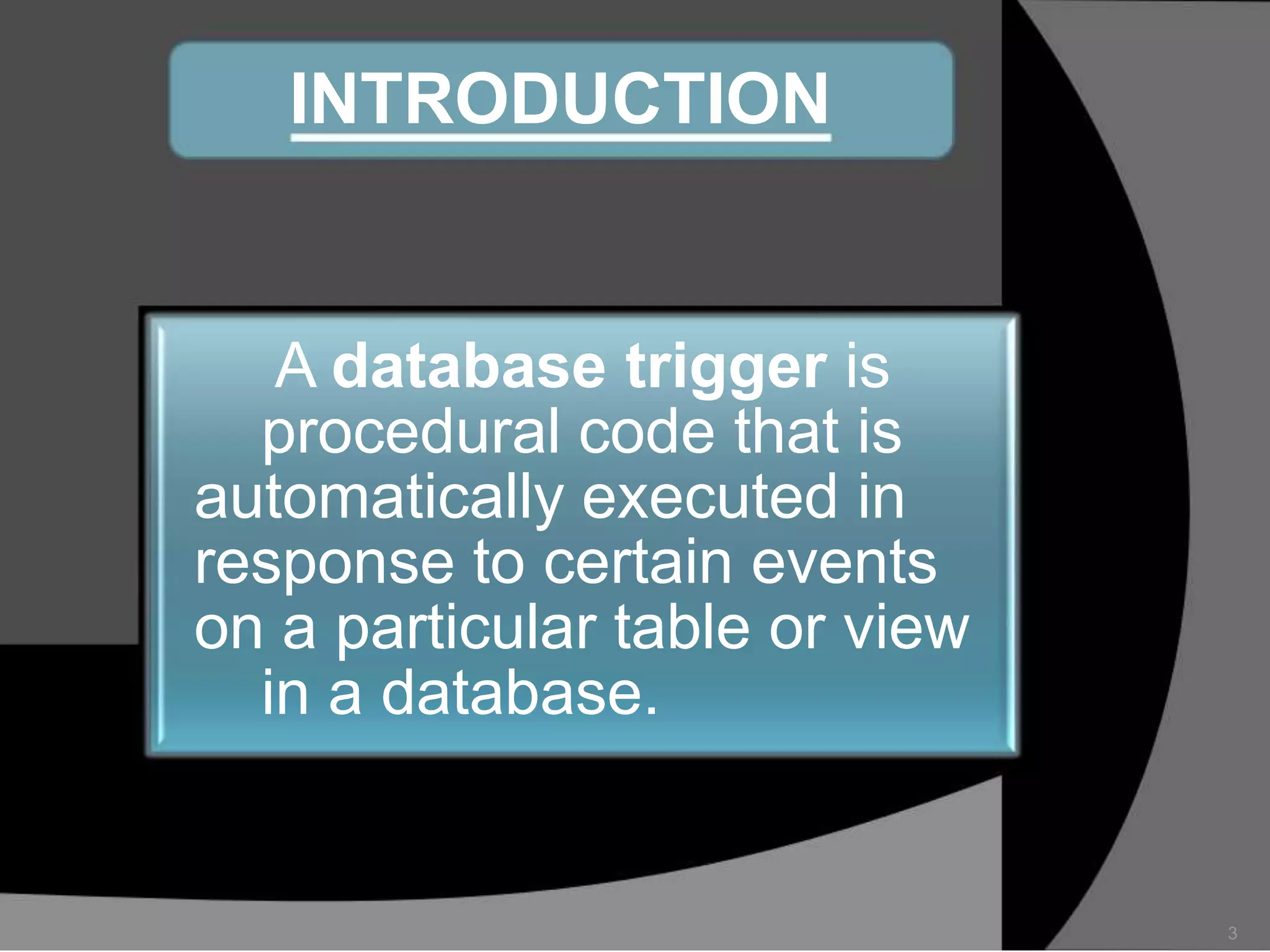
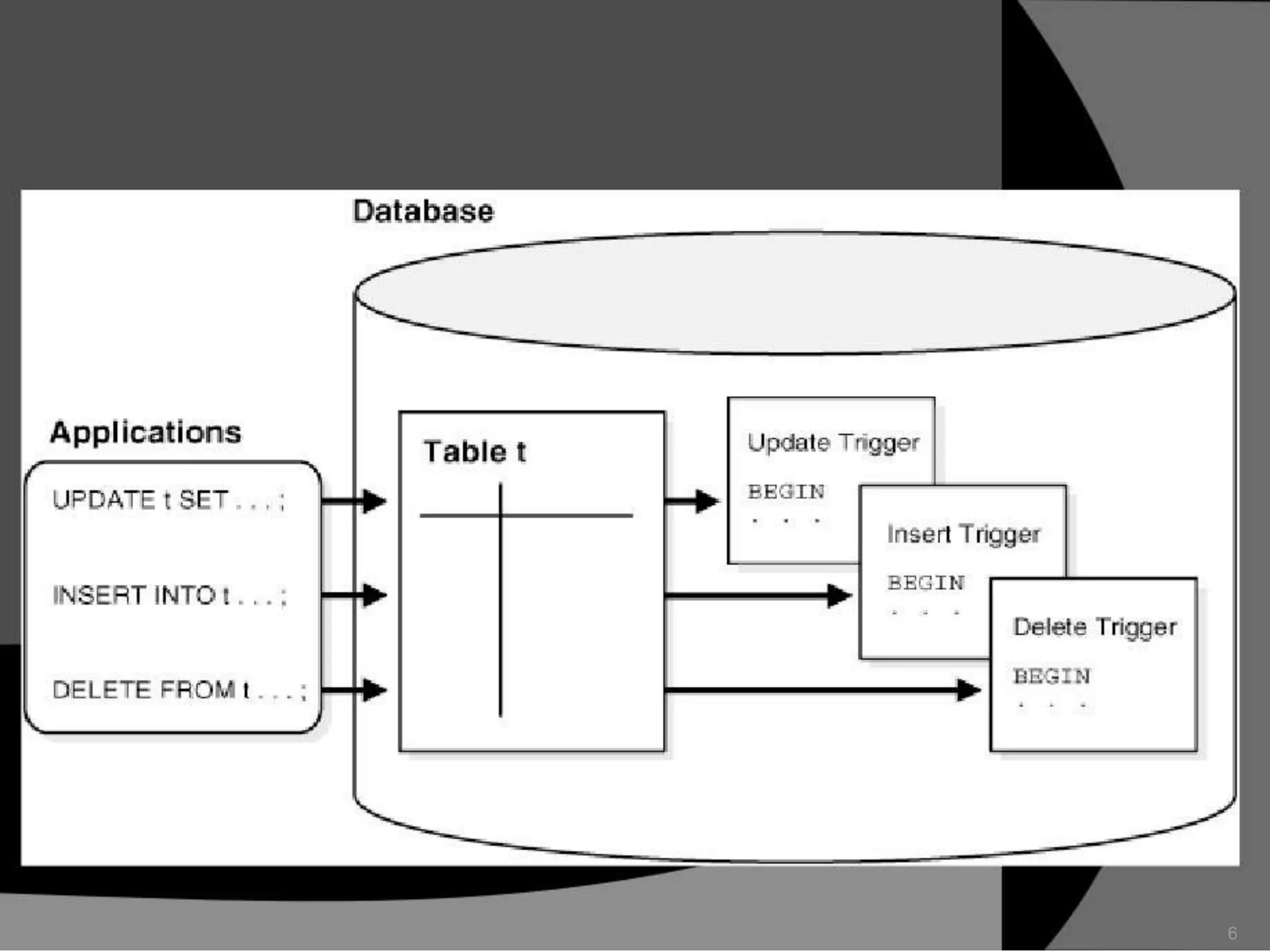
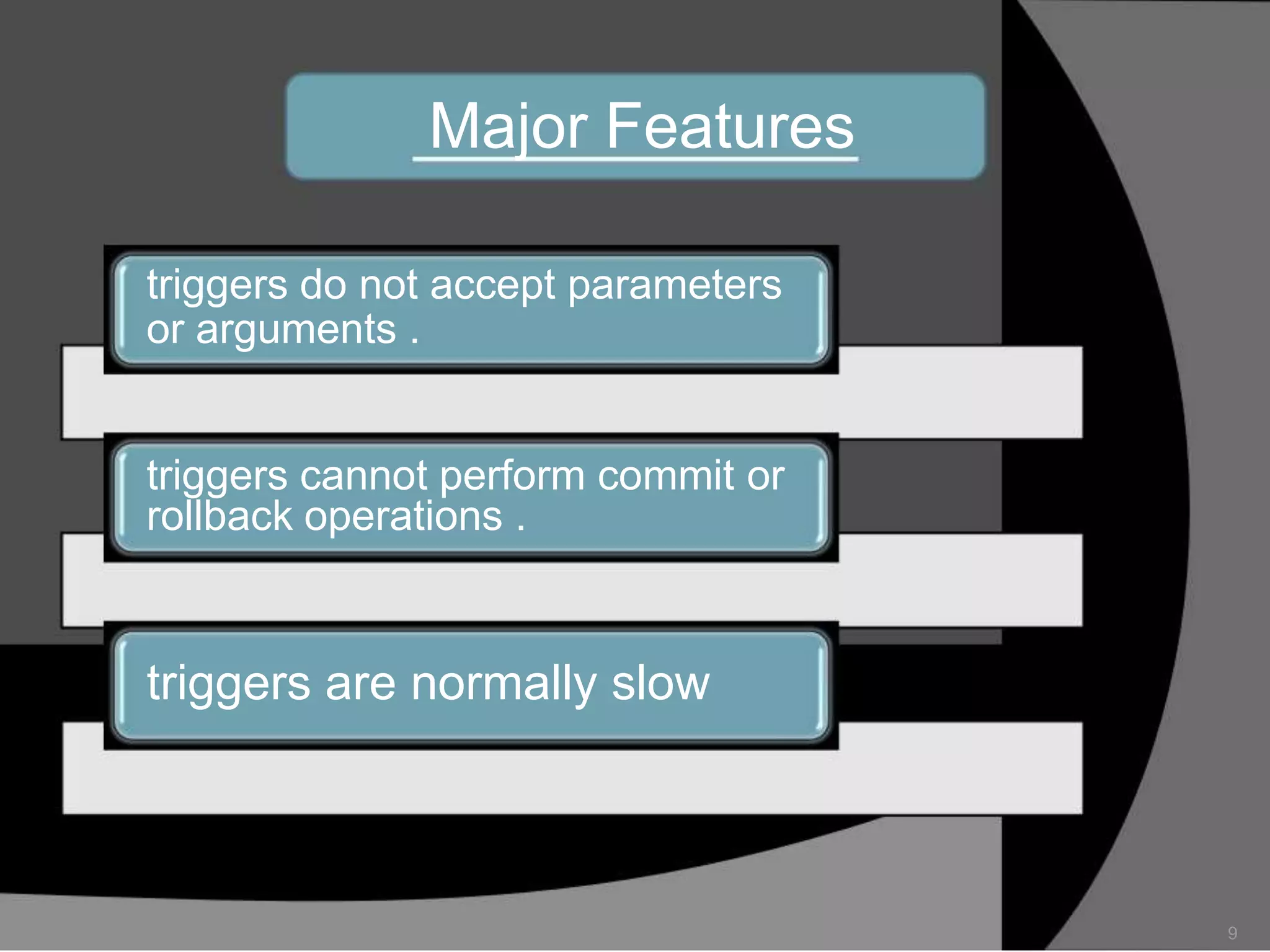
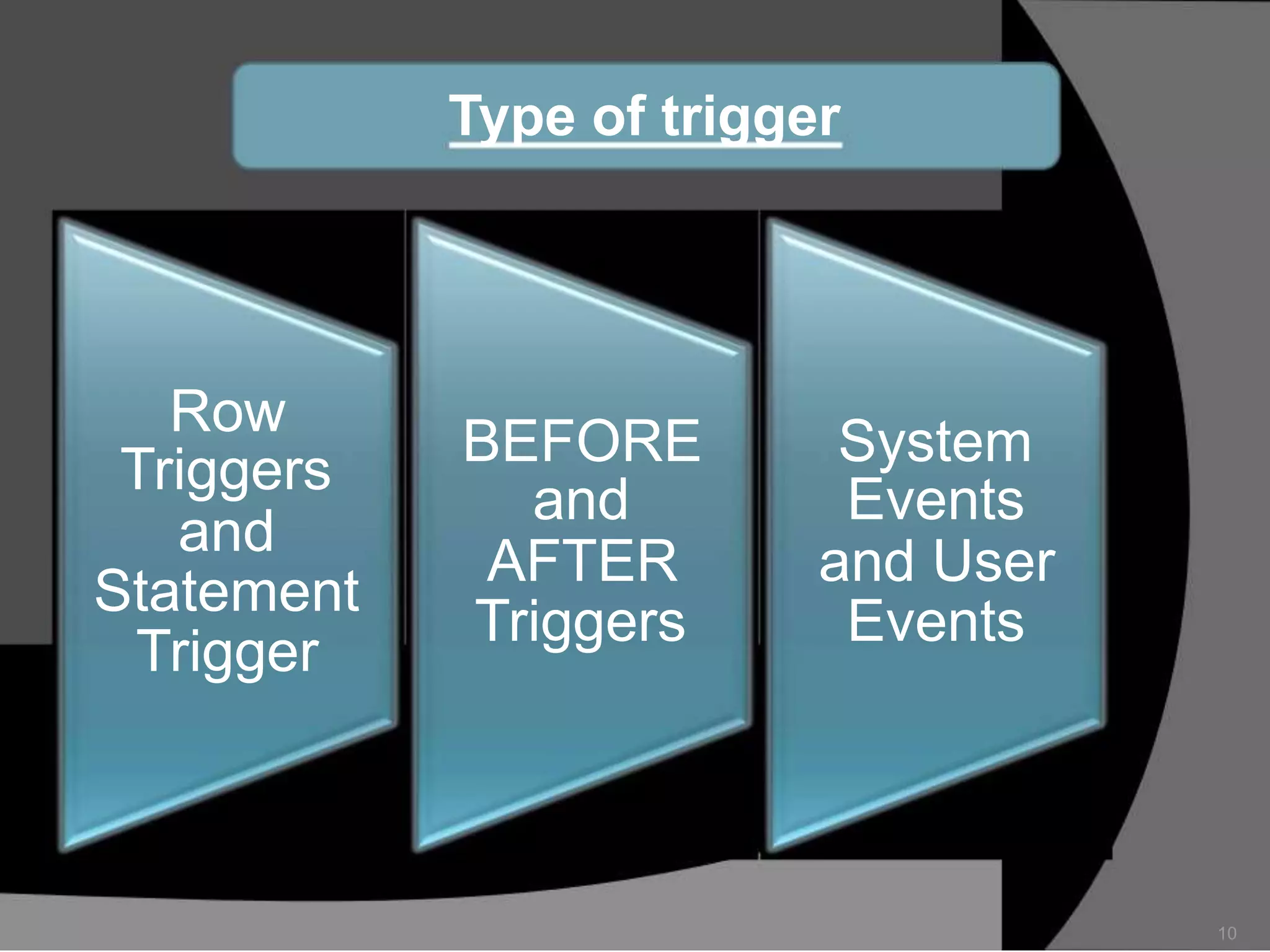
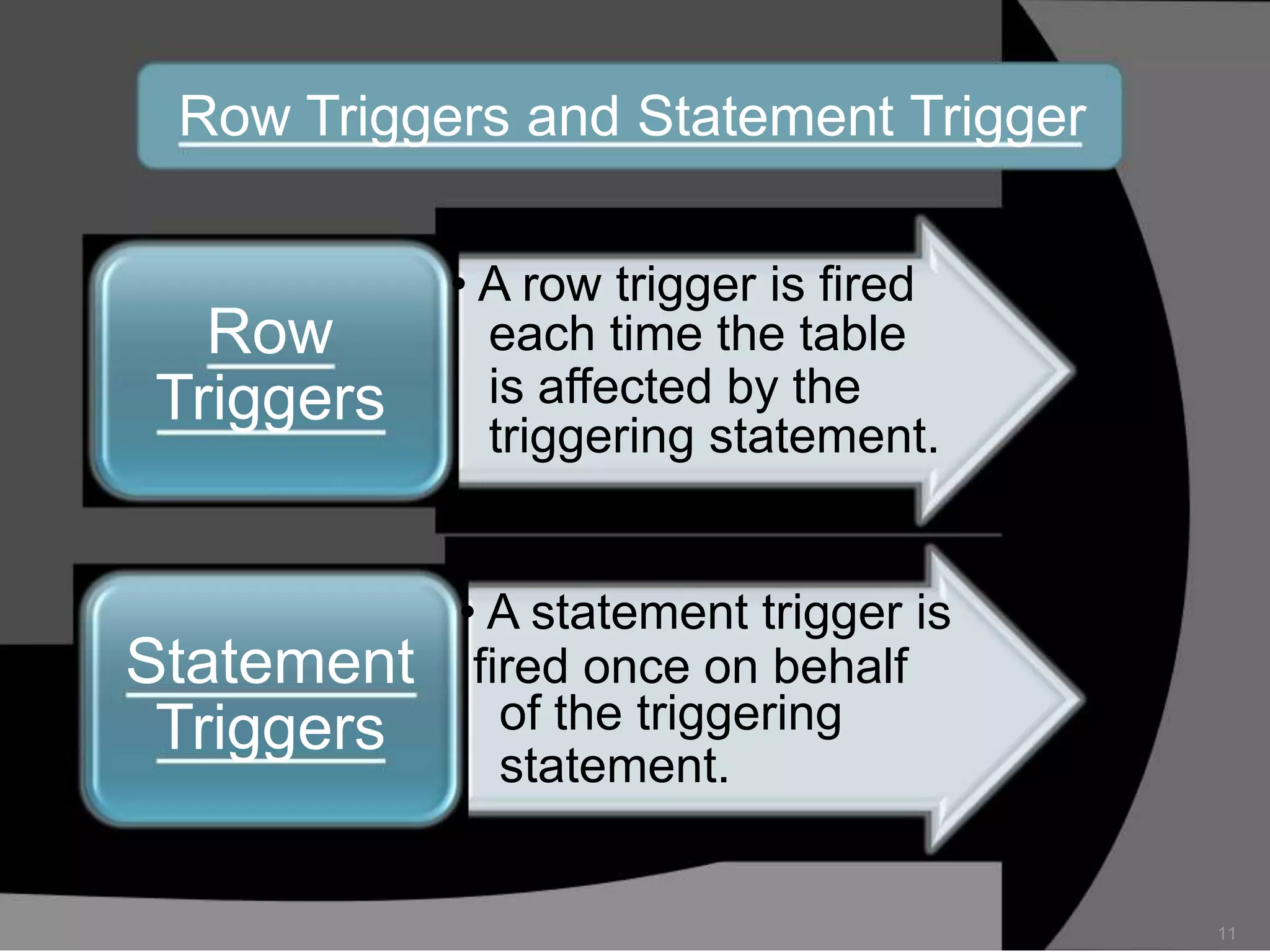
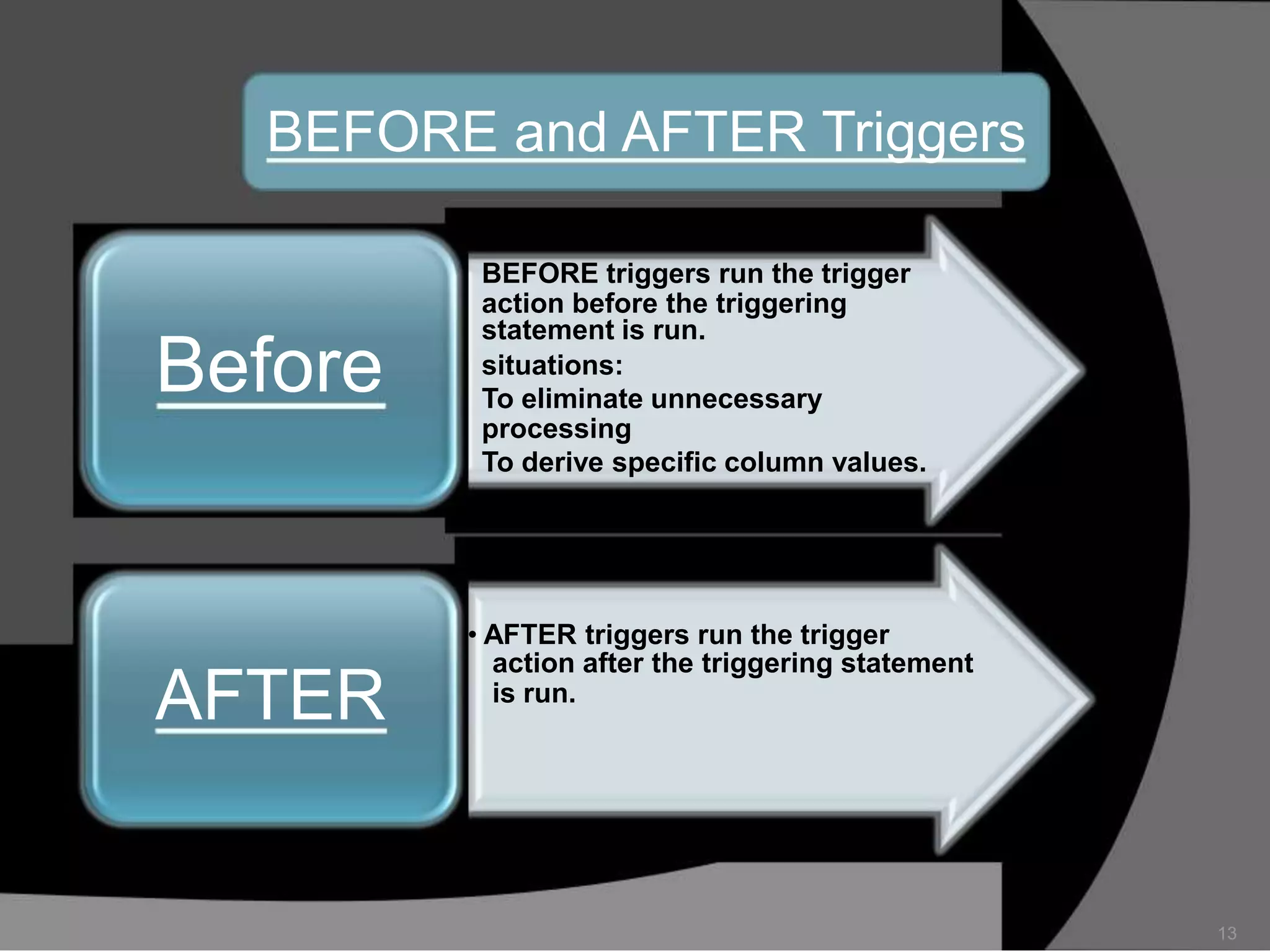
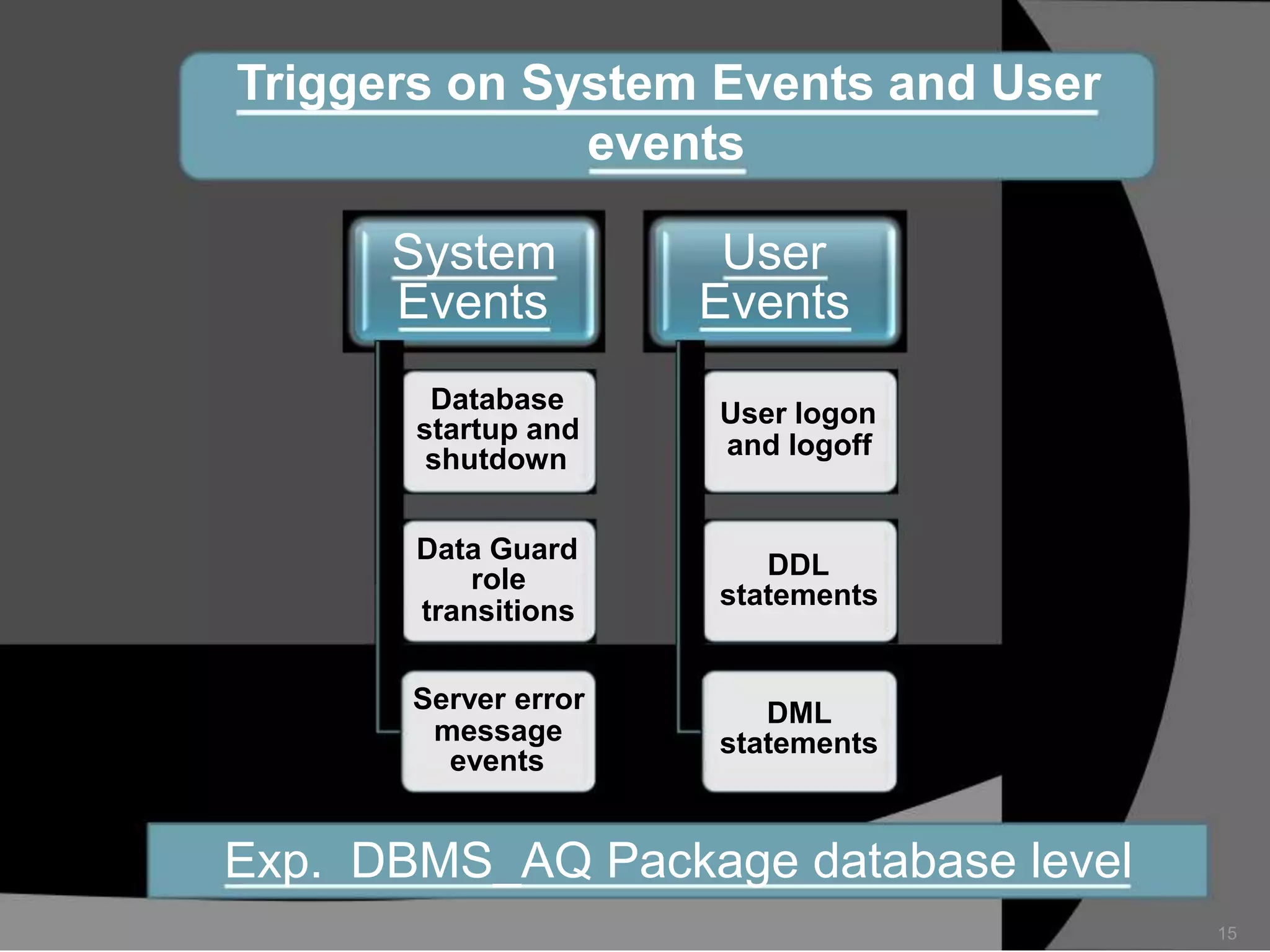
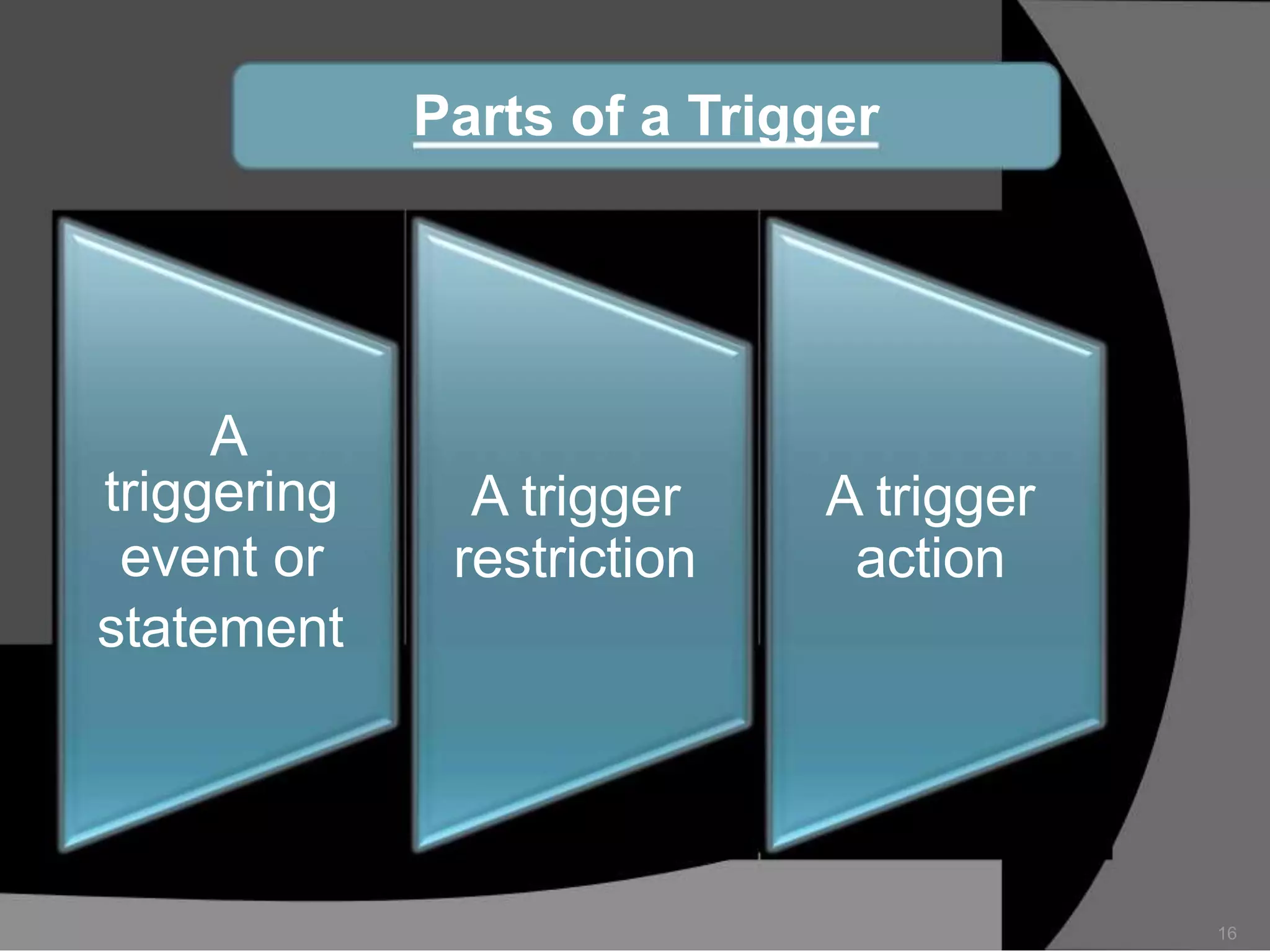
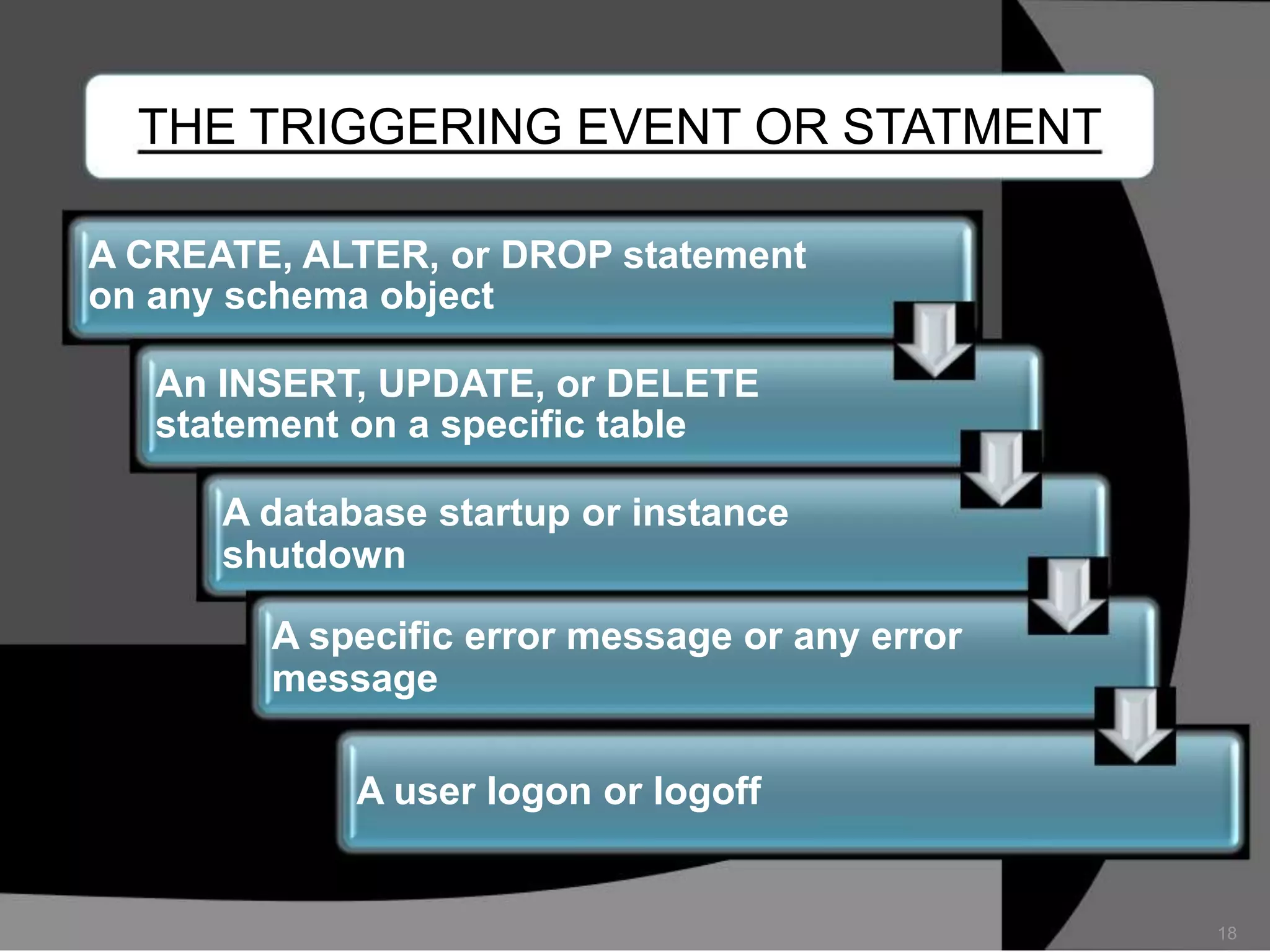
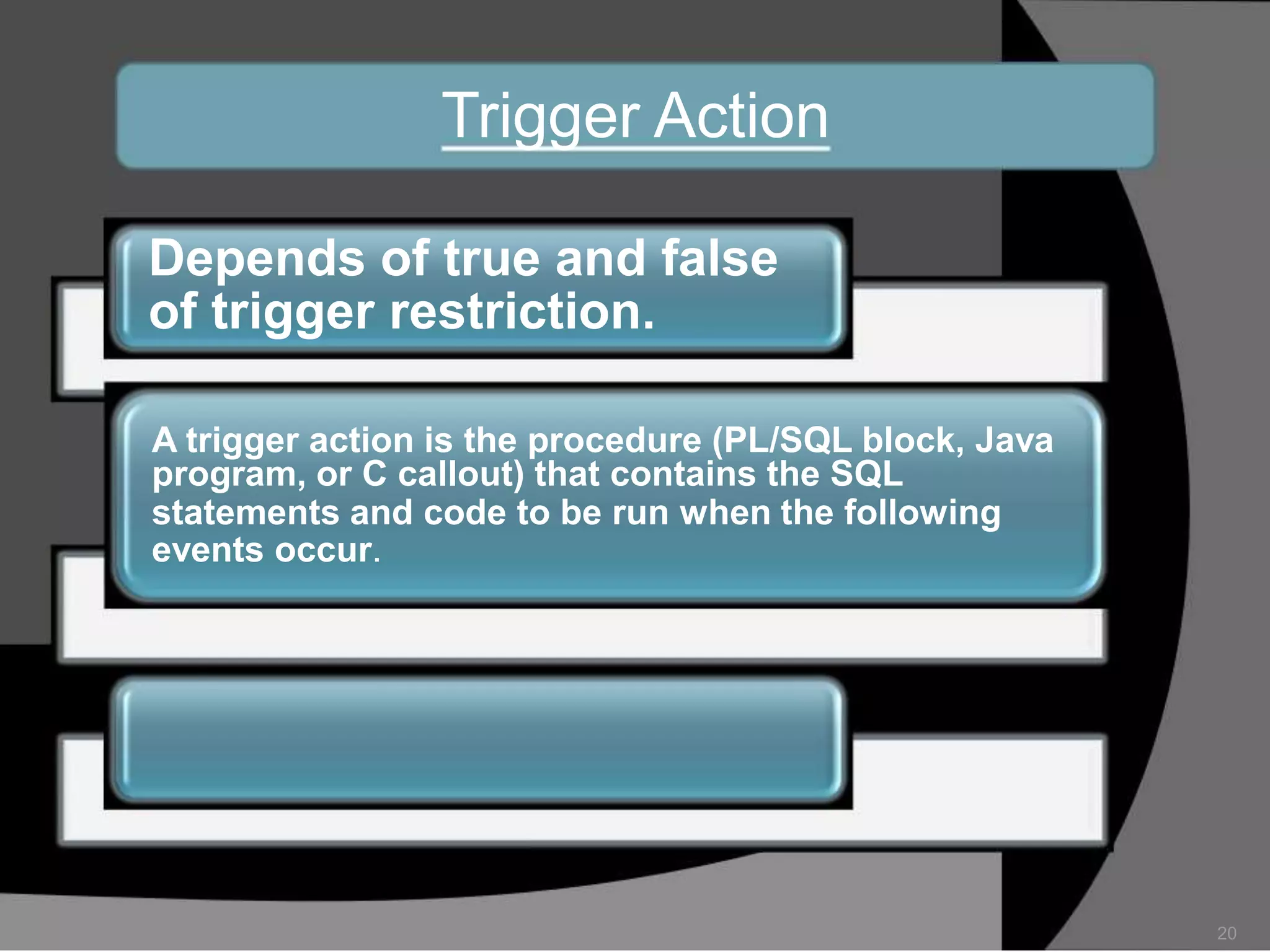
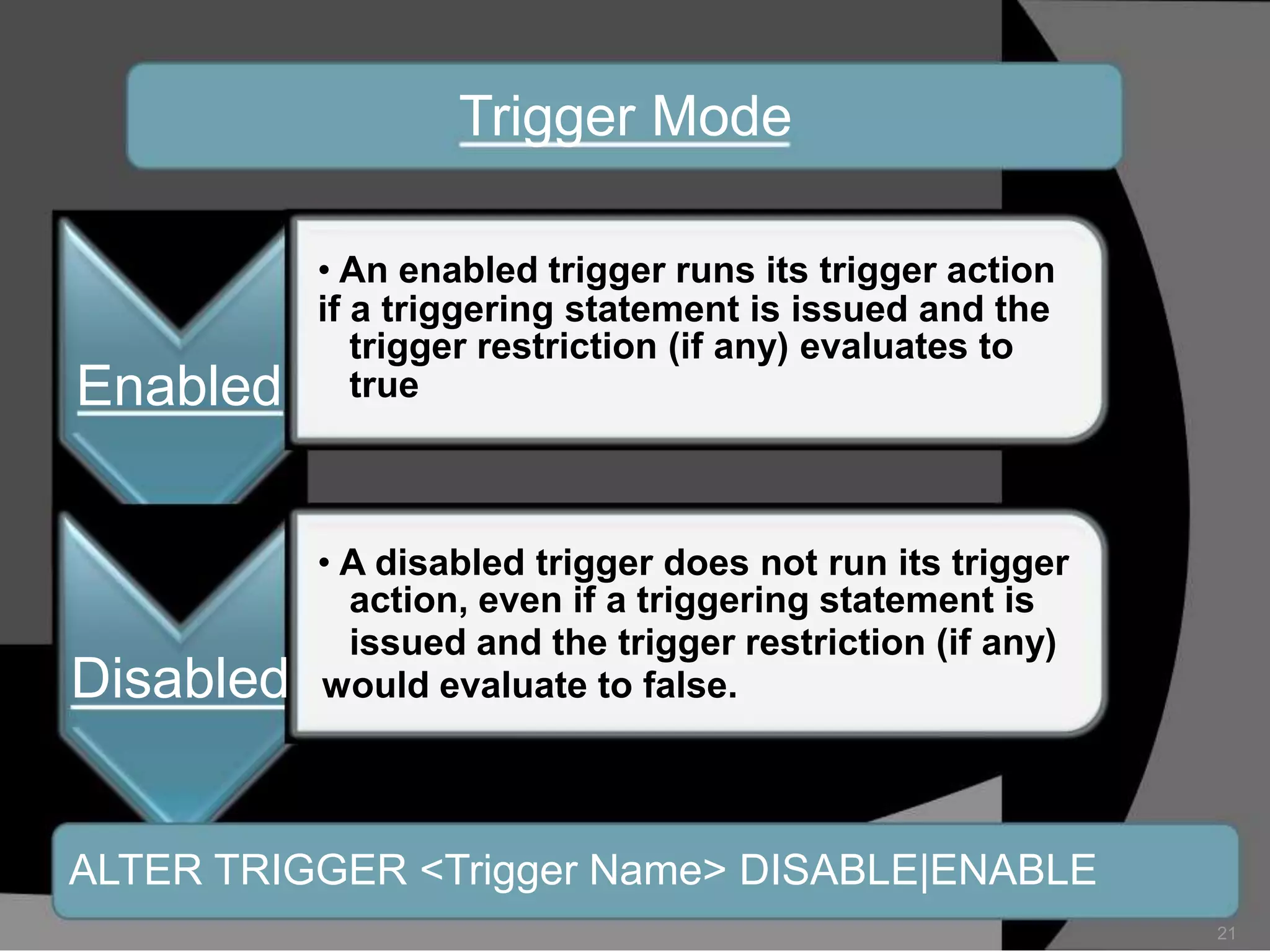
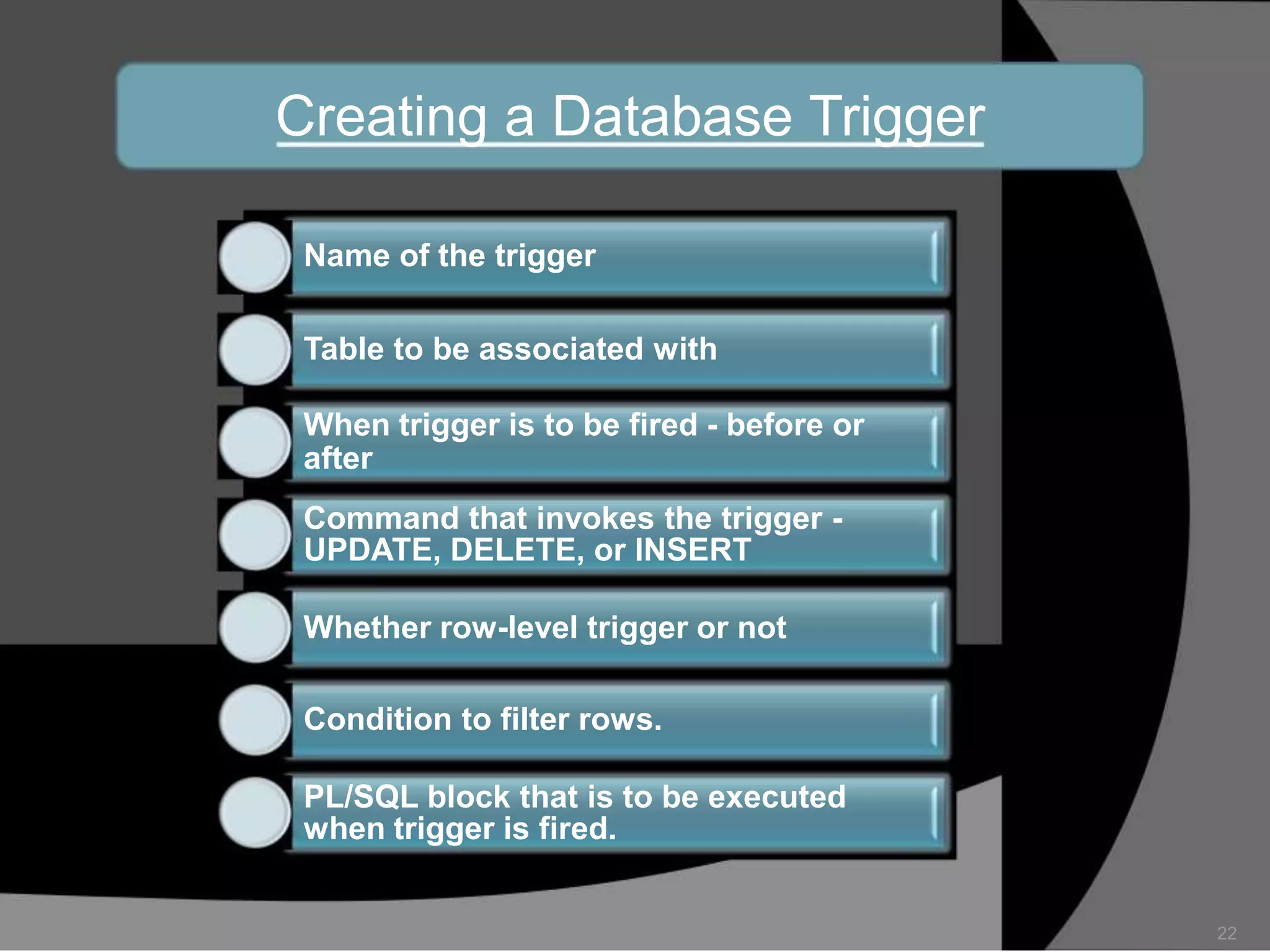
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on database triggers. It defines a database trigger as procedural code that is automatically executed in response to certain events on a table or view. It discusses the types of events that can fire a trigger, including DML, DDL, system, and user events. It also outlines the need for triggers to enforce business rules, audit changes, and enhance performance. The document provides details on the major features of triggers, including the different types of triggers based on timing (before and after), scope (row and statement), and triggering event (DML, DDL, system, user). It concludes with an example of the syntax for creating a database trigger.






![General Structure
CREATE [OR REPLACE]
TRIGGER trigger_name
BEFORE (or AFTER)
INSERT OR UPDATE [OF COLUMNS] OR DELETE
ON tablename
[FOR EACH ROW [WHEN (condition)]]
BEGIN
END;
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kuldeepseminar-131224130421-phpapp02/75/trigger-dbms-19-2048.jpg)
![Trigger Syntax
CREATE TRIGGER <triggerName>
BEFORE|AFTER INSERT|DELETE|UPDATE
[OF <columnList>] ON <tableName>|<viewName>
[REFERENCING [OLD AS <oldName>] [NEW AS
<newName>]]
[FOR EACH ROW] (default is “FOR EACH
STATEMENT”)
[WHEN (<condition>)]
<PSM body>;
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kuldeepseminar-131224130421-phpapp02/75/trigger-dbms-20-2048.jpg)


