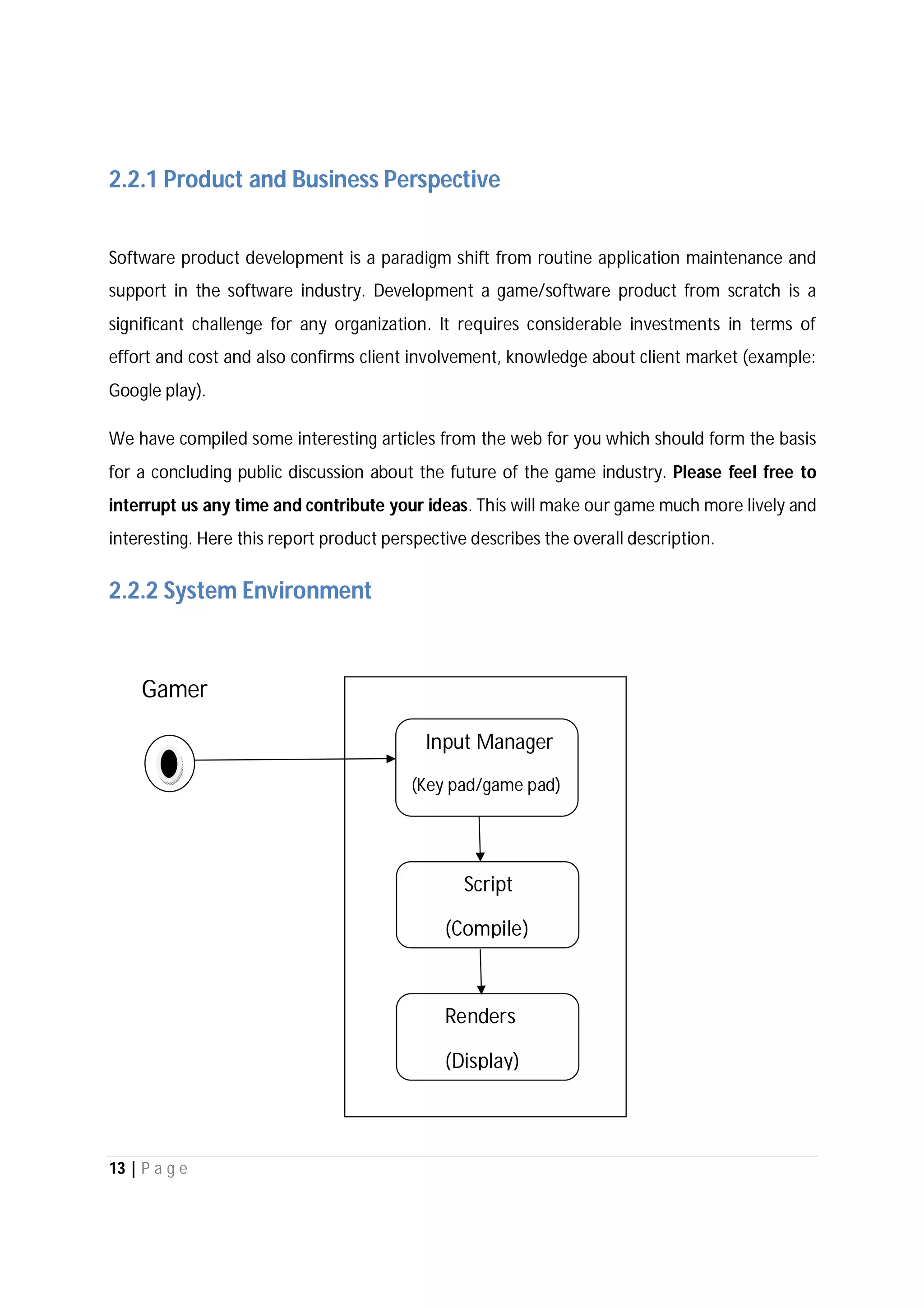
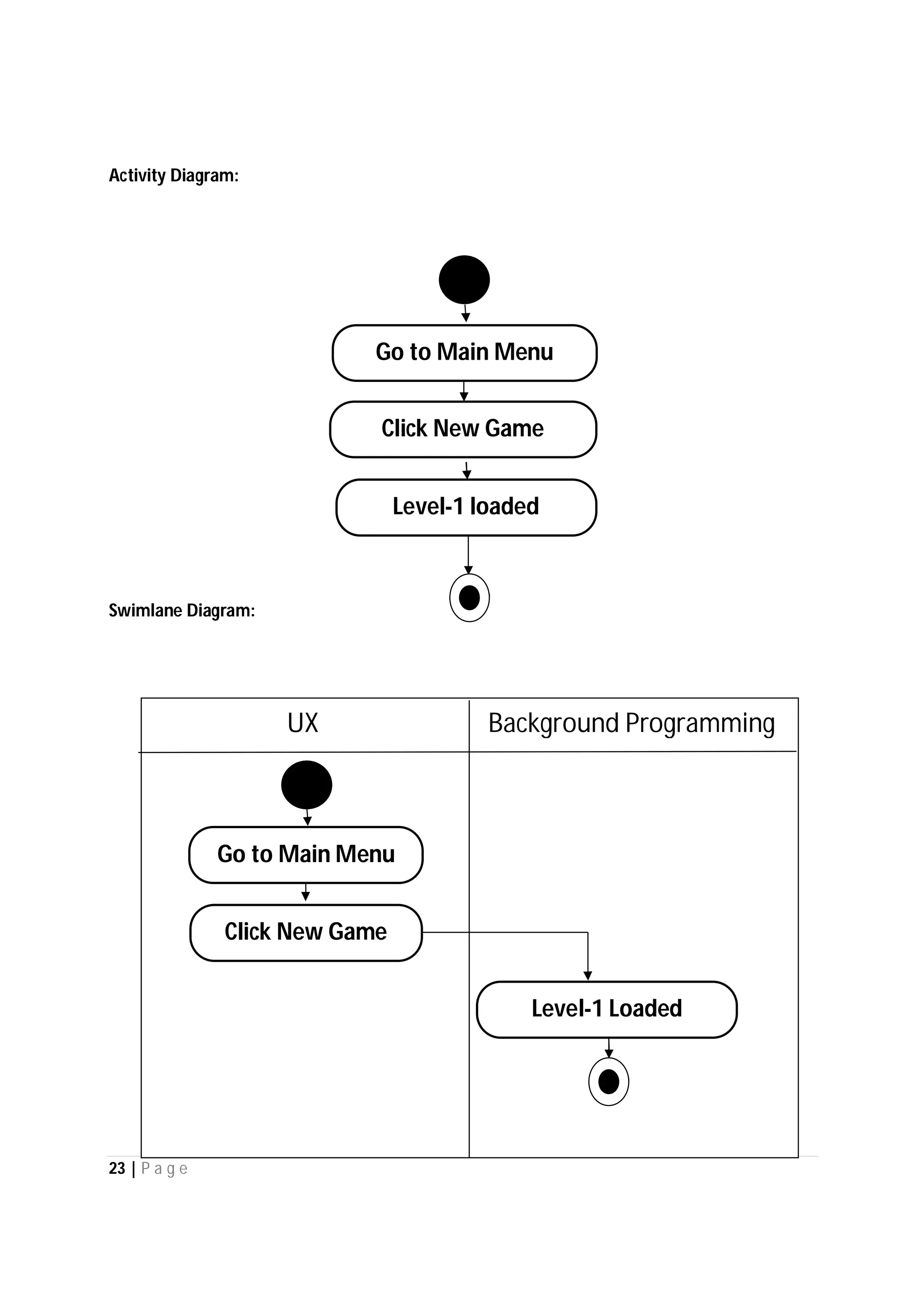
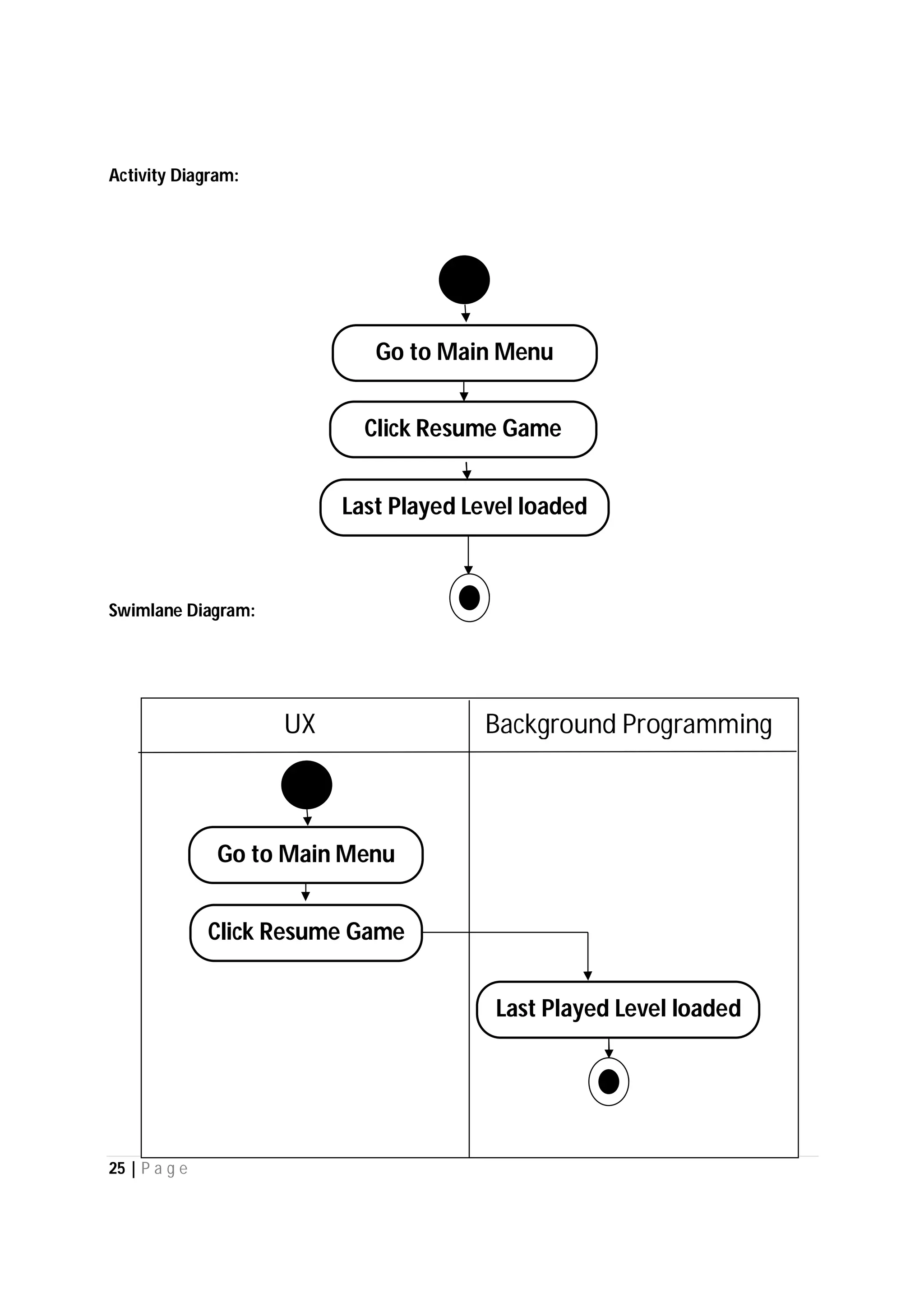
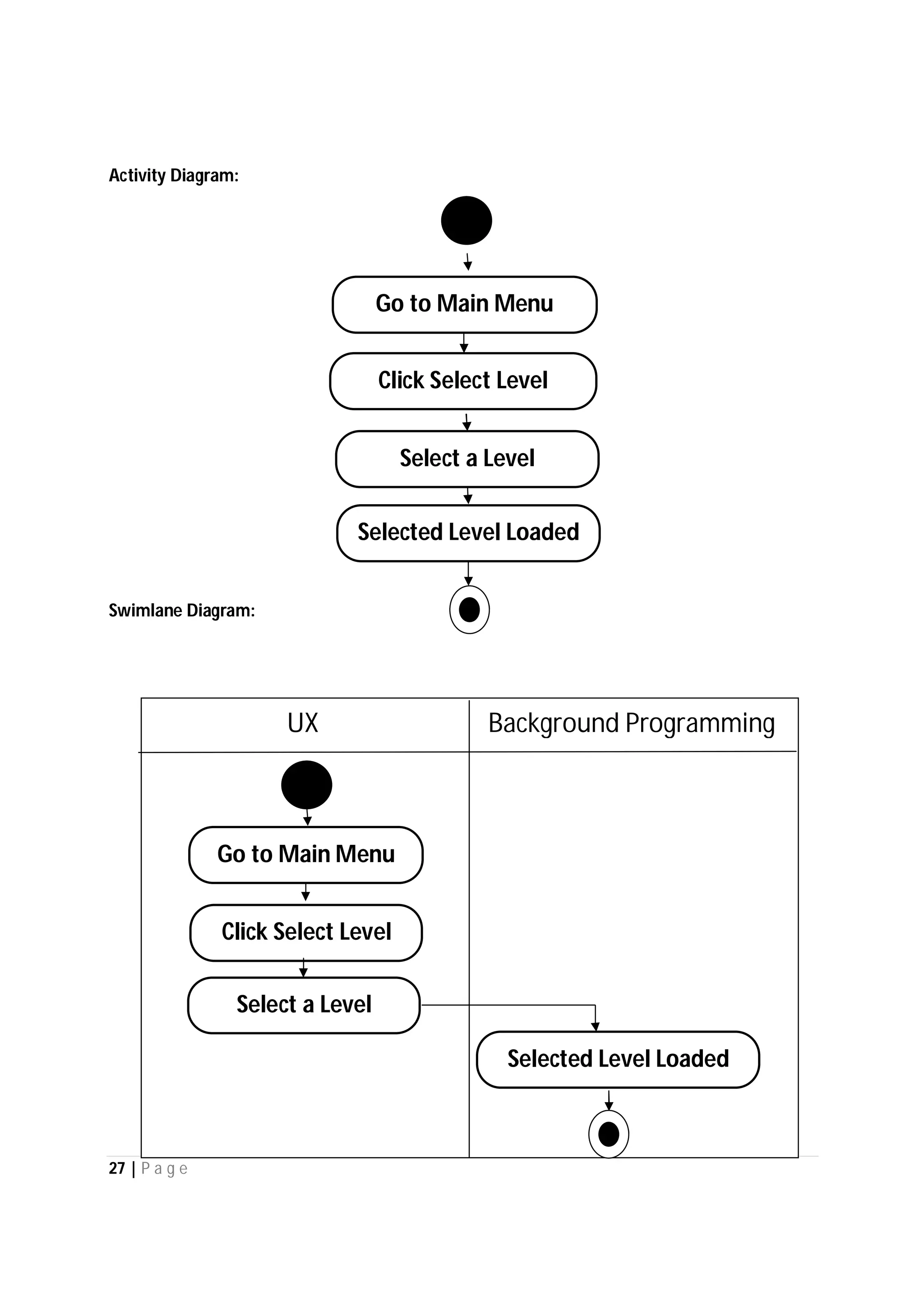
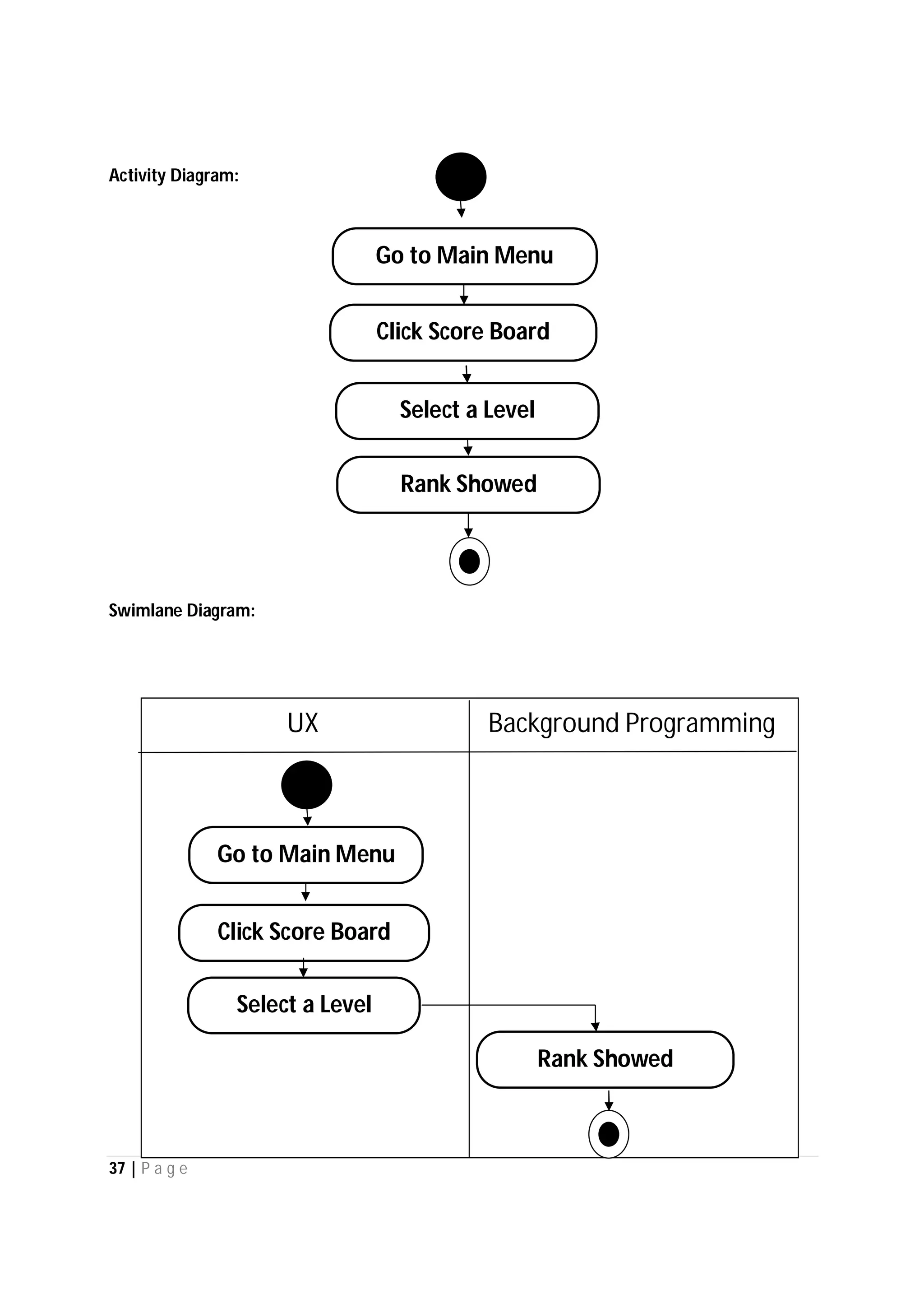
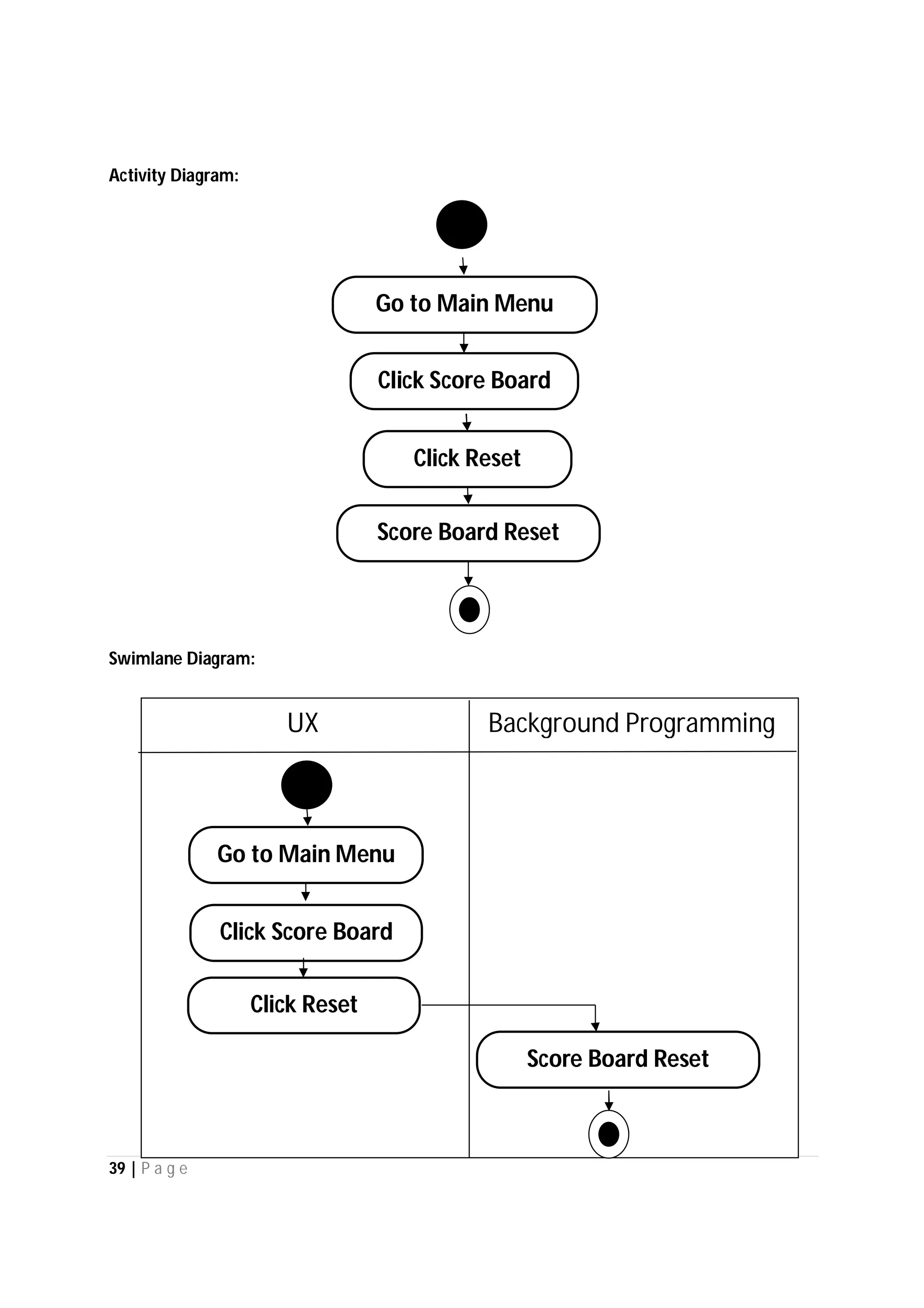
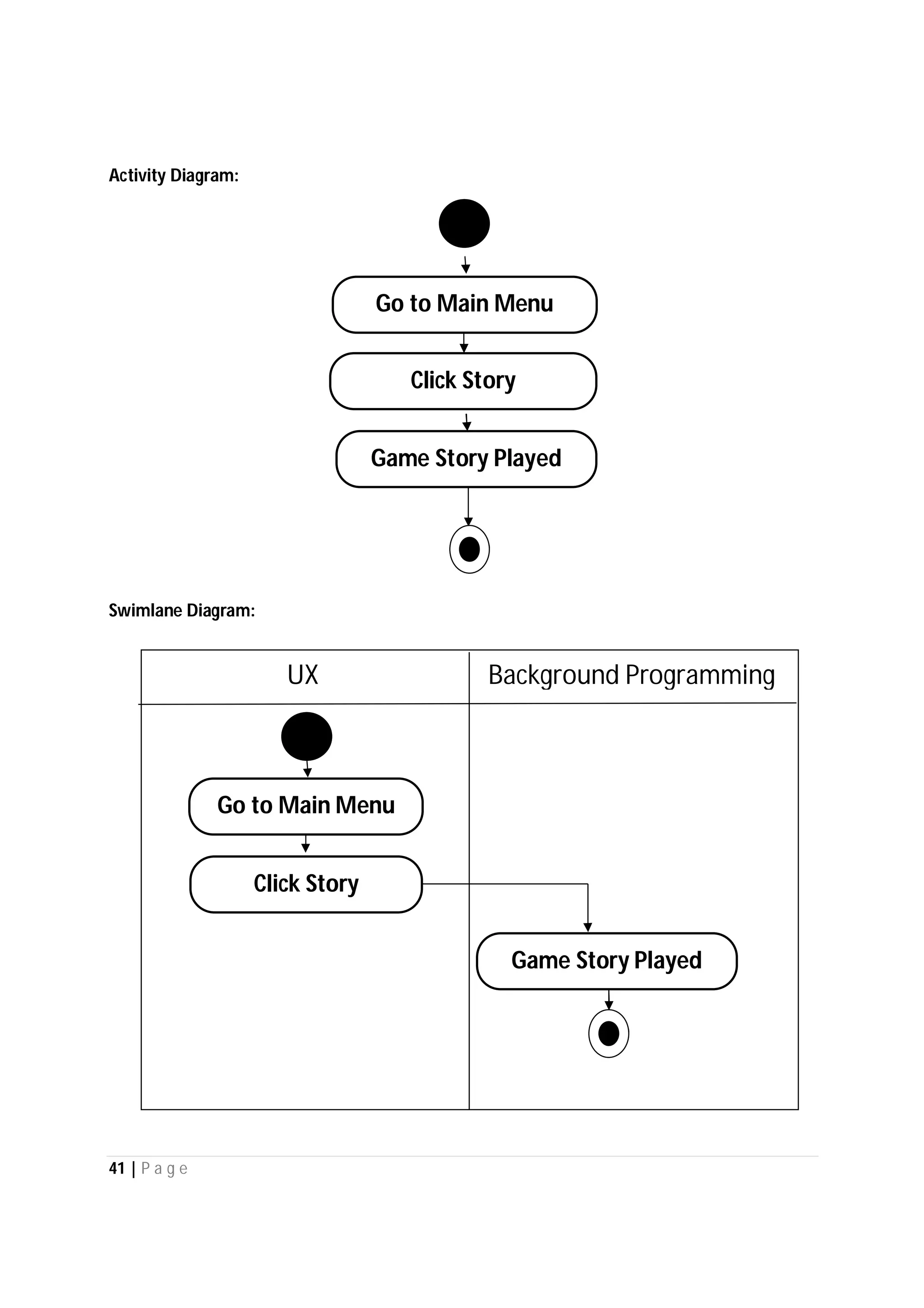
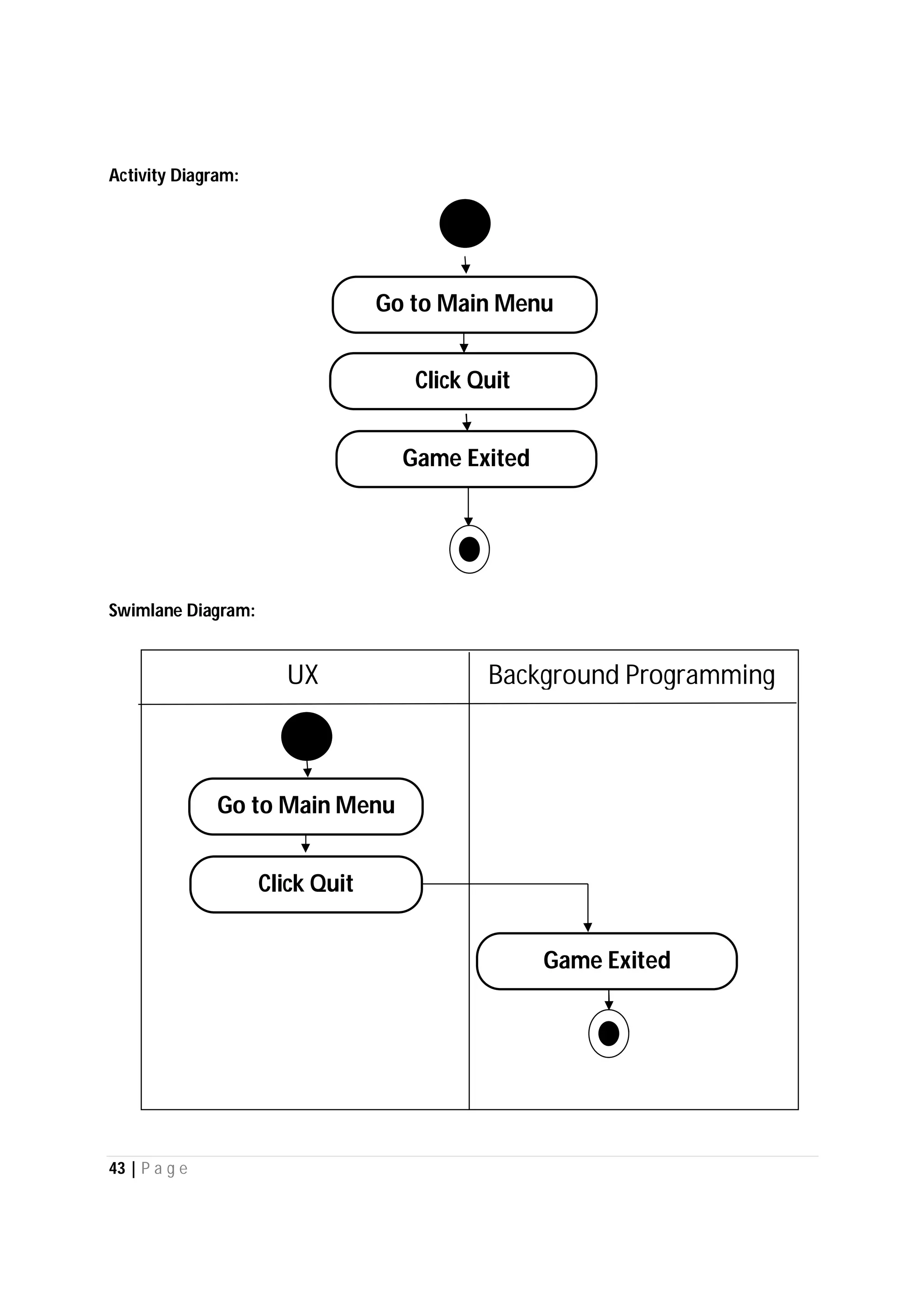
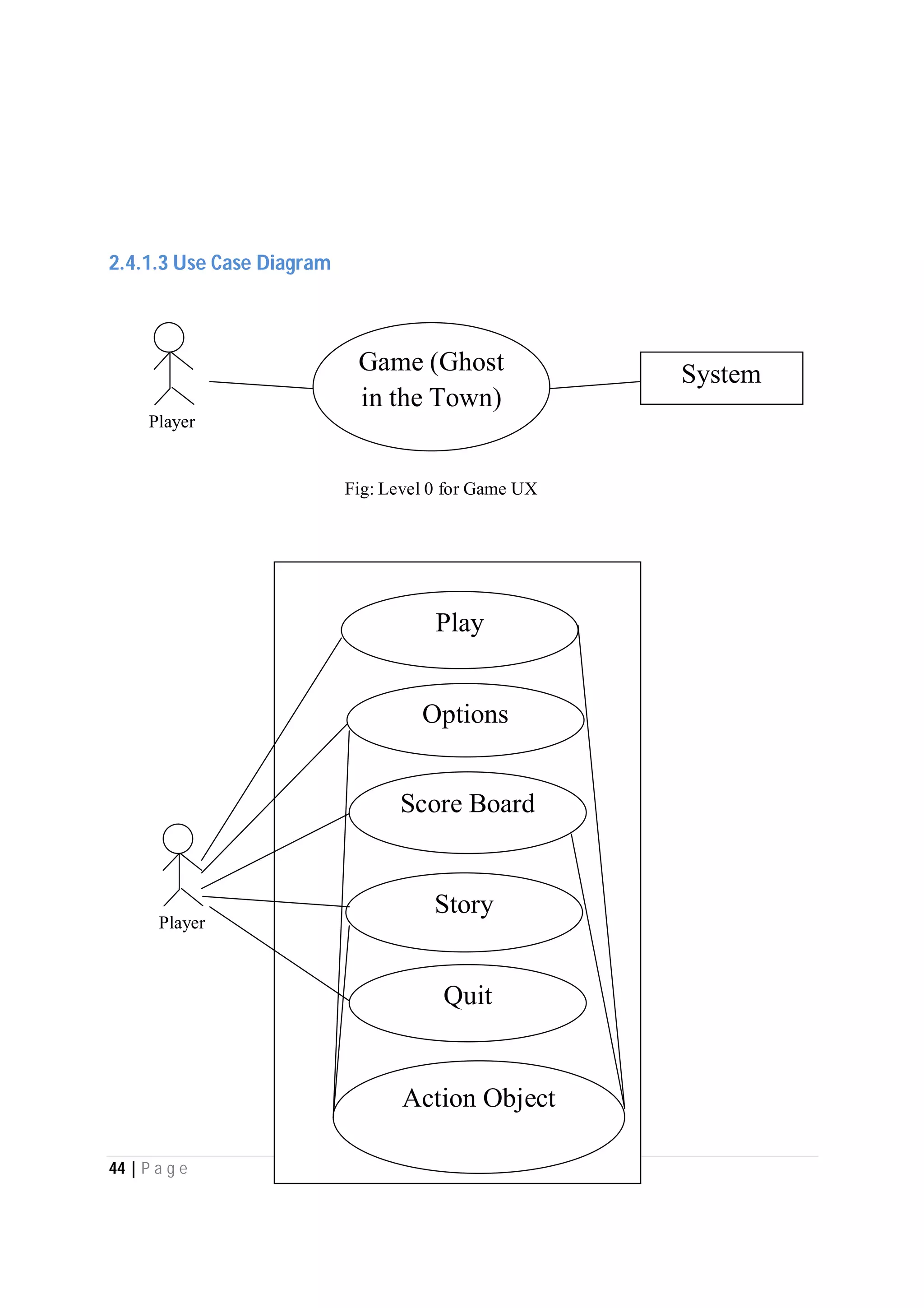
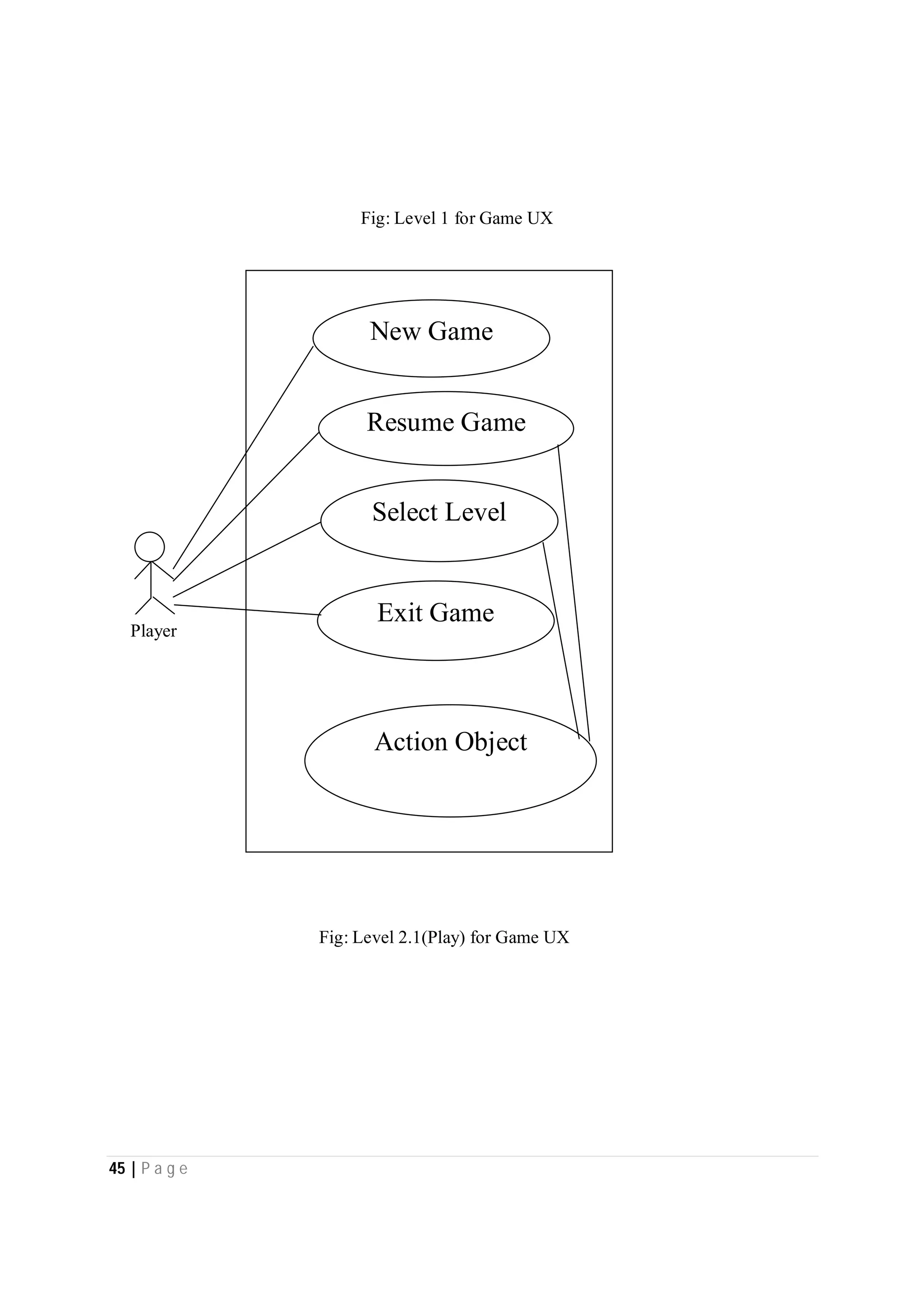
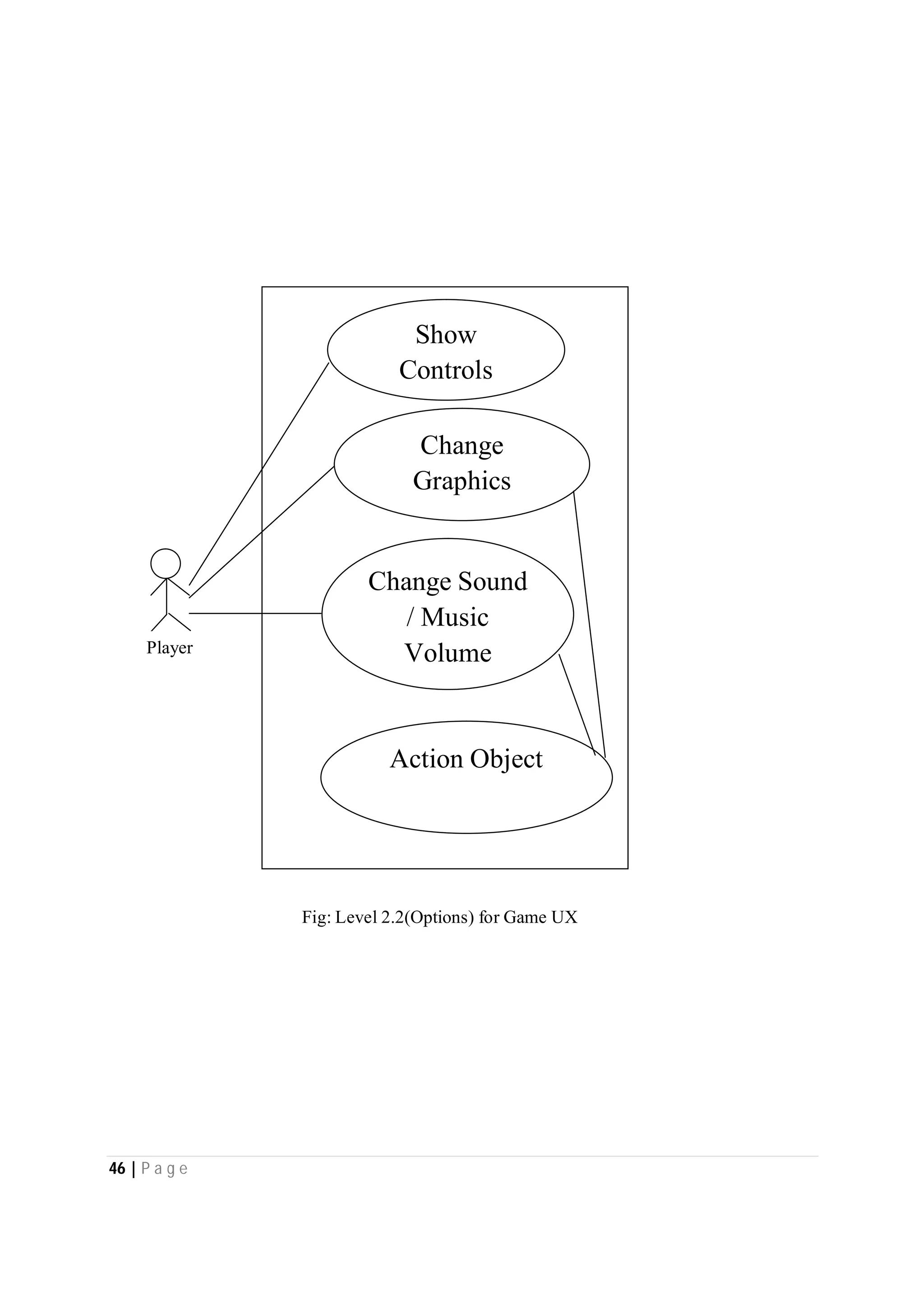
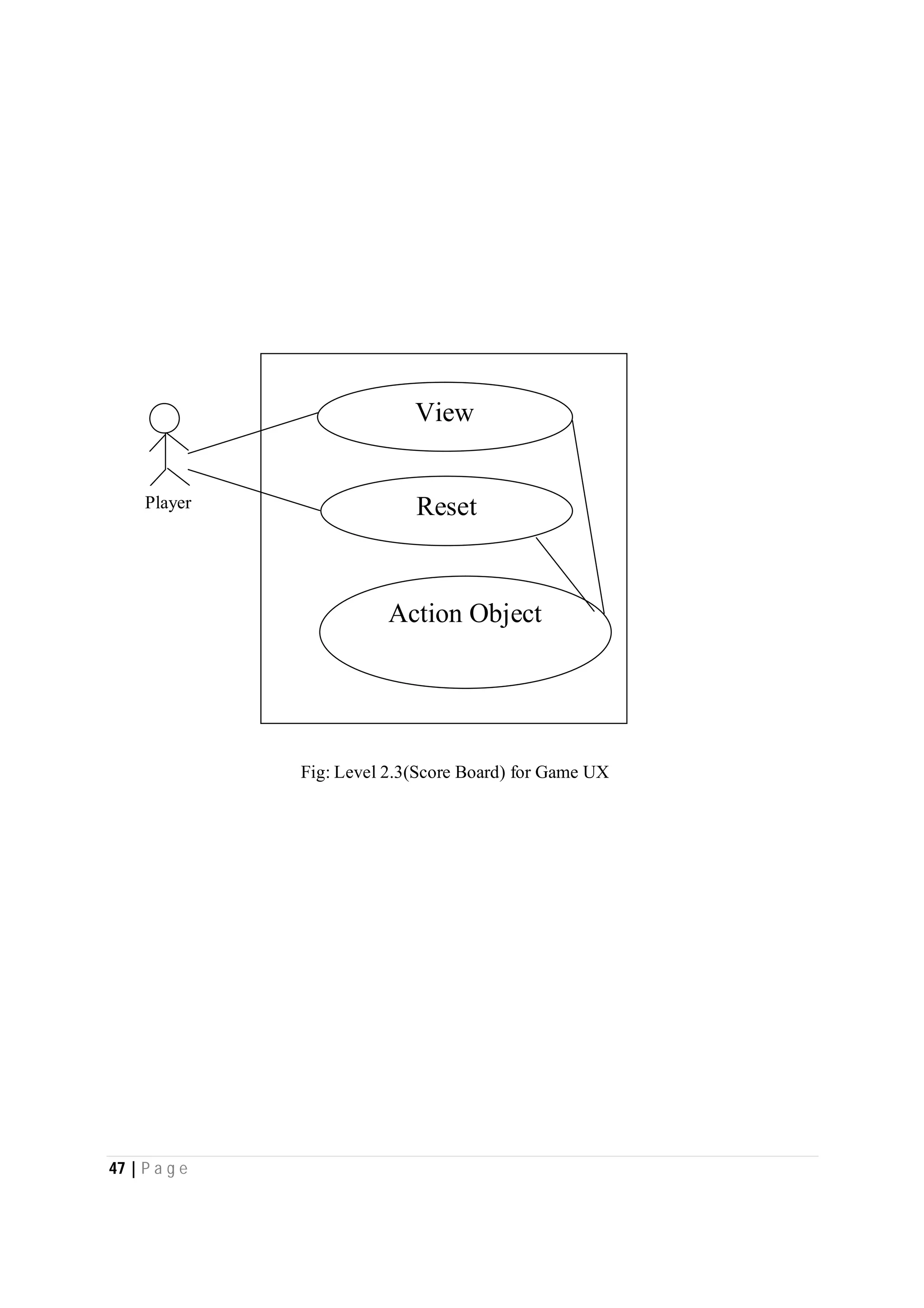
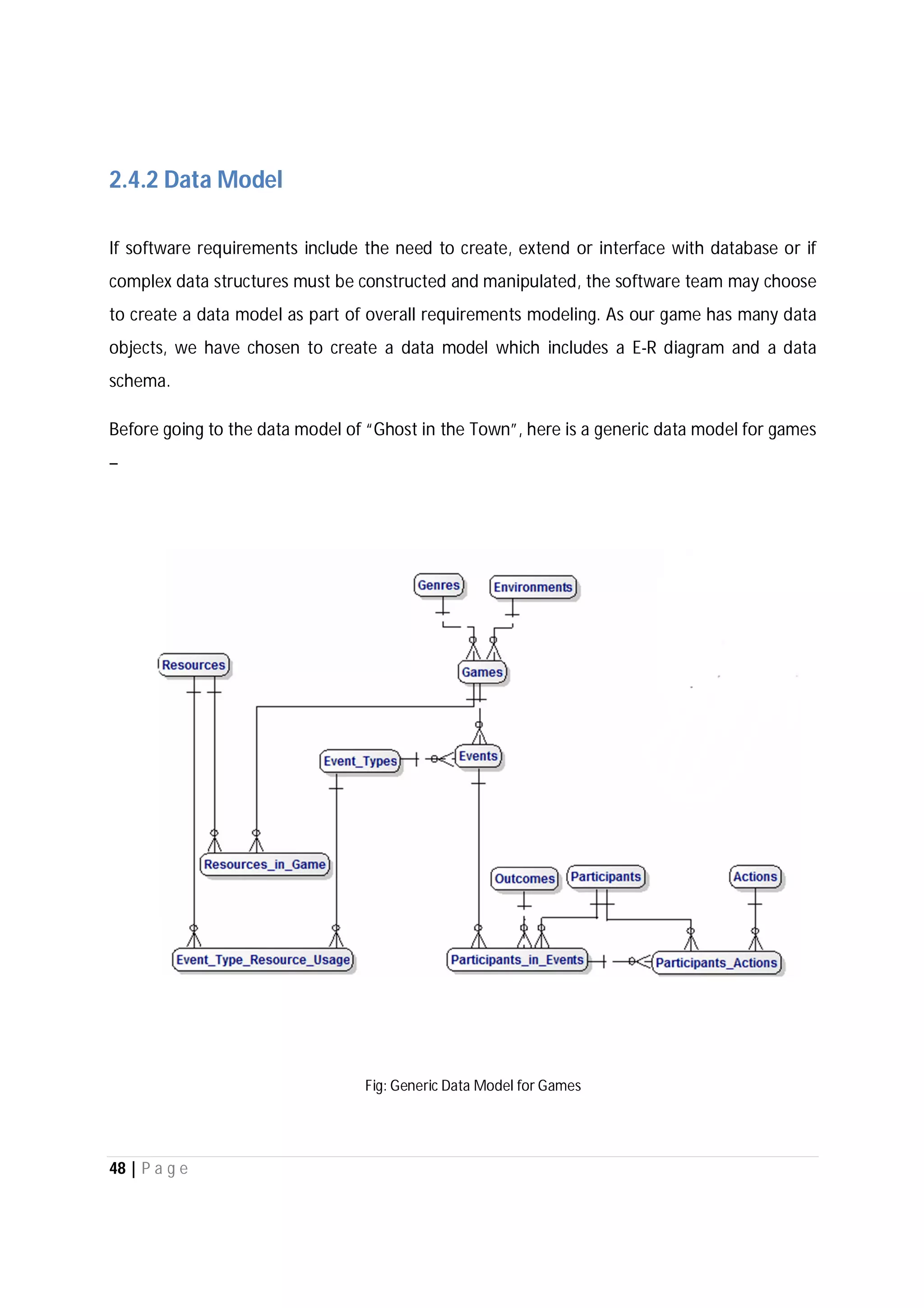
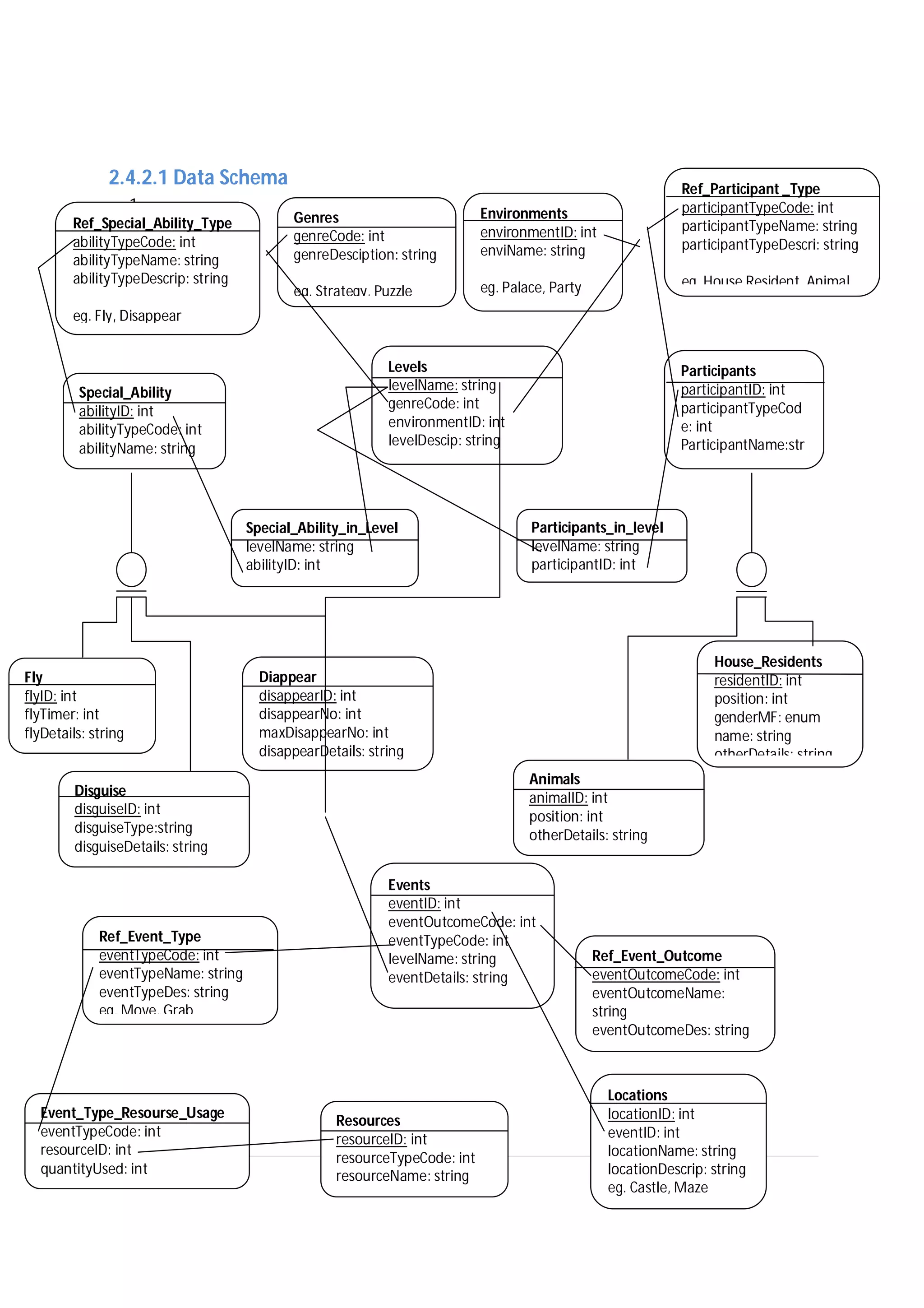
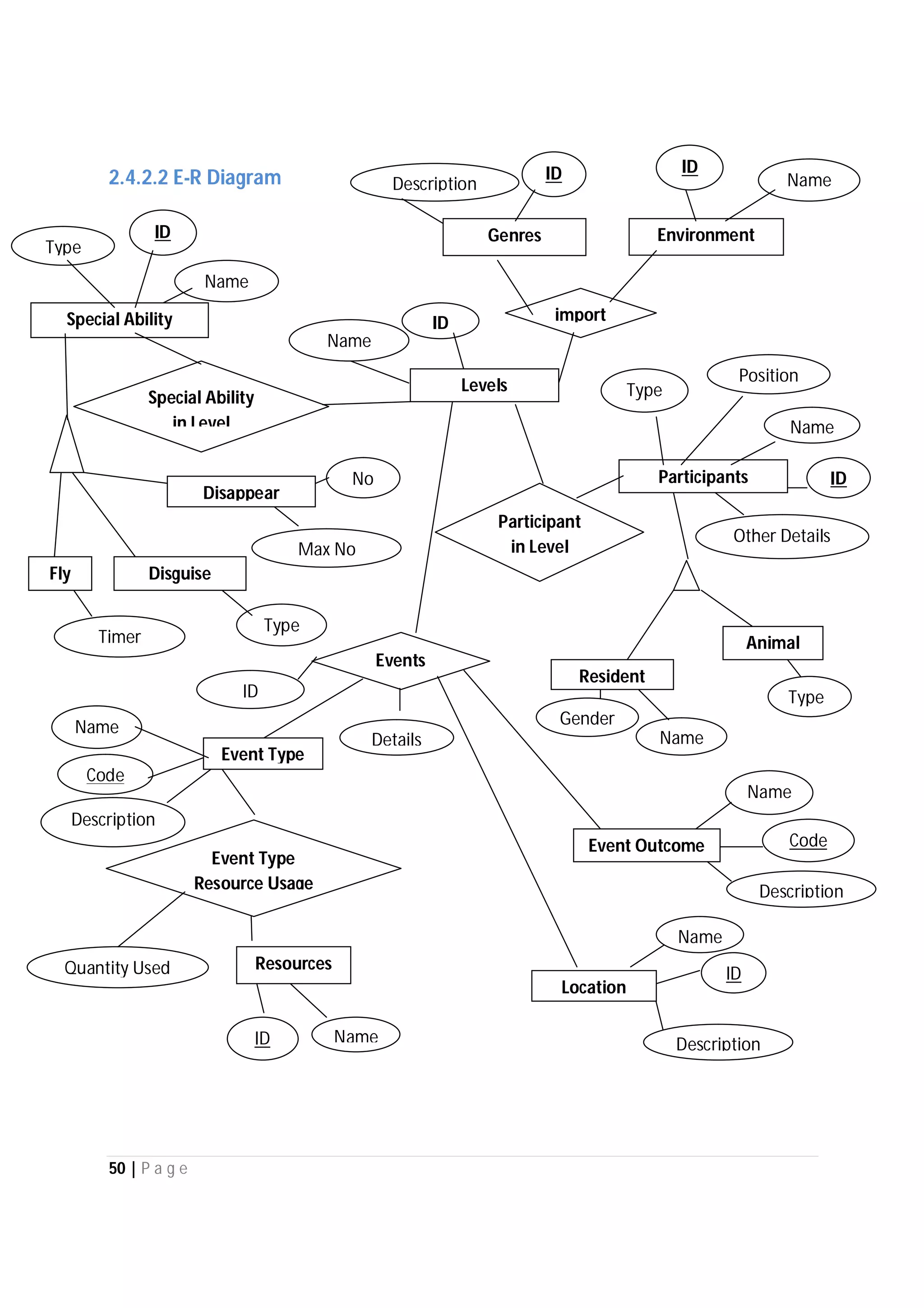
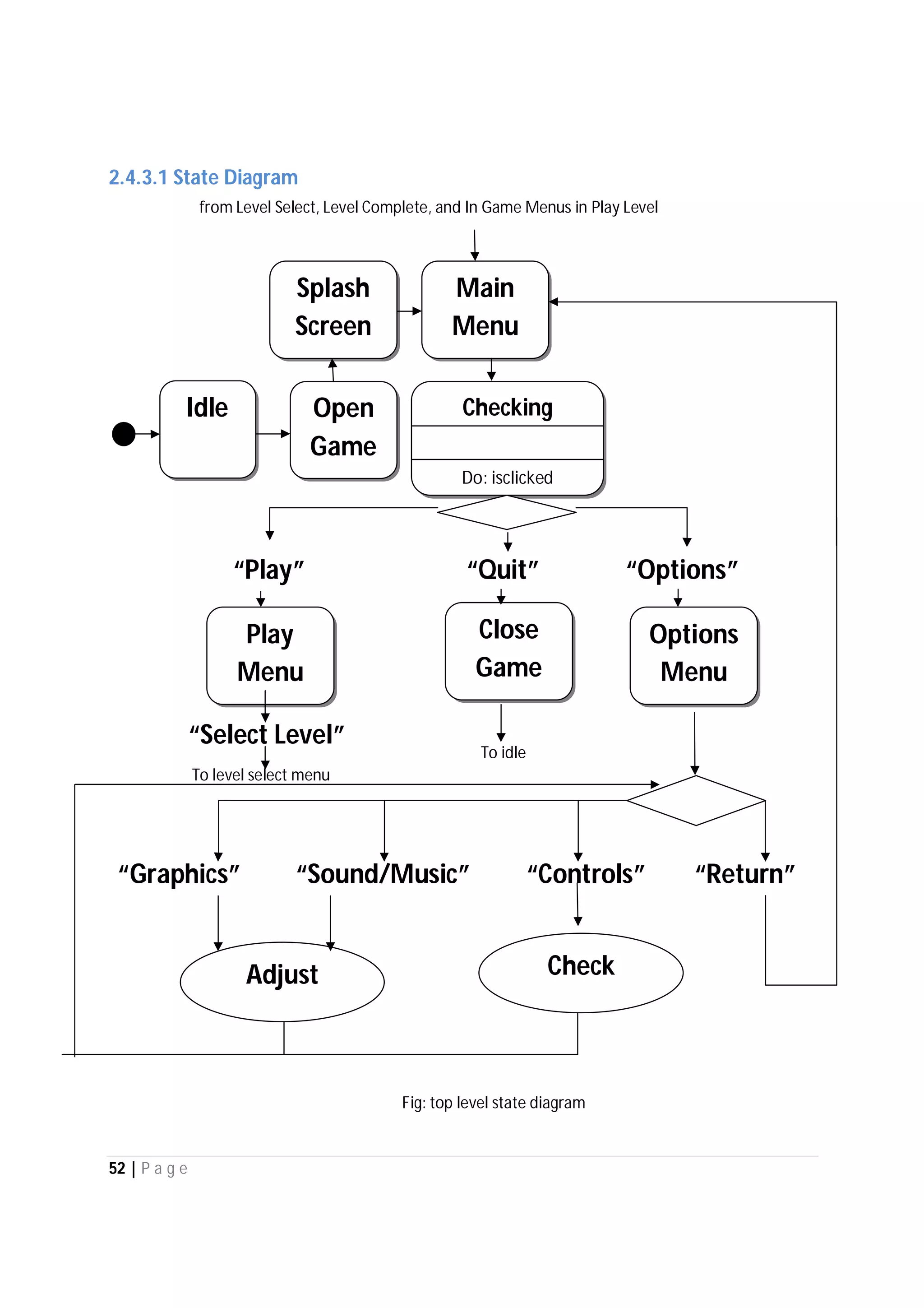
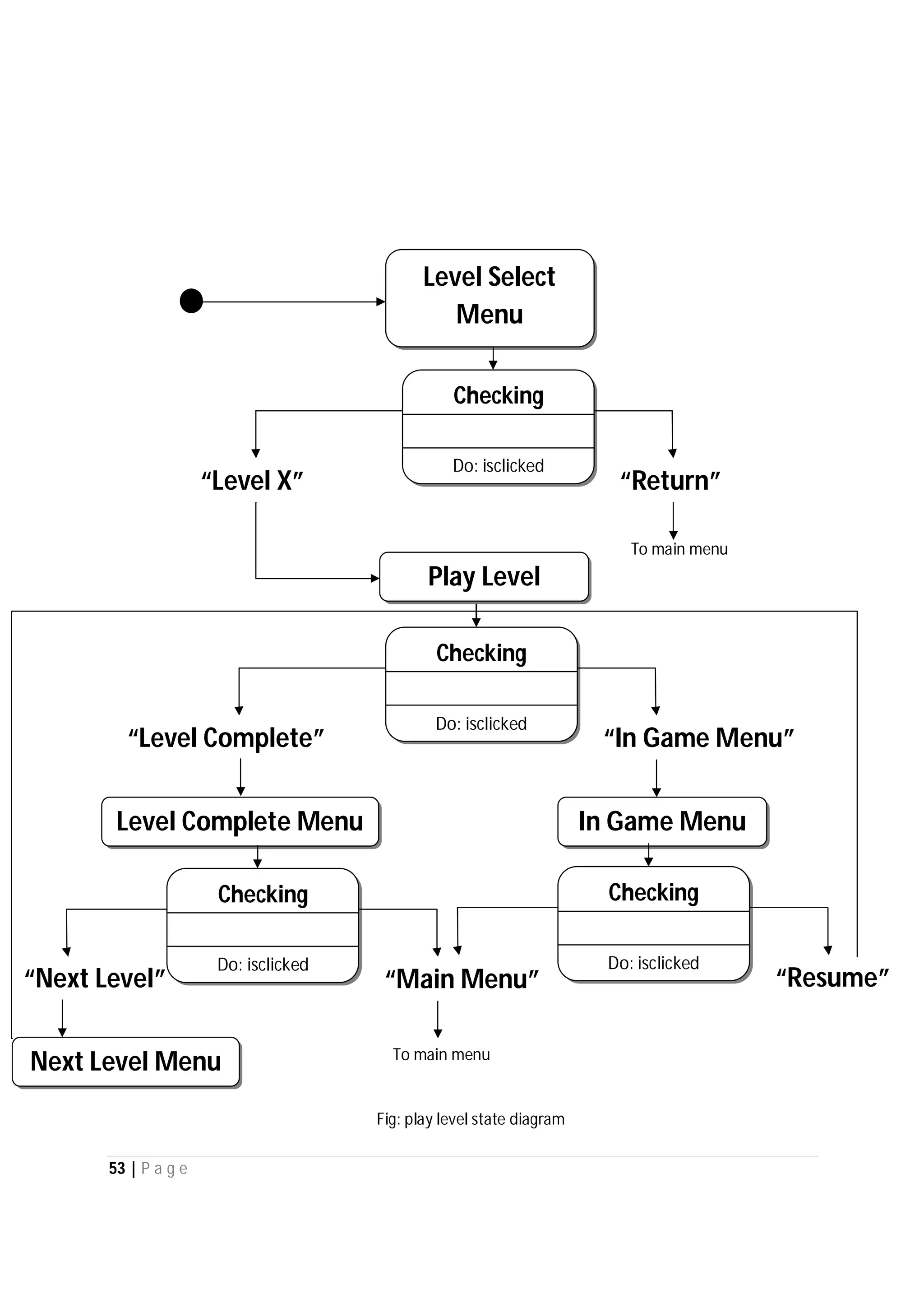
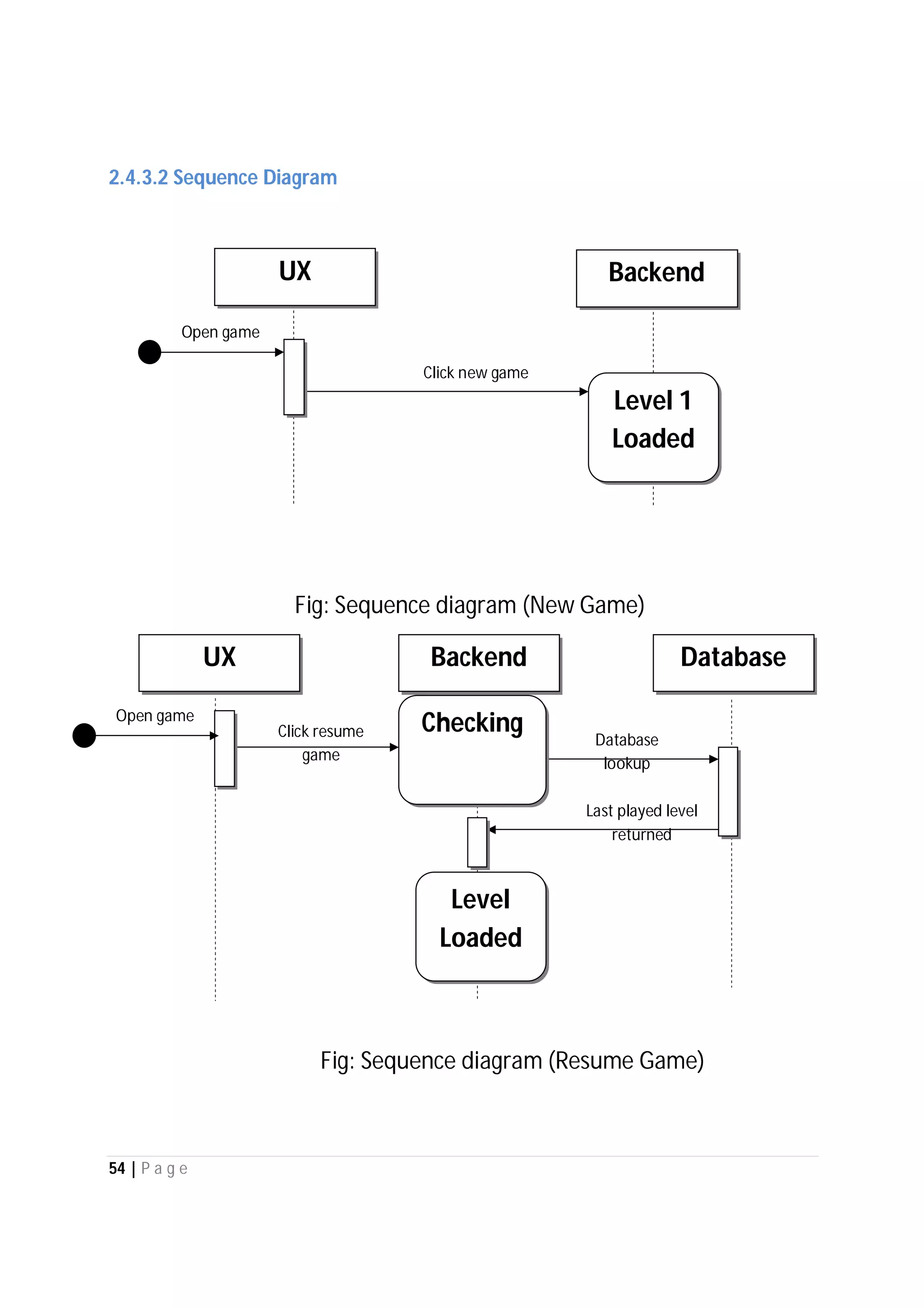
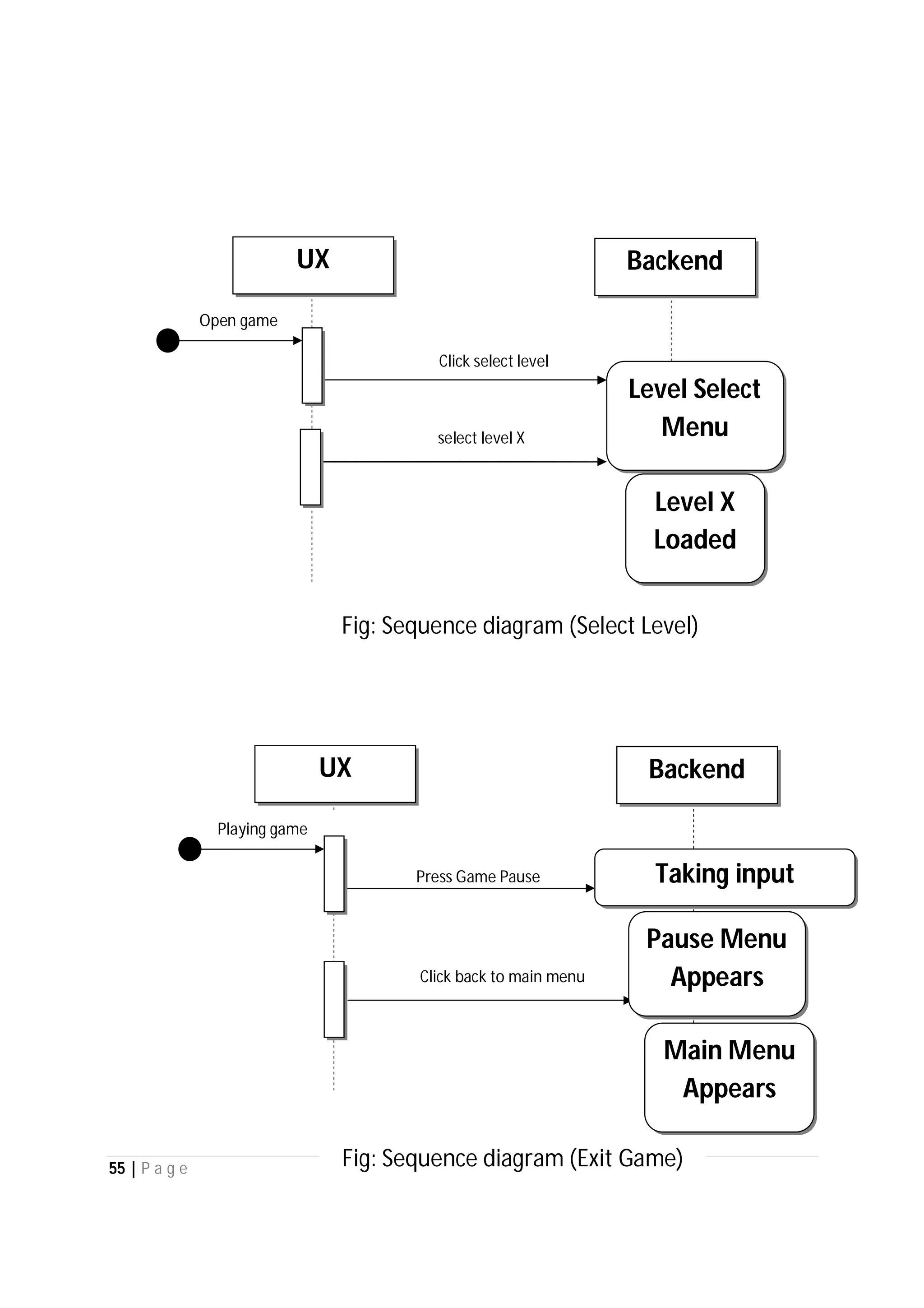
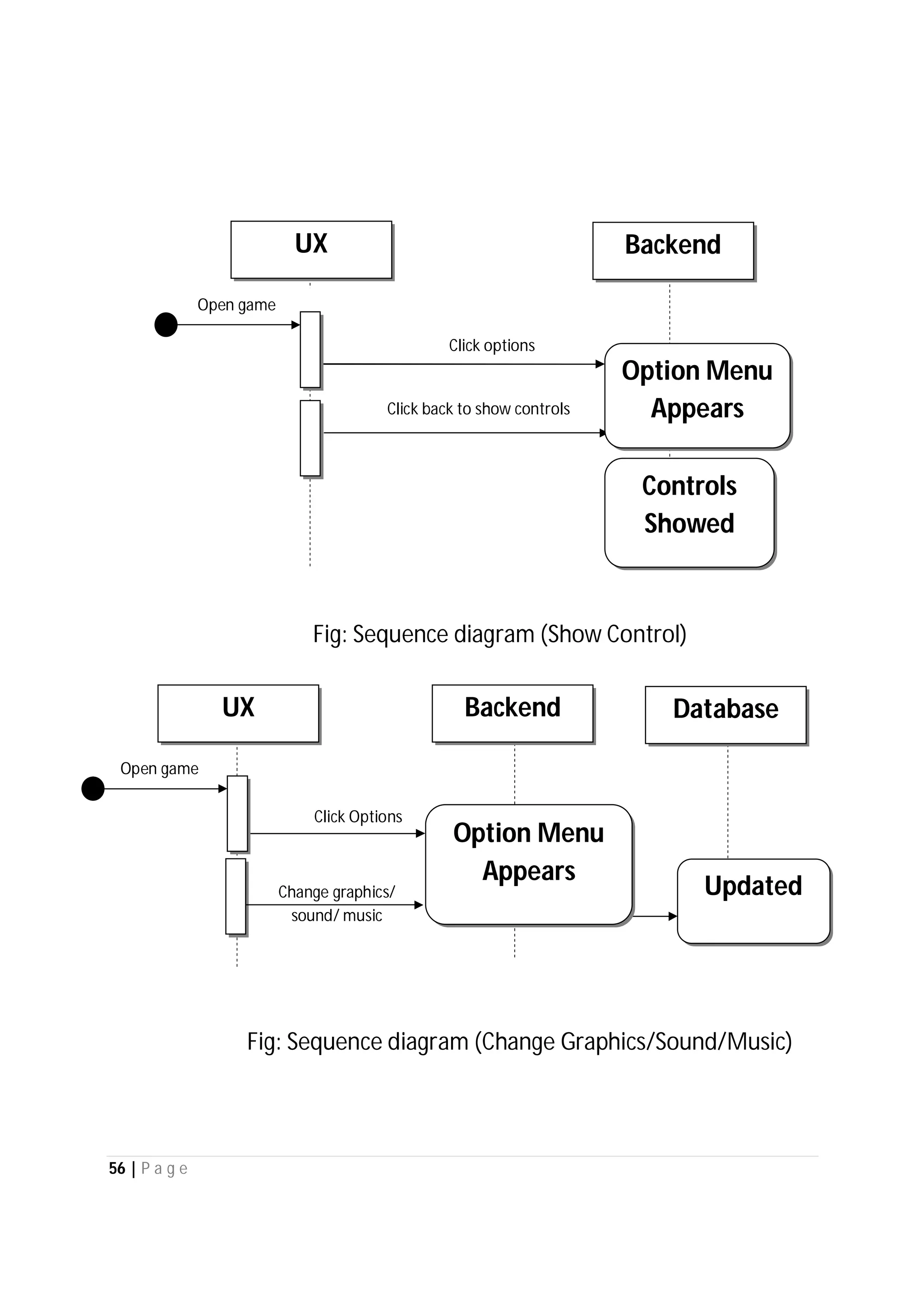
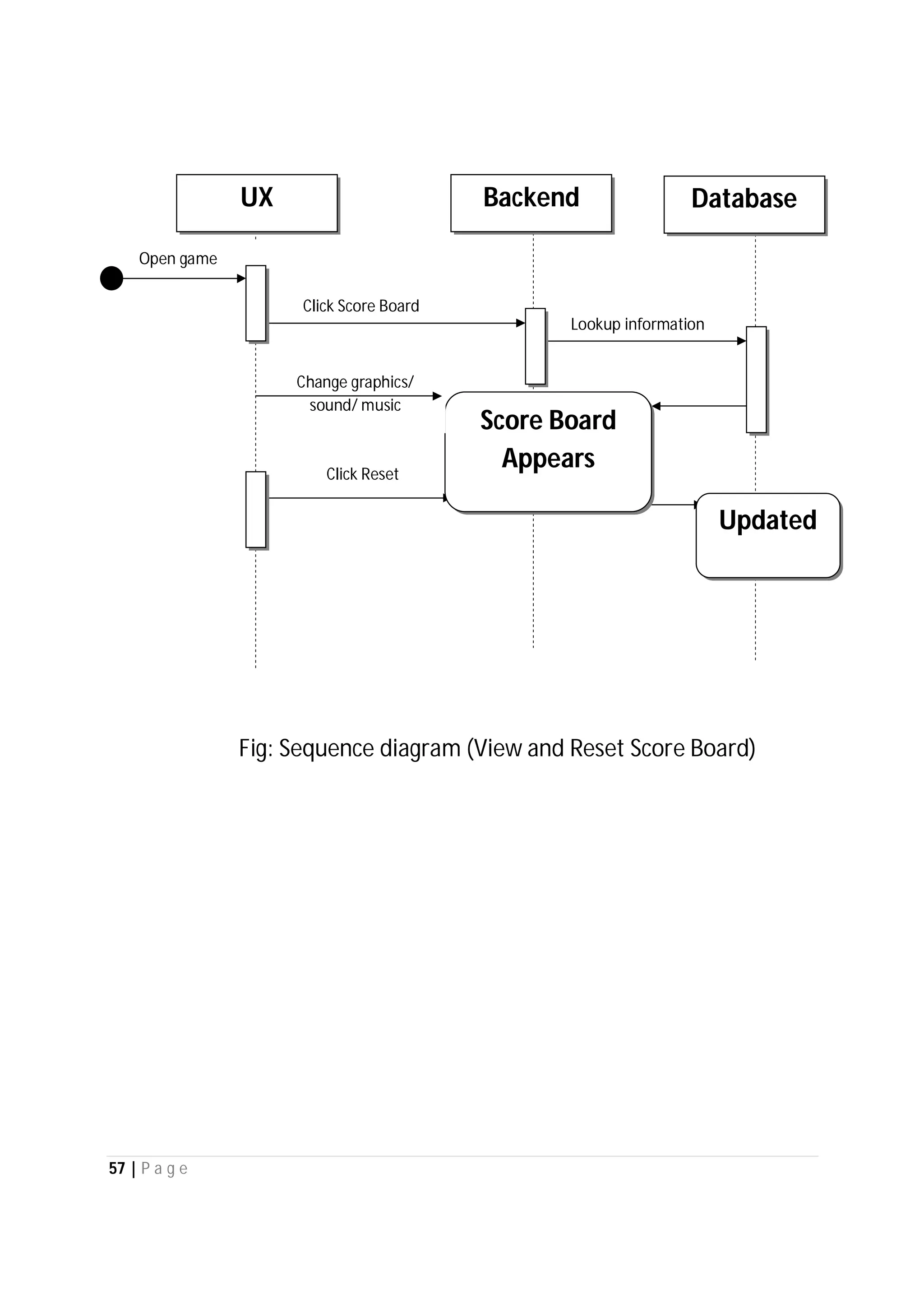
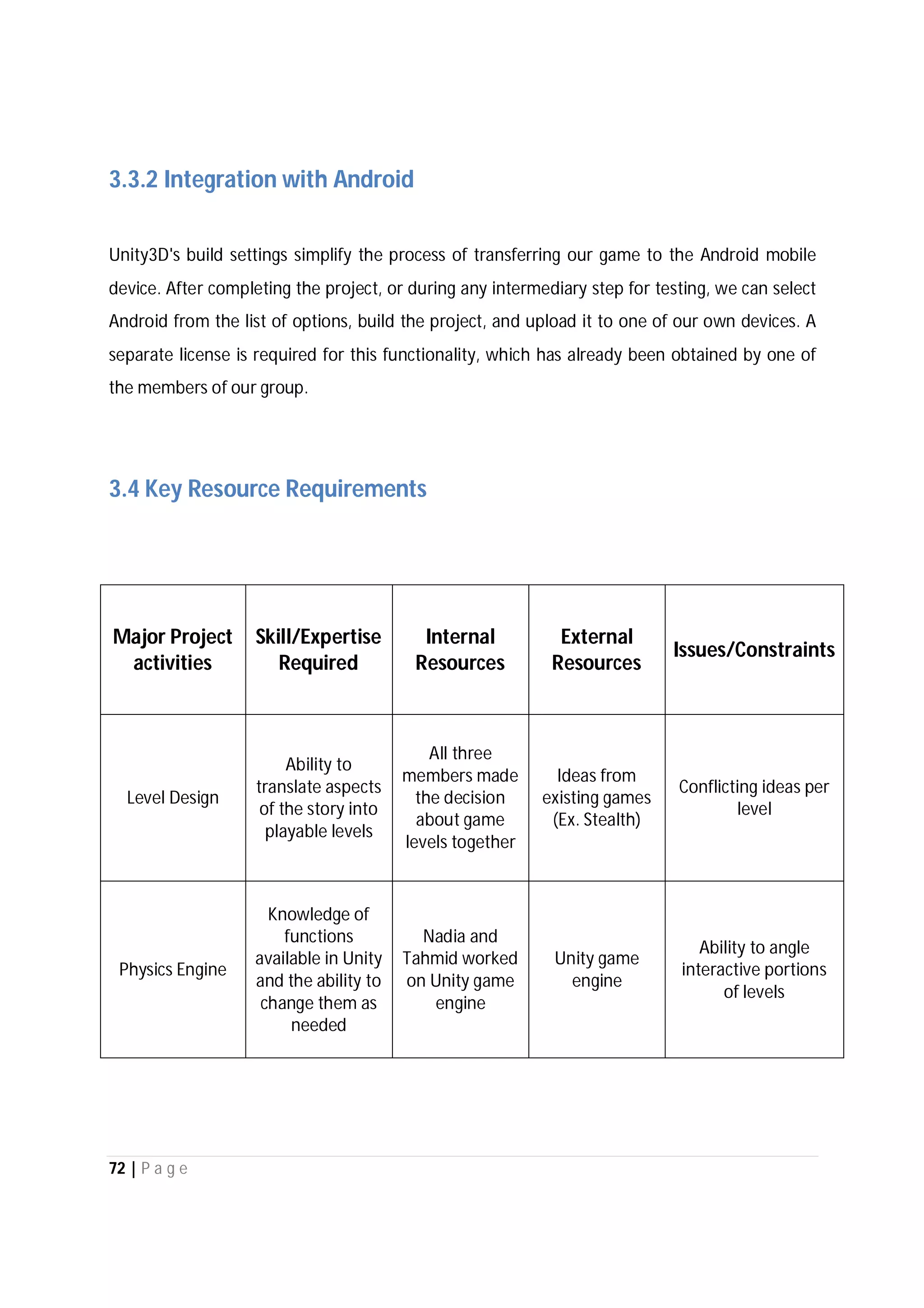
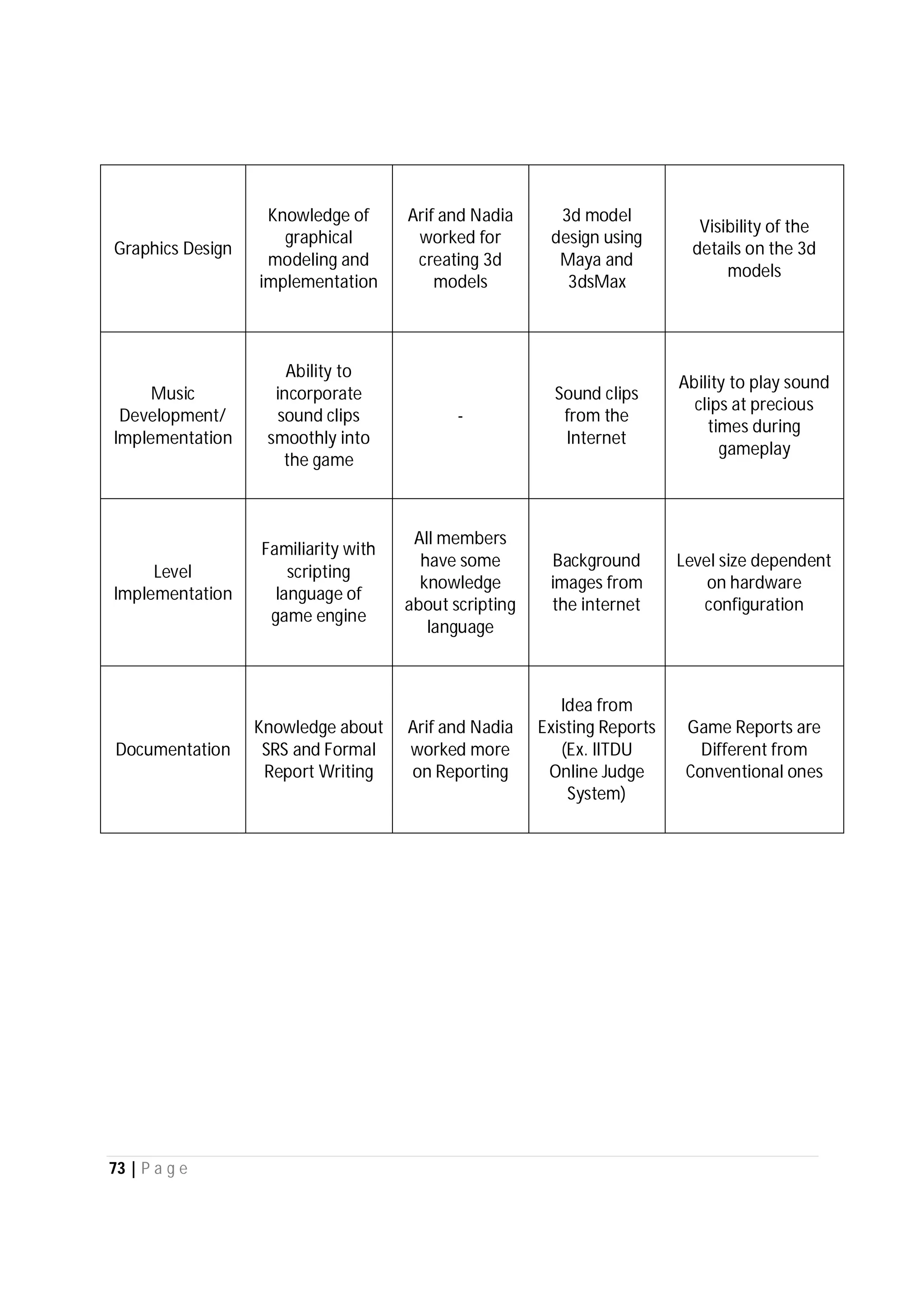
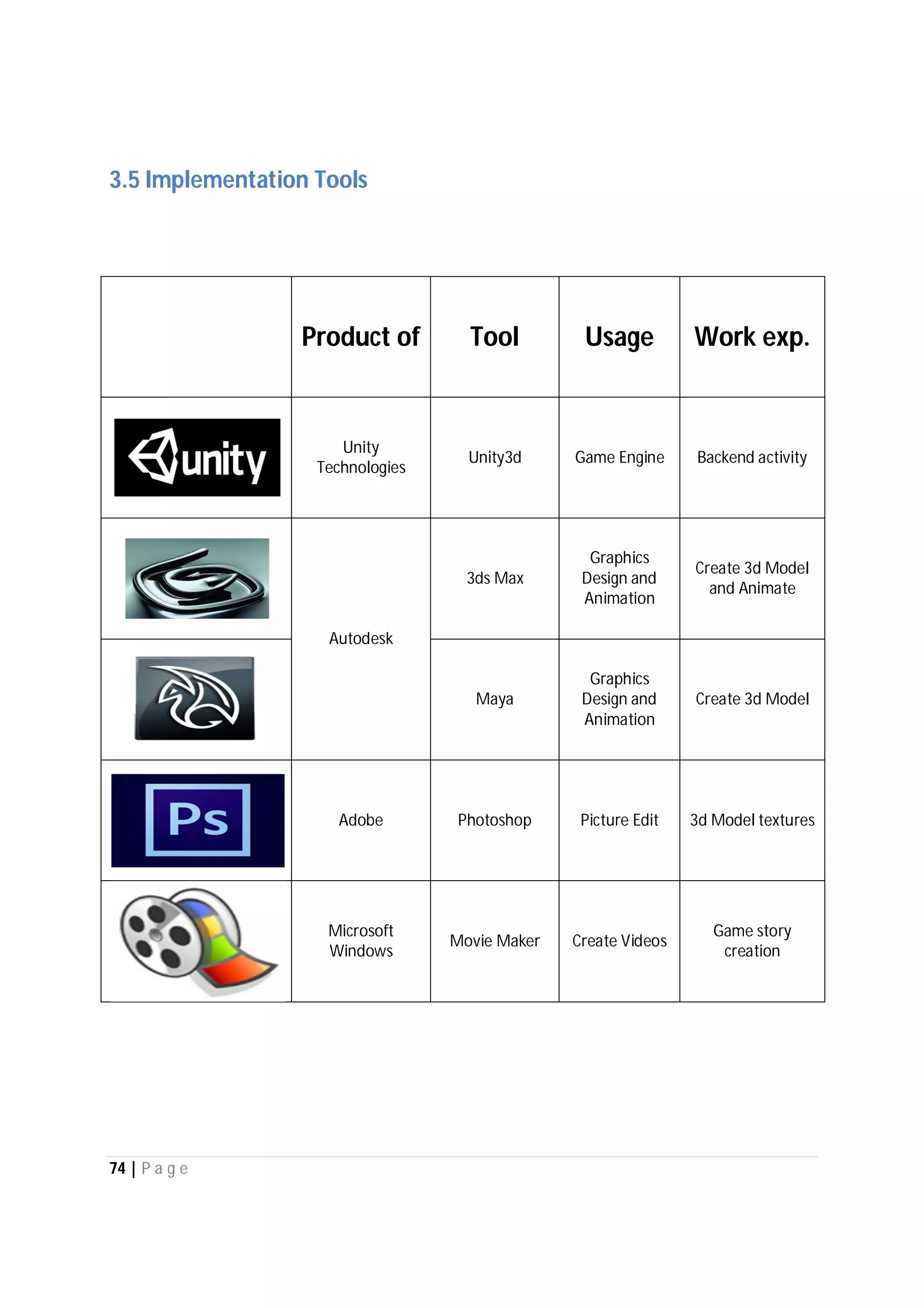
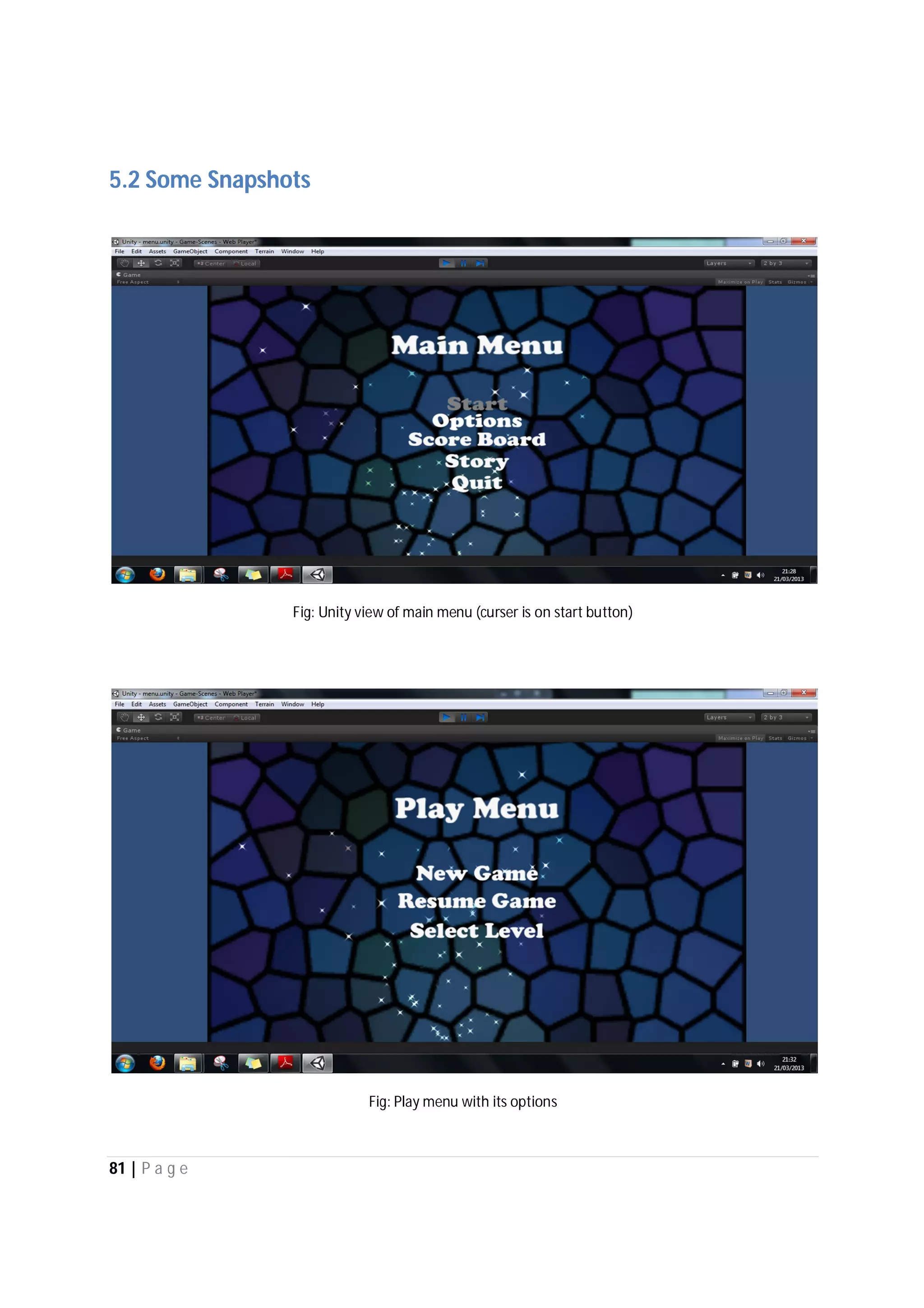
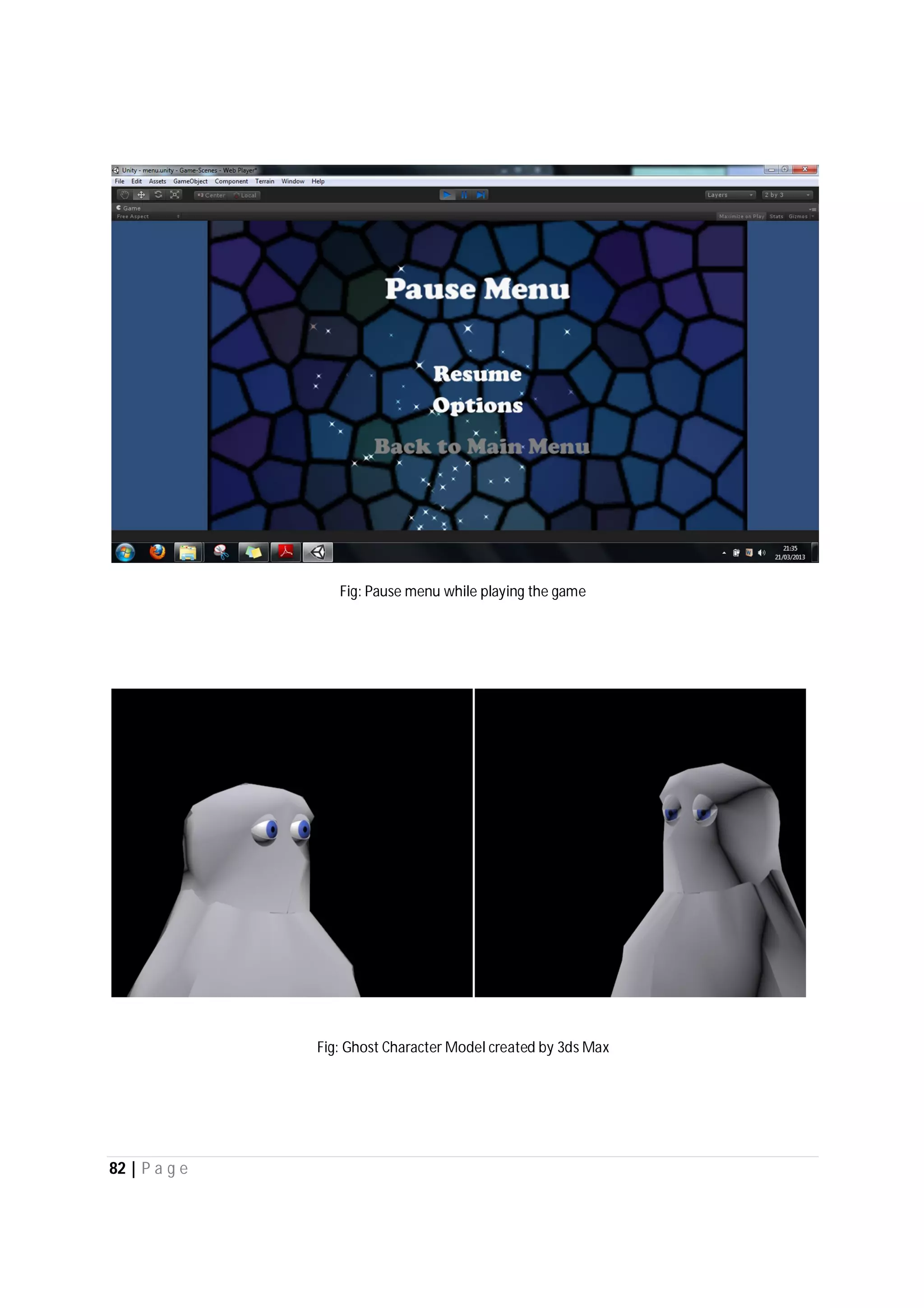
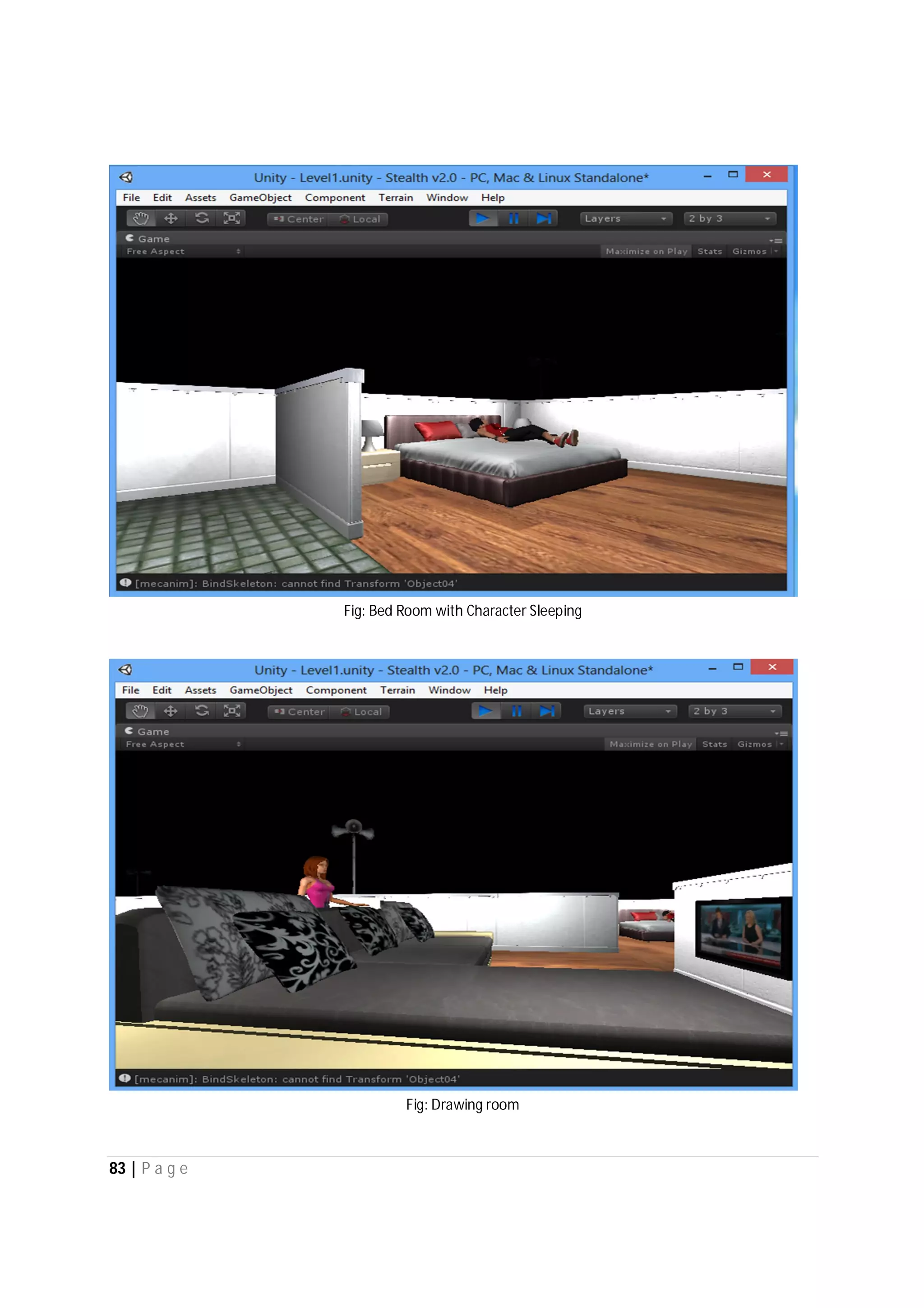
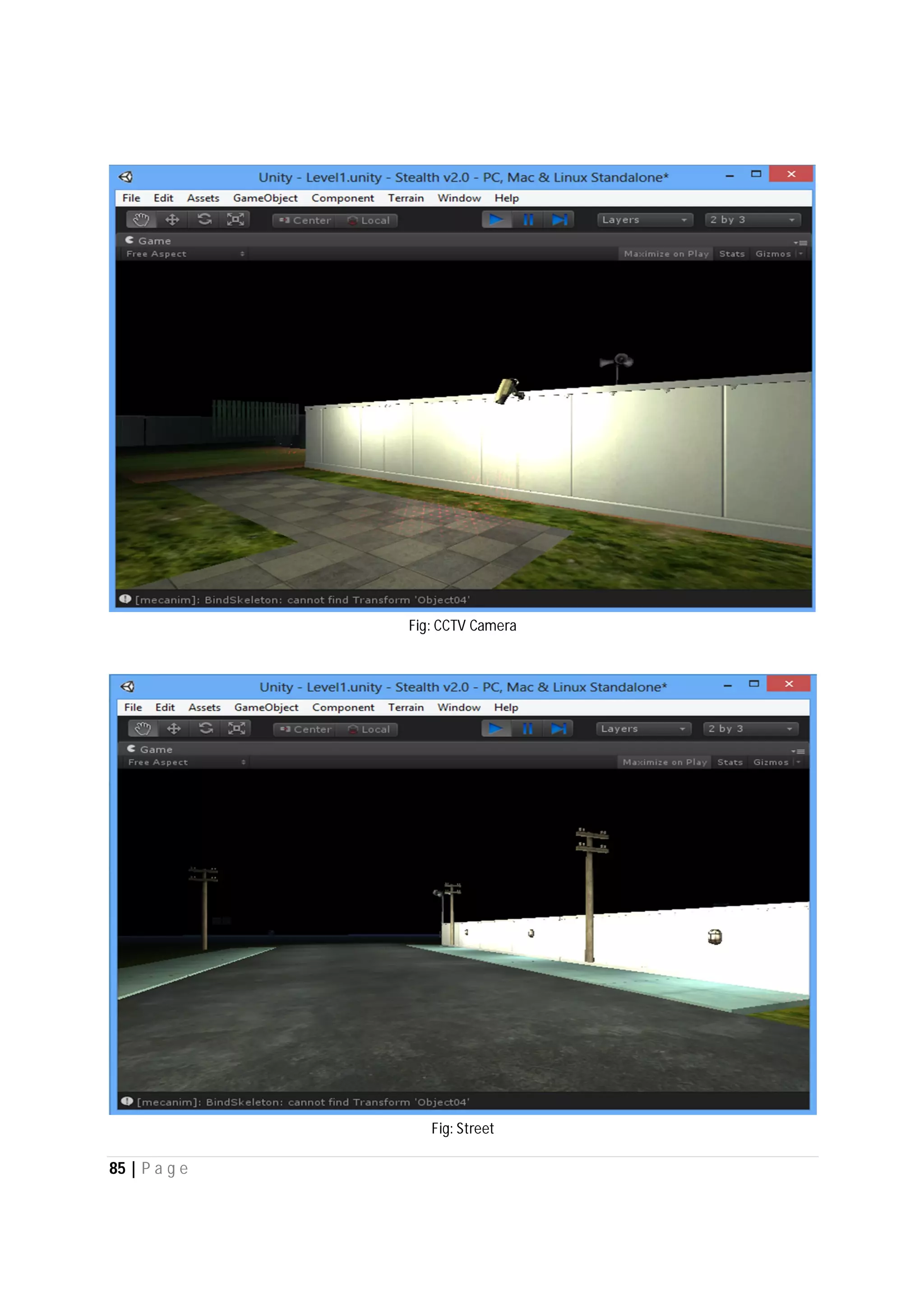
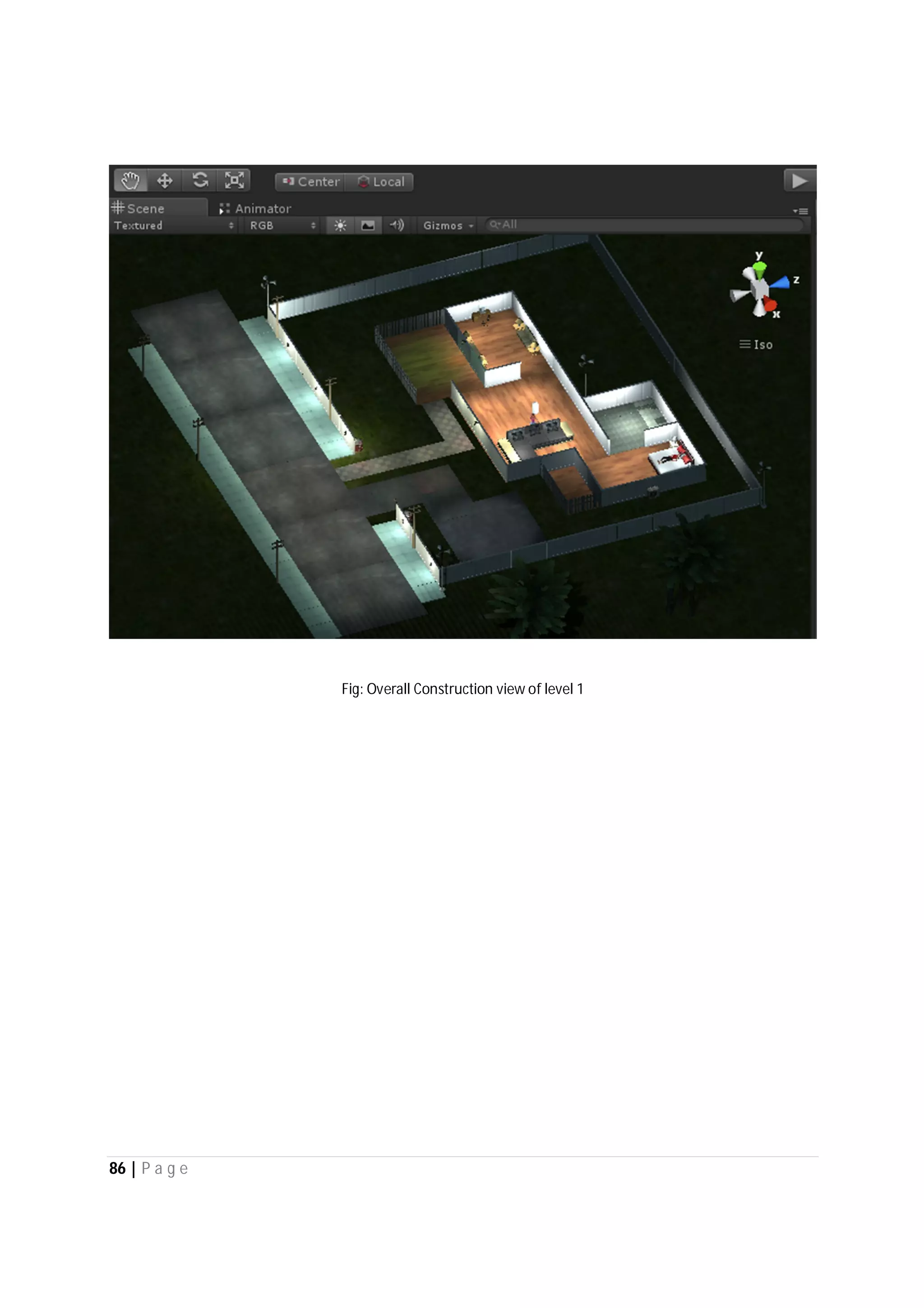
Here are the use case descriptions with activity and swimlane diagrams for the "Play" use case:
Use Case Description:
This use case allows the player to start playing the game. They can either start a new game or resume a previously saved game.
Basic Flow:
1. Player selects "Play" from the main menu
2. System displays option to start new game or resume saved game
3. Player selects "New Game" or "Resume Game"
4. If new game selected, system loads level 1
5. If resume selected, system loads last saved game state
Swimlane Diagram:
Player System
| |
|--> Select "Play" |