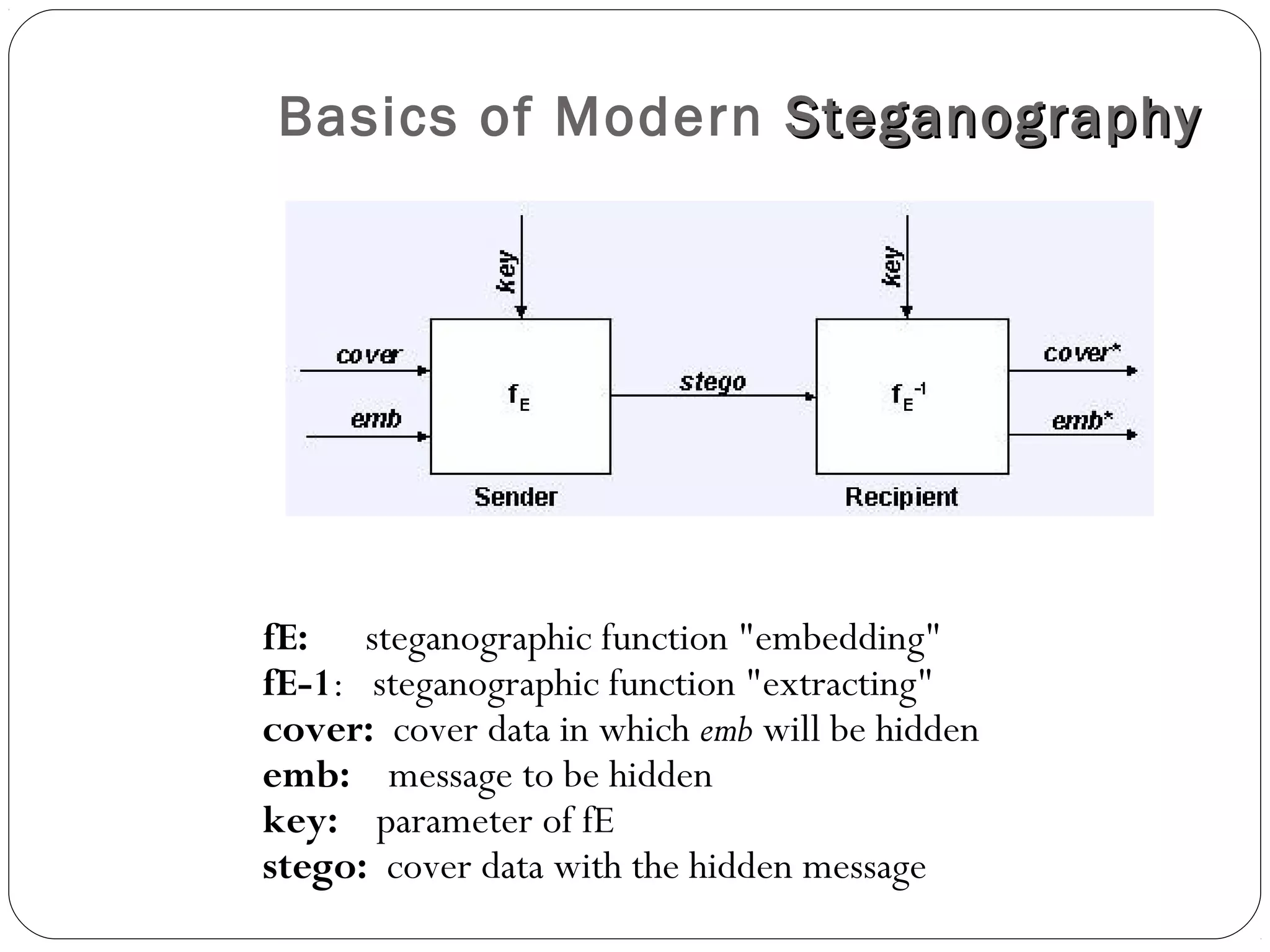
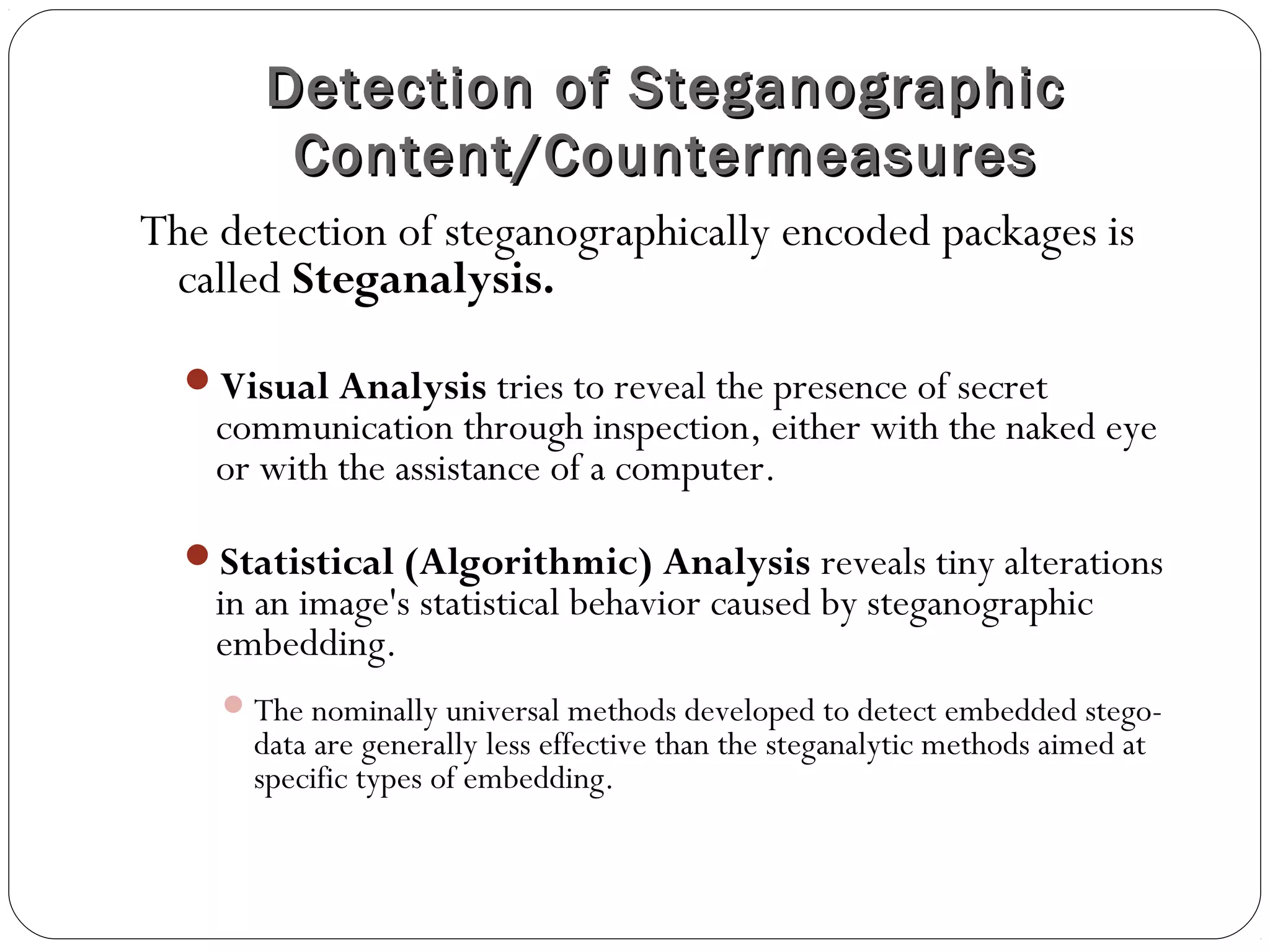
Steganography is the practice of concealing a file, message, image, or video within another file, message, image, or video. The concealed message is hidden in a way that prevents detection. It differs from cryptography, which encrypts a message to hide its meaning but not its existence. Modern steganography techniques include least significant bit insertion to hide messages in image files with minimal distortion. Detection of concealed messages is called steganalysis and involves visual or statistical analysis to reveal alterations caused by message embedding.