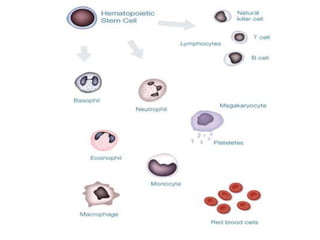
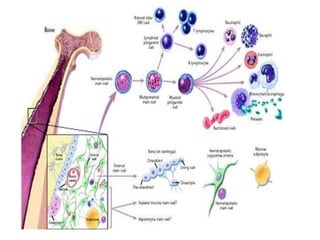
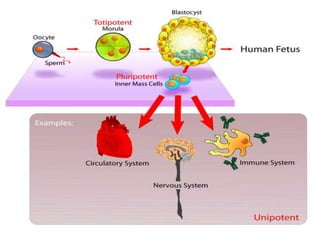
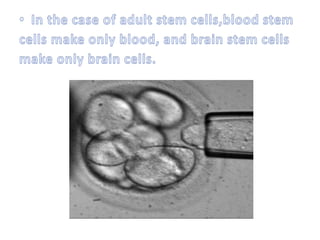
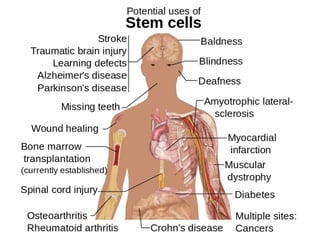
This document discusses the origin and types of stem cells. It notes that the term "stem cell" was coined in 1908 and that hematopoietic stem cells were discovered in human cord blood in 1978. It describes the two main types of stem cells as embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells and explains their potential (totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent, oligopotent, unipotent). Stem cell research offers promise for developing prevention methods and treating cancers and rare blood diseases in the future.