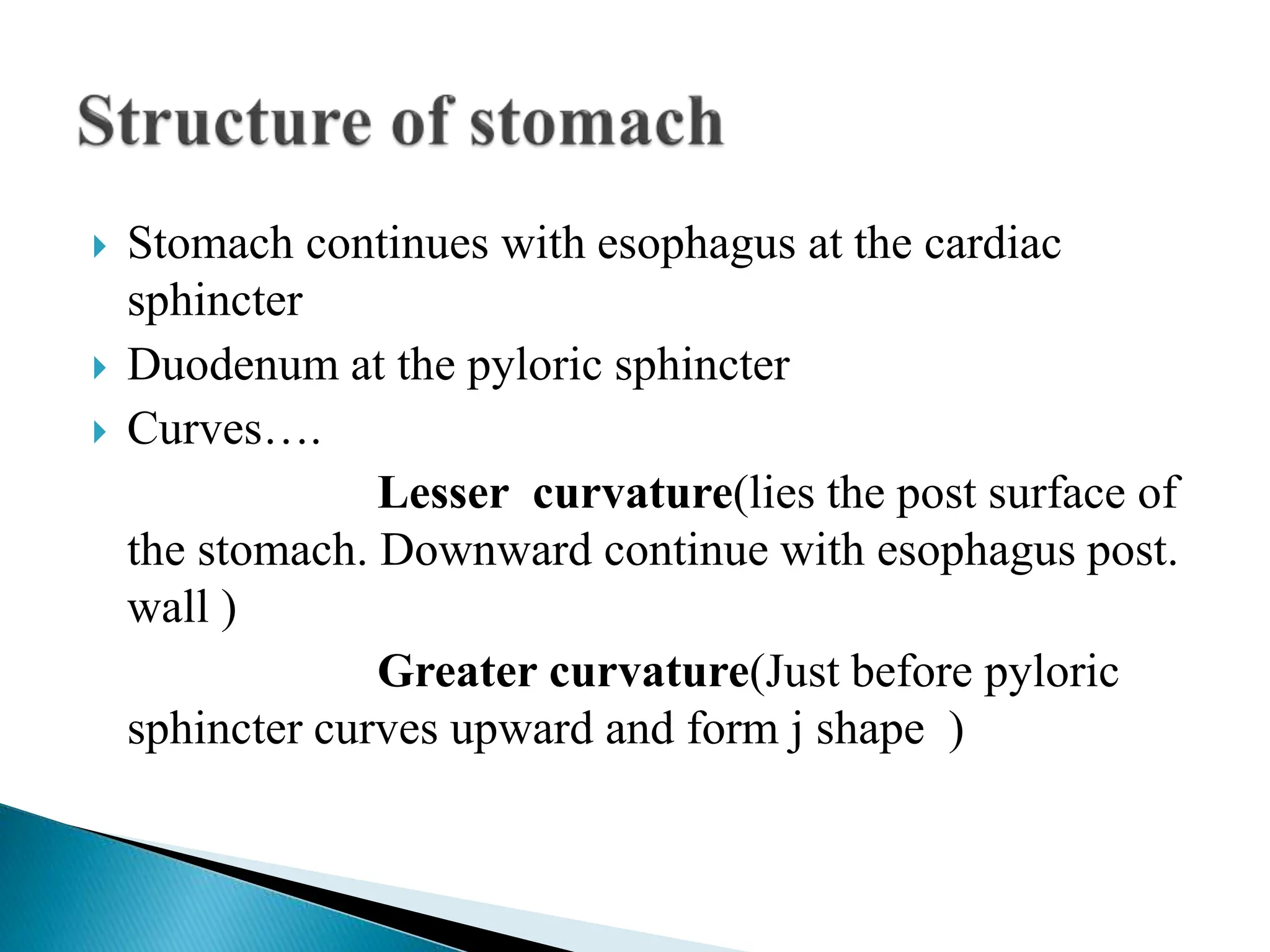
The stomach digests food through the secretion of enzymes and acids. It has five sections - the cardia, fundus, body, antrum, and pylorus. The stomach walls have four layers - mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa. Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid, lipase, and pepsin to digest food and kill microbes before entering the small intestine. The stomach secretes gastric juice in response to food in the stomach and signals from the duodenum to break down proteins and prepare nutrients for absorption.