries lesions non-invasively through remineralization to prevent disease progression. • Oral hygiene -The pH level around braces can easily decrease in patients receiving orthodontic treatment. If patient has good oral hygiene, pH level will not exceed the critical level in early stages of acid attacks. -Tooth brushing is a commonly used method for mechanically controlling plaque. Mouthwashes involving different ingredients that provide chemical plaque control are also effective agents that reduce bacterial count by 99.9% without damaging the surrounding oral tissues. Mouthwashes containing chlorhexidine are the most effective. • Fluoride Mechanism of action: -The concentration of fluoride in saliva and plaque is effective in prevention of demineralization and formation of remineralization. The organic acids formed by cariogenic bacteria cause decrease in pH level of plaque, which results in fluoride diffusion into enamel from plaque and saliva in response. -Displacement of hydroxyl ions of enamel structure with fluoride causes existence of fluorapatite crystals. This new crystal form is more resistant to acids. There is a critical pH level for fluoride to be effective in formation of fluorapatite. The pH levels between which fluoride works more effectively are reported as 4.5-6. -Fluoride also affects the activities of cariogenic bacteria and prevents formation of caries. Laboratory studies have shown that low concentrations of fluoride cause Streptococcus mutans to produce less amount of acid.
- 10. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 10 Dose: -Low-dose topical fluoride is recommended over long periods of time with frequent exposures in order to avoid dental fluorosis. - highly concentrated fluoride leads to hypermineralization of surface layer of WSLs. Therefore, the penetration of calcium and phosphate ions into the body of lesion is blocked. This is referred to as (lamination). It may have some undesirable esthetic consequences. Limitations: 1. Fluoride has low solubility and tends to accumulate on enamel surface. It cannot go deeper in enamel layers after porous cavities are filled with it. 2. it is reported that the ability of fluoride ion to remineralize is less than its ability to prevent demineralization. Delivery methods: 1. Toothpastes -Fluoride toothpaste is the most commonly used form of fluoride to provide a constant and low amount of fluoride in oral environment formulations, including sodium fluoride, sodium monofluorophosphate, amine fluoride, and stannous fluoride. -The concentration of fluoride in toothpastes recommended by WHO is between 1000 and 1500 parts per million -There has been a recently introduced additive, which is called Arginine, for toothpaste and other dental care products containing fluoride. Arginine is an amino acid that occurs naturally in a range of food products and in the saliva. When applied in oral cavity, arginine is deaminated by the arginine deaminize system in saliva, producing ammonia, which is highly alkaline and leads to an increase in the pH in the oral biofilm, so that plays an active role with an insoluble calcium compound, and sodium monofluorophosphate for remineralization of WSLs. 2. Mouthrinses Both daily uses of mouthrinses containing 0.05% NaF and weekly rinsing programs with 0.2% NaF were found to decrease the incidence of enamel demineralization.
- 11. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 11 3. Fluoride varnishes Advantage: Bond to the enamel for greater periods and prevent the immediate loss of fluoride after application. Therefore, they take the role of reservoir for slow release and facilitate greater fluoride uptake. Recommendation: 1. Patients should avoid eating for 2–4 h after the application and to avoid brushing their teeth the night of the application. 2. AAPD guideline recommended that fluoride varnishes should be applied at least twice in a year for primary teeth and two or four times in a year for permanent teeth. Products: Duraphat (5% NaF), fluorprotector (1% difluorosilane and 0.1% F), duraflor (5% NaF) are the commonly used Fluoride varnishes. 4. Fluoride gel Advantage: Can be applied both by professionals and by self-application of patients. Methods of applications: 1. mouth tray: In this method, fluoride gel is placed into a mouth tray and applied to entire dental arch at same time. Tray application is easily accepted by children. 2. cotton balls and toothbrushes. Recommendation: -Fluoride gel is professionally applied up to four times a year for 4 min. -Due to risk of swallowing the fluoride gel, use in children under 6 years old is not recommended
- 12. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 12 Products: The commonly used gels are 1.23% sodium fluoride gel and acidulated phosphate fluoride (APF) gel. 5. Fluoride in Luting Cement -It has been advocated to use cements containing fluoride for banding. -It had been suggested that fluoride releasing cements such as zinc polycarboxylate and resin modified GIC demonstrated less enamel demineralization than the zinc phosphate cement. 6. Fluoride in Bonding Agents -It was reported that fluoride releasing adhesives provided protection for an area of 1 mm around brackets, whereas fluoride-free adhesives cannot prevent demineralization around and under brackets. Example: a. Glass ionomer cements Adv: ability to chemically bond to tooth structure and their sustained fluoride release following bonding. Disadv: significant poor bond strength of GICs compared with conventional bonding adhesives. b. resin-modified glass-ionomer (RMGIC) bonding systems These bonding systems have been developed to combine the desirable properties of composite resin bond strength and glass ionomer fluoride release.
- 13. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 13 c. Composite resins The most common adhesive used for direct orthodontic bonding because of their acceptable bond strength and ease of application. Incorporation of fluoride into the composite resins was done in many products as EagleBond, Enlight LV, and Transbond XT. d. Polyacid modified resin composites (compomers) have intermediate composition, properties and fluoride ions release compared to those of GICs/RMGICs and composite resins. 7. Fluoride releasing elastomeric modules Many investigations have also suggested that fluoride releasing elastomeric modules were effective in reducing plaque accumulation and enamel decalcification around the brackets. However, some authors concluded that fluoridated elastomers had no effect on the quantity of disclosed plaque around orthodontic brackets. Even the fluoride release from a fluoride containing elastic chain was high for the 1st week and decreased significantly after that. To address to this problem, it has been suggested to prescribe fluoridated toothpaste and mouth rinse so that fluoridated elastomers may imbibe fluoride from their environment. • Calcium-phosphate-based delivery systems Formulations: They can be examined under three headings: A. Stabilized amorphous formulation as Casein Phosphopeptide–Amorphous Calcium Phosphate (CPP-ACP): Mechanism of action: 1. CPP-ACP is a bioactive agent with a base of milk products able to bind calcium and phosphate ions to stabilize calcium phosphate in solution and to increase the level of calcium phosphate in dental plaque.
- 14. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 14 2. CPP-ACP also adheres to hydroxyapatite, soft tissues, and supplies free calcium and phosphate ion, thereby helping to maintain reducing demineralization and promote remineralization by reforming into calcium phosphate crystals. 3. It can interact with hydrogen ions from the surface of the tooth and so it can penetrate to enamel’s subsurface layer in order to produce mineral gain. 4. There are studies showing that CPP inhibits adherence and functioning of cariogenic streptococcus bacteria in mouth Delivery methods: CPP-ACP agents are produced in various ways such as foam, mouthwash, topical paste, chewing gum to transport calcium and phosphate. Products and recommendation: Tooth Mousse/MI Paste (GC, Tokyo, Japan) is a topical remineralizing cream containing CPP-ACP. It is suggested to be applied on tooth surfaces twice a day after brushing. The patients should refrain from drinking or eating for 30 min subsequent to application. In addition high fluoride toothpaste should be used for 6 months in order to succeed in treating postorthodontic demineralized WSLs. B. Unstabilized amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) formulation -Developed by mixing calcium ions with phosphate ions to produce an ion active phase so that it could be precipitated as quickly as ACP or, in the presence of fluoride ions, amorphous calcium fluoride phosphate (ACFP). -The desired effect is dissolution into the saliva and to promote tooth remineralization, but these unstabilized forms can cause dental calculus C. Crystalline as functionalized Tricalcium Phosphate (fTCP): -It is a hybrid material produced by a milling technique that fuses beta tricalcium phosphate (ßTCP) and sodium lauryl sulfate or fumaric acid. This blending produces a functionalized calcium and a free phosphate, designed to improve the efficacy of fluoride remineralization
- 15. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 15 -Laboratory and clinical studies have demonstrated that the combination of fluoride and fTCP can produce more acid-resistant and stronger mineral relative to fluoride. Products: Duraphat®, MI Varnish TM, Embrace Varnish, Enamel Pro® Varnish, Clinpro TM White Vanish (5% NaF plus TCP) • Lasers Several types of laser such as Nd:YAG, CO2, Er,Cr:YSGG, Argon and Er:YAG with various parameters have been used for caries prevention Mechanism of action: -After laser absorption, the high temperature of surface and near surface layer results in structural and chemical alternations in enamel. These alternations include decomposition of organic matrix, decrease in carbonate compounds, melting and recrystallization of hydroxyapatite crystals ….. reduction of permeability and the solubility of enamel….. prevent demineralization. -It has been shown that using laser with topical fluoride leads a synergistic effect like increased uptake and less consumption of fluoride and decreased dissolution rate of the enamel. Laser parameters: -There is lack of uniformity in terms of parameters being used with different laser types. -CO2 laser (with 9.3, 9.9, 10.3 and 10.6 µm wavelengths) is considered as a main laser type in inhibition of caries formation because the absorption bands of phosphate, carbonate, and hydroxyl groups of enamel and dentin structures are in the range of 9-11 µm.
- 16. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 16 -The ablation threshold of the Er:YAG laser is also a controversial topic: it varies between 7 and 18.6 J/cm2 in the literature. -Apel et al suggested Er:YAG laser with energy densities below the ablation threshold, this is not to ablate or melt the surface but to change its structure or chemical composition attempting to increase its acid resistance. Altan et al preferred a subablative dose in his study utilized 100 mJ per pulse (12.73 J/cm2) with water spray surface cooling. The temperature increase in pulpal tissue caused by laser irradiation with ablative doses should be considered. From this point of view, White and Goodish determined the safe limits for pulpal health to be 1 W and 10 Hz. By considering this, it is preferred to use subablative dose with water cooling.* -Studies that compared the effectiveness of 2 or more laser beams in demineralization inhibition during orthodontic treatment were all in vitro. Studies that compared the effect of different parameters of the same laser type were also in vitro and did not concern orthodontic treatment. There were no studies undertaken during orthodontic treatment comparing the improvement in demineralization resistance among different laser types or different laser settings.† Advantages: quick, comfortable, and simple application, especially in children, considering the difficulty of using a fluoride Disadvantage: When laser is applied at high energy levels, it may cause undesired changes like cracks, glazed surfaces, columns separated by voids in the enamel surface during cooling. * Garma et al. The effect of ER: YAG laser on enamel resistance to caries during orthodontic treatment: An in vitro study. J Bagh College Dentistry. 2015:27;182-88 † T. Raghis, G. Mahmoud, O. Hamadah. Effectiveness of laser irradiation in preventing enamel demineralization during orthodontic treatment: A systematic review. Dent Med Probl. 2018;55(3):321–332
- 17. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 17 • Usage of antimicrobial agents Action: Chemotherapeutic agents cannot prevent formation of dental plaque, but they can be used to remove microorganisms, which is one of the main factors that cause enamel demineralization. Example: Chlorhexidine and benzalkonium chloride are the most preferred antimicrobial agents for this purpose Disadvantage: Regular use of these agents twice a day causes discoloration on teeth. Therefore, it has been reported that 0.2% chlorhexidine mouthwash can be used at certain intervals in addition to other protection methods during orthodontic treatment, in order to reduce its side effects. • Use of Nanoparticles A.Nano silver coating of brackets Action: -Silver nanoparticles with their unique chemical and physical properties have been proved as an alternative for the development of new antibacterial agents. The silver coating decreased the adhesion of both S. mutans and S. Sobrinus to the orthodontic brackets, which demonstrates their antibacterial properties. -This newly introduced nano-coated orthodontic bracket may be an essential non- compliant appliance in avoidance of WSLs for patients especially with poor oral hygiene during fixed orthodontic treatment B. Bioactive glass Action: -Bioglass (NovaMin® ) is a class of bioactive material which is composed of essentially calcium, sodium, phosphate and silicate. -Bioactive glass is reactive when exposed to body fluids, and when bioglass particles come in contact with an aqueous environments such as saliva, sodium ions (Na+ ) in calcium sodium phosphosilicate particles immediately (within one minute) begin to exchange with hydrogen cations (H+ or H3O+ ) . This rapid exchange of ions allows calcium (Ca2+ ) and phosphate (PO4 3– ) to be released from the particle structure.
- 18. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 18 - Transient and localized increase in pH facilitates the precipitation of calcium and phosphate from the particles and from saliva to form a calcium phosphate layer on tooth surfaces. -As the reactions and the deposition of calcium phosphate layer complexes continue, this layer crystallizes into hydroxycarbonate apatite, which is chemically and structurally similar to biological apatite. Example: NUPRO® extra care prophy paste is a new desensitizing agent contains calcium sodium phosphosilicate (NovaMin® ) and sodium fluoride as active ingredients. Treatment of WSL After the orthodontic appliances are removed, it is common to see a regression appearance of WSLs due to natural remineralization by saliva and abrasion due to brushing in the presence of oral and food hygiene. This improvement depends on the severity of lesions and occurs in the order of 6 months of the debonding process; however, it is not sufficient and these WSLs should be treated. As a result, Guzmán- Armstrong et al. recommend a delay of 6 months before treating these lesions. -The initial stage of WSLs can be treated successfully with good oral hygiene, topical fluoride application, and/or other caries remineralizing agent. • Tooth bleaching agents Action: -Bleaching can be applied to camouflage remaining white spot lesions, following natural remineralization which occurs by itself without any intervention by using gel bleaching systems involving different dosages of hydrogen peroxide with the help of transparent trays in patients suffering from yellowish discoloration. -It should be remembered that the bleaching process only improves the esthetic appearance with a camouflage effect on WSLs and does not treat the lesion. -A recent systematic review showed that bleaching of WSL can diminish color disparities between carious and non-affected areas but researchers also reported that the certainty of the evidence was very low and further prospective in vivo studies are necessary
- 19. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 19 Disadvantage: The most important reason for not having a wide use is that microhardness of sound and demineralized enamel surfaces may decrease after bleaching treatment. • Microabrasion Application and action: -The most common method of microabrasion to remove white spot lesions is polishing labial/buccal surface of teeth with a rotating device by using a gel formed mixture of 18% hydrochloric acid (HCl) and medium grained pumice. -Microabrasion process removes some amount of enamel from tooth surface and forms a smoother enamel texture. Calcium and phosphate minerals seals interprismatic spaces as a result of microabrasion and enamel surface becomes more resistant to external factors Advantages: Some researchers reported that the microabrasion technique can reduce the size of white spot lesions by 83% and they concluded that it could be a treatment option for post-orthodontic demineralized enamel lesions. Disadvantage: There is a limitation to its use. It was reported that the technique is effective if the lesion sizes do not exceed from 0.2 to 0.3 mm in depth. • Ozone Action: due to its oxidizing power and a reliable microbiocidal effect in the gaseous or aqueous phases, it was reported that ozone application can reduce Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus counts on saliva-coated glass beads. Disadvantage: ozone application’s clinical and cost effectiveness are still unknown; as well as the optimal concentration, application period, and how long effects might last, how deep it might penetrate, or whether having other side effects
- 20. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 20 • Resin infiltration Infiltrants are light-curing resin materials developed in a structure that can easily penetrate into the capillary configuration of enamel lesions. The viscosity of these materials is low, have high penetration coefficient, their contact angles to enamel are narrow and their surface tensions are high. Action: ✓ The basic principle of the resin infiltration technique is; inhibition of lesion progression by blockage of micropores that provide a diffusion pathway for acids. ✓ This treatment could be used for arresting enamel lesions as well as improving the esthetic appearance of buccal WSLs using resins with a similar refractive index (RI of infiltrant: 1.52) as apatite crystals Application: 1. Etching the hypermineralized surface layer for 2 min with 15% hydrochloric acid gel to allow deeper resin penetration of lesion body 2. After rinsing, ethanol is applied for 30 s to remove the water from the lesion body. 3. Resin infiltrant is applied for 3 min on the lesion surface to occlude the porous of carious lesion, and to reduce diffusion of acids and minerals. 4. Excess resin was removed with cotton wad, before light curing. Based on the results of in-vivo and in-vitro studies ICON (resin infiltrant material) is effective in treatment of white spot lesions. Disadvantage: They are not appropriate for treatment of lesions exceeding the superficial 1/3 of dentin and that have visible cavitation.
- 21. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 21 • Combined bleaching and resin infiltration, what is performed first? Applying resin infiltration before bleaching: Advantage: When the white spot lesion is masked by the caries infiltration technique, the chalky white appearance is removed and the area is restored to the original enamel color. Drawbacks: The penetration of infiltrant agent resin inside white spot lesions acts as a blocking and can alter the permeability of enamel to bleaching agents, possible interfering with the bleaching treatment. ✓ Bleaching before resin infiltration: -If general tooth color alteration is desirable, the bleaching treatment should be performed before resin infiltration, because the presence of a light cured resin inside tooth structure may hamper the action of whitening agents. N.B. After performing external bleaching, the adhesion of resin to the enamel becomes compromised for up to 14 days, and so a two- to three-week waiting period is necessary. Moreover, it was recently demonstrated that performing resin infiltration, directly after a bleaching procedure, affects negatively the penetration depth of the infiltrant.‡ - In conclusion, to aesthetically manage stained enamel opacities, the stain must be totally removed by performing an external bleaching. Once the latter is successfully achieved, resin infiltration technique may subsequently allow a significant improvement in the appearance of teeth in a relatively short working time. ‡ Santos LFTF, Rêgo HMC, Borges AB, Pucci CR, Torres CRG. Efficacy of Bleaching Treatment on Demineralized Enamel Treated with Resin Infiltration Technique. World J Dent 2012;3(4):279-283. Marouane et al. A Combined Approach for the Aesthetic Management of Stained Enamel Opacities: External Bleaching Followed by Resin Infiltration. Case Reports in Dentistry. 2018 https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1605842
- 22. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 22 Suggested protocol for prevention and treatment of WSL White spot lesion Prevention Treatment By patient: Maintenance of good oral hygiene by: • Use fluoridated tooth paste e.g colgate cavity protection tooth paste, Sensodyne F • Daily use of fluoride containing mouth rinses e.g Oral B pro health, Listerine total care, Colgate neutraflour • Antimicrobial mouthwash as chlorhexidine can be used at intervals but not regularly to avoid discoloration of teeth. By orthodontist: • Fluoride luting cement during cementing bands e.g Medicem • Flouride releasing composite resin in bonding e.g Transbond XT • Application of fluoride varnish two to four times a year e.g Duraphat , fluorprotector By patient and orthodontist: • Fluoride gel by trays up to 4 times a year but not for children under 6 years e.g sodium fluoride gel and acidulated phosphate fluoride (APF) gel By patient: Maintenance of good oral hygiene by: • Use fluoridated tooth paste e.g colgate cavity protection tooth paste, Sensodyne F • Daily use of fluoride containing mouth rinses e.g Oral B pro health, Listerine total care, Colgate neutraflour • Antimicrobial mouthwash as chlorhexidine can be used at intervals but not regularly to avoid discoloration of teeth. • Use MI paste twice a day after brushing with high fluoride containing toothpaste can successfully treat initial lesions. By orthodontist: According to the lesion severity: Initial lesion : • Delay treatment for 6 months …natural remineralization with good oral hygiene can result in lesion regression. • These lesions can be treated with topical fluoride application or other caries remineralizing agents e.g MI Varnish, Clinpro TM White Vanish larger lesions bot not cavitation: • Micro abrasion can treat lesions 0.2-0.3 mm depth • Bleaching or resin infiltration or combination, but resin after bleaching after 2-3 weeks period. Both techniques can camouflage the appearance of WSL
- 23. SAFA BASIOUNY WSL&ORTHODONTICS 23 References 1. Temel SS, Kaya B (2019) Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment of White Spot Lesions Related to Orthodontics. Int J Oral Dent Health 5:085. 2. Srivastava et al. Risk factors and management of white spot lesions in Orthodontics. Journal of Orthodontic Science. 2013; 2:43-47 3. Paris et al. Masking of white spot lesions by resin infiltration in vitro. J Dent. 2 0 1 3; e 2 8 – e 3 4 4. Bergstrand et al. A Review on Prevention and Treatment of Post-Orthodontic White Spot Lesions – Evidence-Based Methods and Emerging Technologies. The Open Dentistry Journal, 2011, 5, 158-162 5. Sudjalim et al. Prevention of white spot lesions in orthodontic practice: a contemporary review. Australian Dental Journal 2006;51:(4):284-289 6. Espinosa-Cristóbal et al. Antiadherence and Antimicrobial Properties of Silver Nanoparticles against Streptococcus mutans on Brackets and Wires Used for Orthodontic Treatments. Journal of Nanomaterials Volume 2018 7. kumar et al. Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles (NovaMin®) for Applications in Dentistry. Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences. 2015;14:30-35