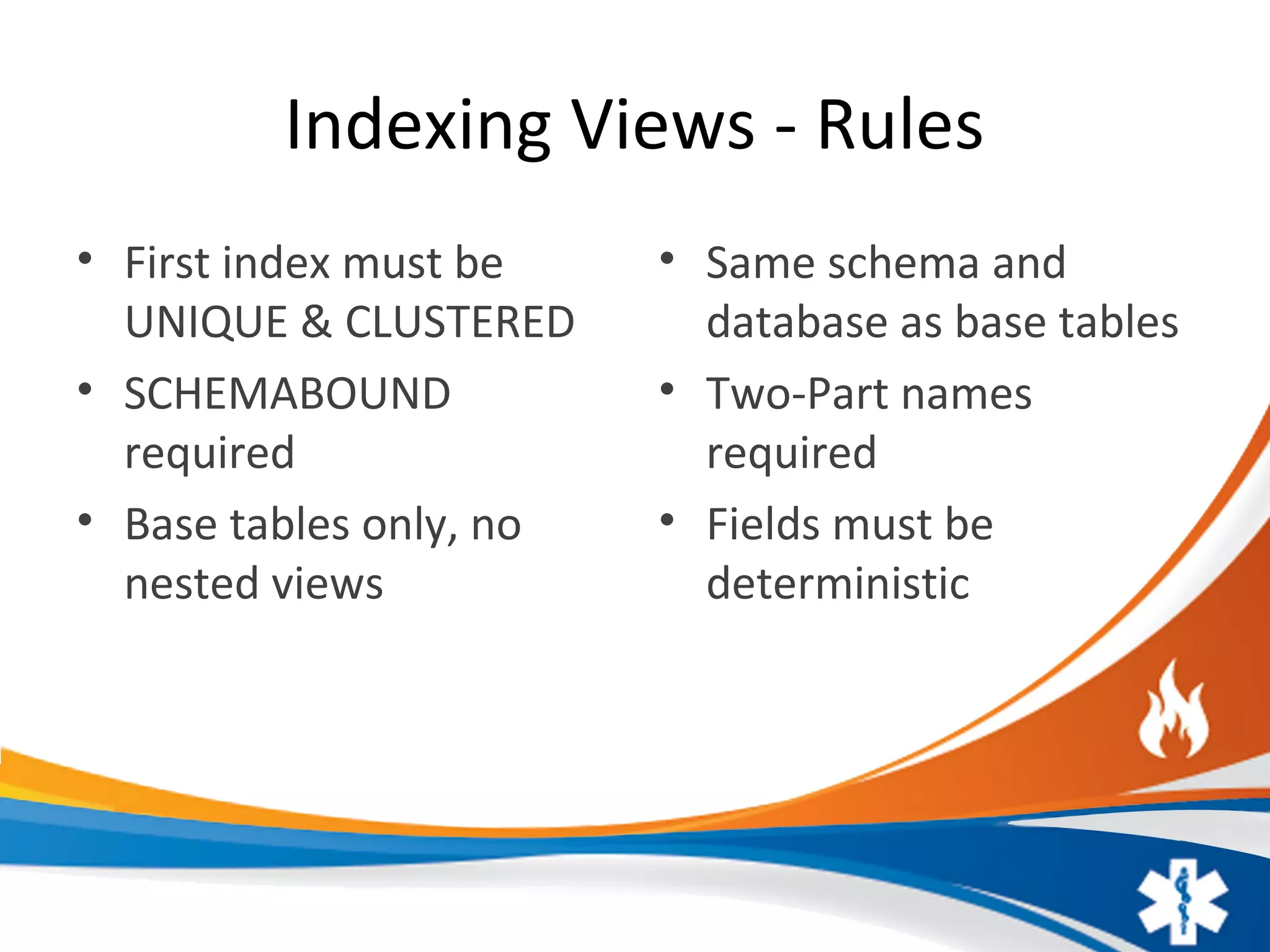
The presentation by Aaron Buma focuses on database views, highlighting their definitions, options, and data manipulation techniques. It discusses the characteristics of views, including their ability to serve as virtual tables, available options like encryption and schemabinding, and the rules for indexing views. The document also emphasizes the limitations of data manipulation on multi-table views and provides resources for further information.