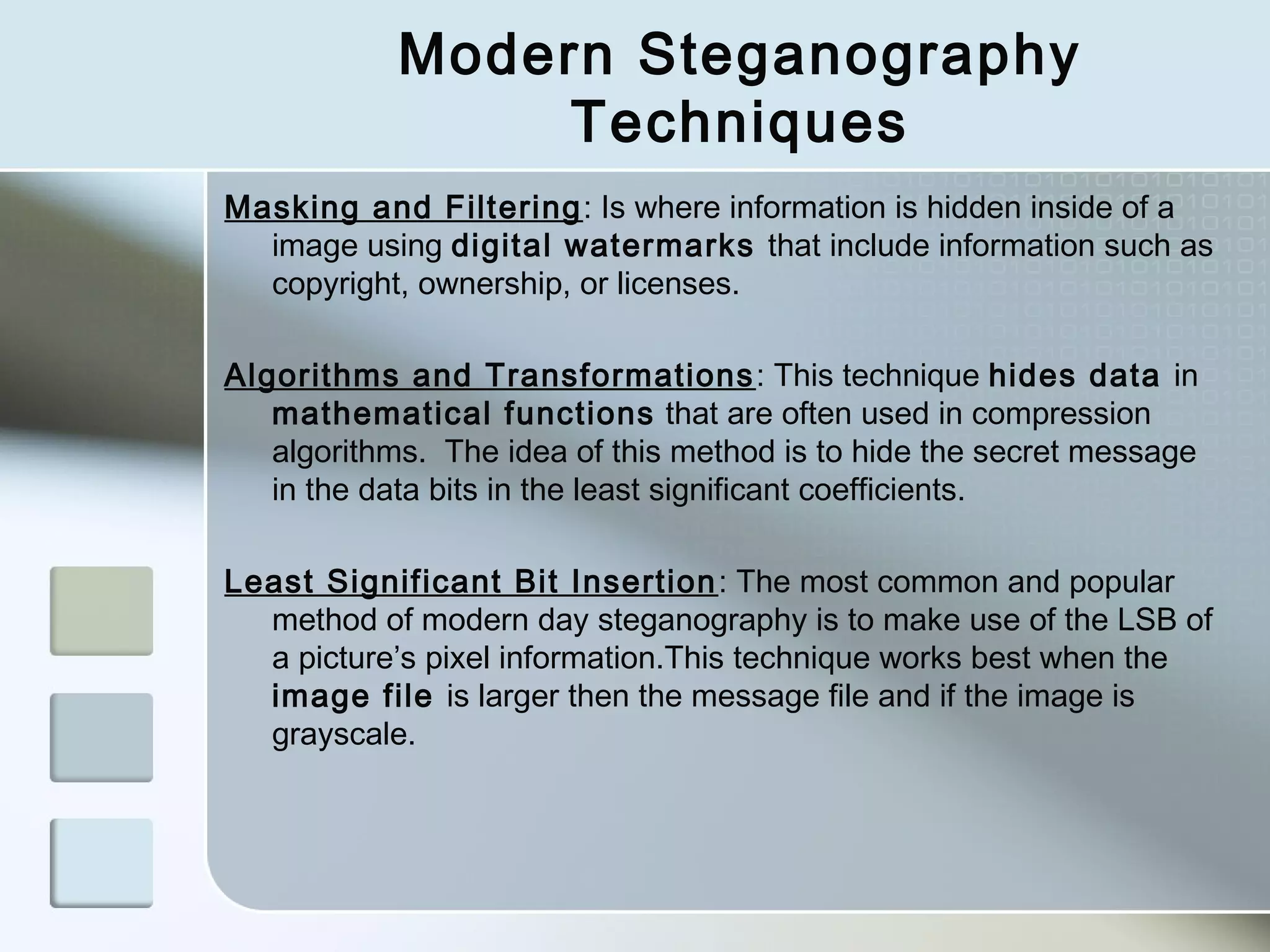
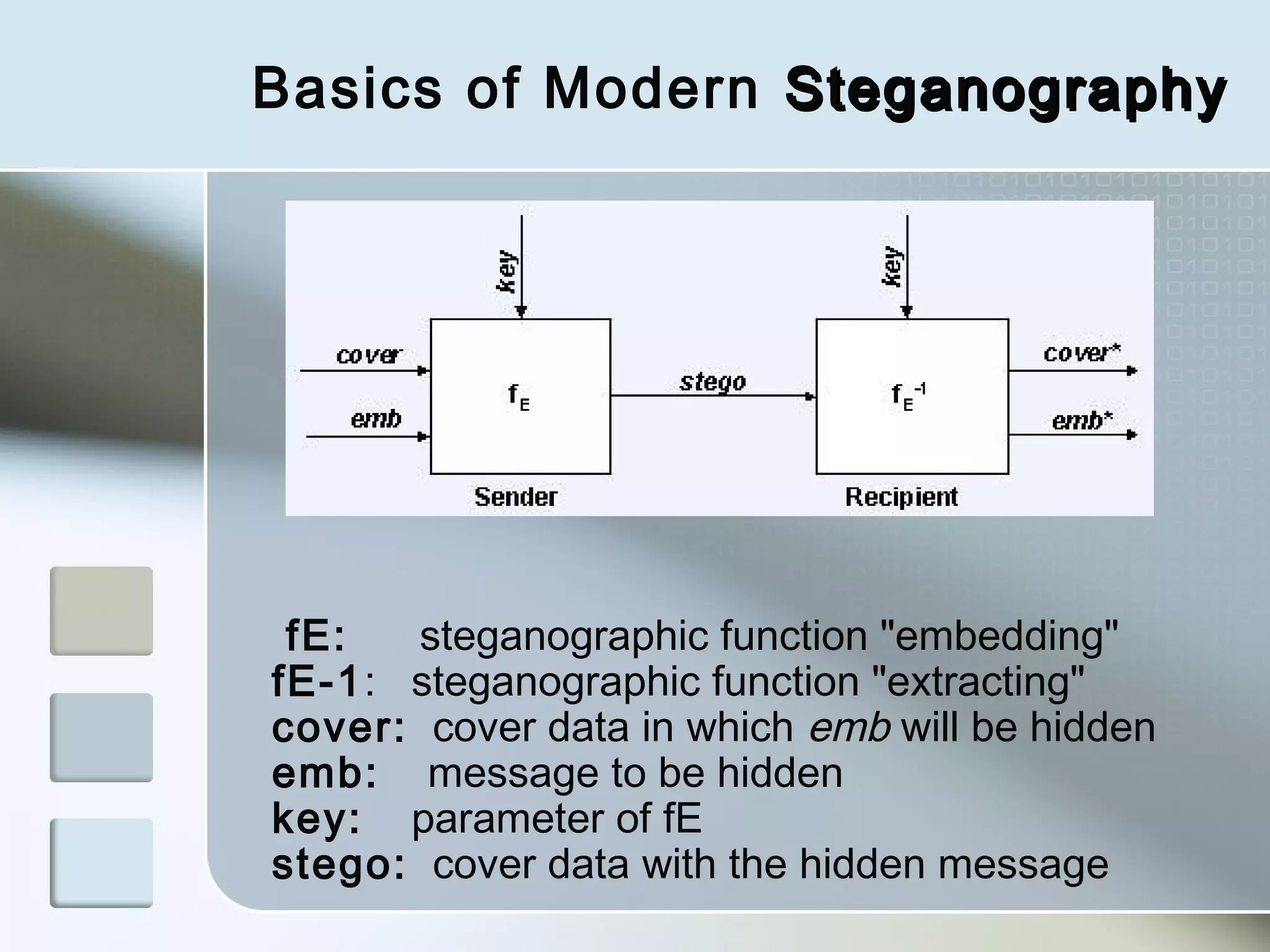
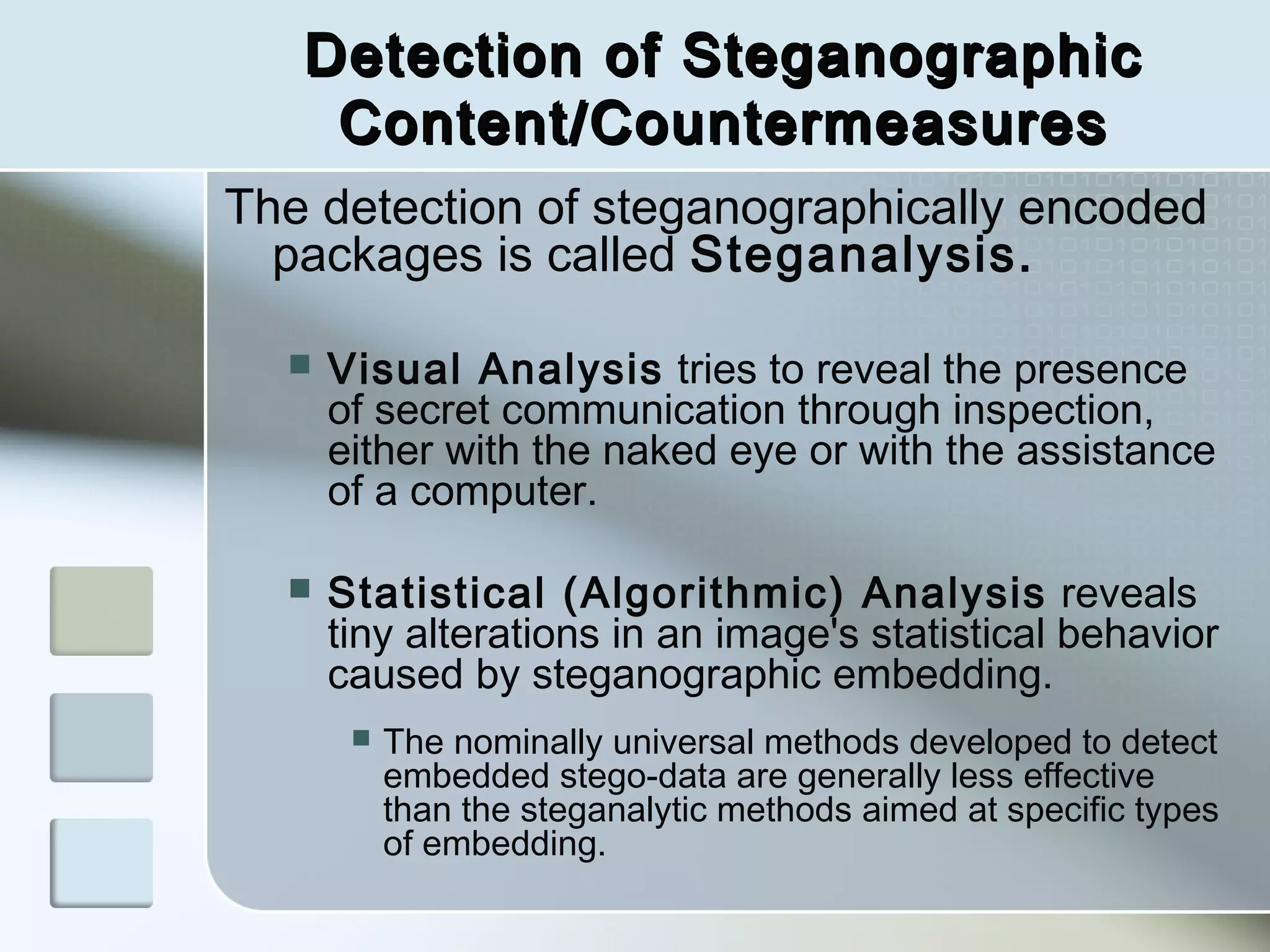
Steganography is the practice of concealing a file, message, image, or video within another file, message, image, or video. There are two main branches - steganography and watermarking. Steganography hides the existence of the message itself, while watermarking involves openly communicating the existence of a message to provide copyright protection. Throughout history, various techniques have been used to hide secret messages, from wax-covered wooden panels to microdots. Modern steganography uses algorithms and least significant bit insertion to hide data in images, audio, and other file types. Detection of hidden messages involves steganalysis to identify subtle statistical changes revealing concealed data.