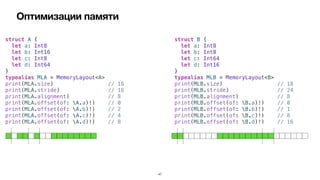
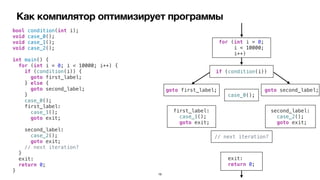
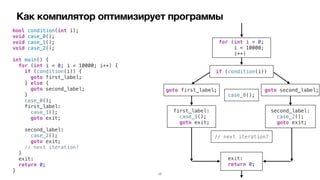
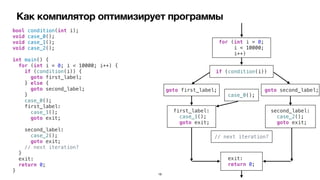
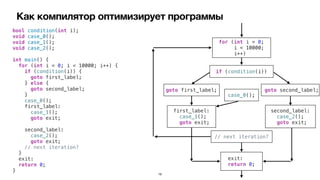
Документ обсуждает оптимизации компилятора для повышения производительности программ на iOS. Рассматриваются различные типы оптимизаций, такие как оптимизация скорости, размера, потребления памяти и безопасности. Приводятся примеры кода и описание, как компилятор выполняет эти оптимизации.












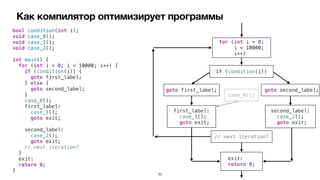
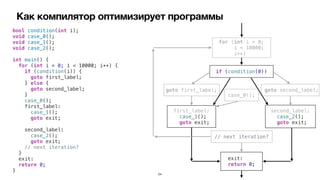

![Control Flow Graph
B1
Entry
B2 B4
B3
B5 B6
Exit
B7
28
Basic Block Predecessors Successors
Entry [ ] [ B1 ]
B1 [ Entry ] [ B2, B4 ]
B2 [ B1 ] [ B5 ]
B3 [ ] [ B5 ]
B4 [ B1 ] [ B6 ]
B5 [ B2 ] [ Exit ]
B6 [ B4 ] [ Exit ]
B7 [ ] [ Exit ]
Exit [ B5, B6, B7 ] [ ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/podlodkaioscrew-compileroptimizations2-220217101909/85/slide-28-320.jpg)
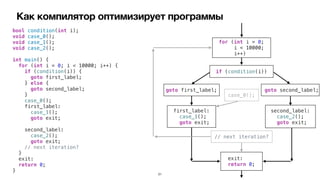
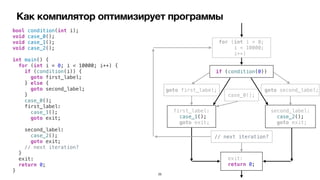
![Control Flow Graph
B1
Entry
B2 B4
B3
B5 B6
Exit
B7
29
Basic Block Predecessors Successors
Entry [ ] [ B1 ]
B1 [ Entry ] [ B2, B4 ]
B2 [ B1 ] [ B5 ]
B3 [ ] [ B5 ]
B4 [ B1 ] [ B6 ]
B5 [ B2 ] [ Exit ]
B6 [ B4 ] [ Exit ]
B7 [ ] [ Exit ]
Exit [ B5, B6, B7 ] [ ]
Entry -> B1 -> B2 -> B5 -> Exit
Entry -> B1 -> B4 -> B6 -> Exit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/podlodkaioscrew-compileroptimizations2-220217101909/85/slide-29-320.jpg)
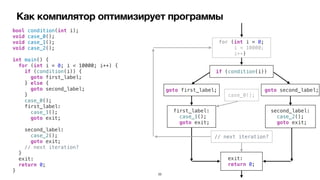
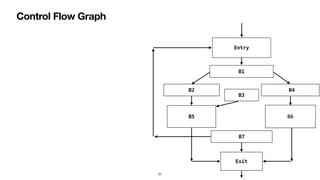
![Control Flow Graph
30
Basic Block Predecessors Successors
Entry [ ] [ B1 ]
B1 [ Entry ] [ B2, B4 ]
B2 [ B1 ] [ B5 ]
B3 [ ] [ B5 ]
B4 [ B1 ] [ B6 ]
B5 [ B2 ] [ Exit ]
B6 [ B4 ] [ Exit ]
B7 [ ] [ Exit ]
Exit [ B5, B6, B7 ] [ ]
func pred(_ bb: BasicBlock) -> [BasicBlock]
func succ(_ bb: BasicBlock) -> [BasicBlock]
func deadCodeElimination(f: Function) {
// 1
var reachable = [BasicBlock]()
var queue = [BasicBlock]()
queue.append(f.entry)
// 2
while !queue.isEmpty {
let head = queue.removeFirst()
reachable.append(head)
queue.append(contentsOf: succ(head))
}
// 3
for bb in f.basicBlocks {
if !reachable.contains(bb) {
f.removeBasicBlock(bb: bb)
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/podlodkaioscrew-compileroptimizations2-220217101909/85/slide-30-320.jpg)










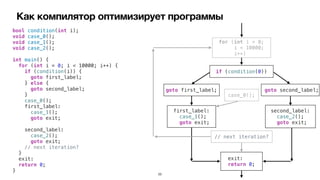
![Оптимизации и безопасность
43
char *getPWHash() {
long i; char pwd[64];
char *sha1 = (char*)malloc(41);
// read password
fgets(pwd, sizeof(pwd), stdin); // <<<
// calculate sha1 of password ... // <<<
// overwrite pwd in memory
// Alternative (A) : use memset
memset(pwd, 0, sizeof(pwd)); // (A)
// Alternative (B) : reset pwd in a loop
for (i=0; i<sizeof(pwd); ++i)
pwd[i]=0; // (B)
// return only hash of pwd
return sha1;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/podlodkaioscrew-compileroptimizations2-220217101909/85/slide-43-320.jpg)