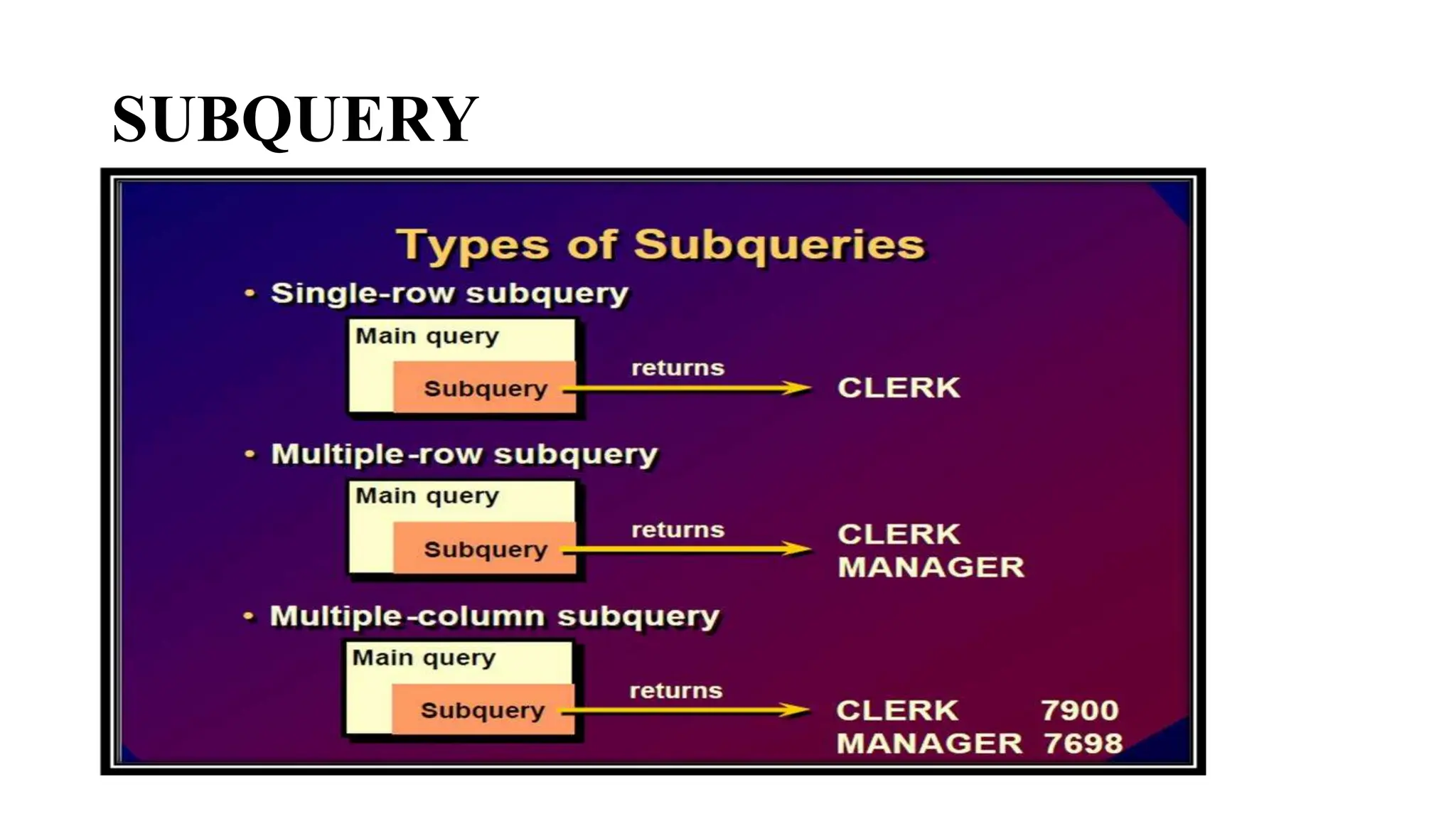
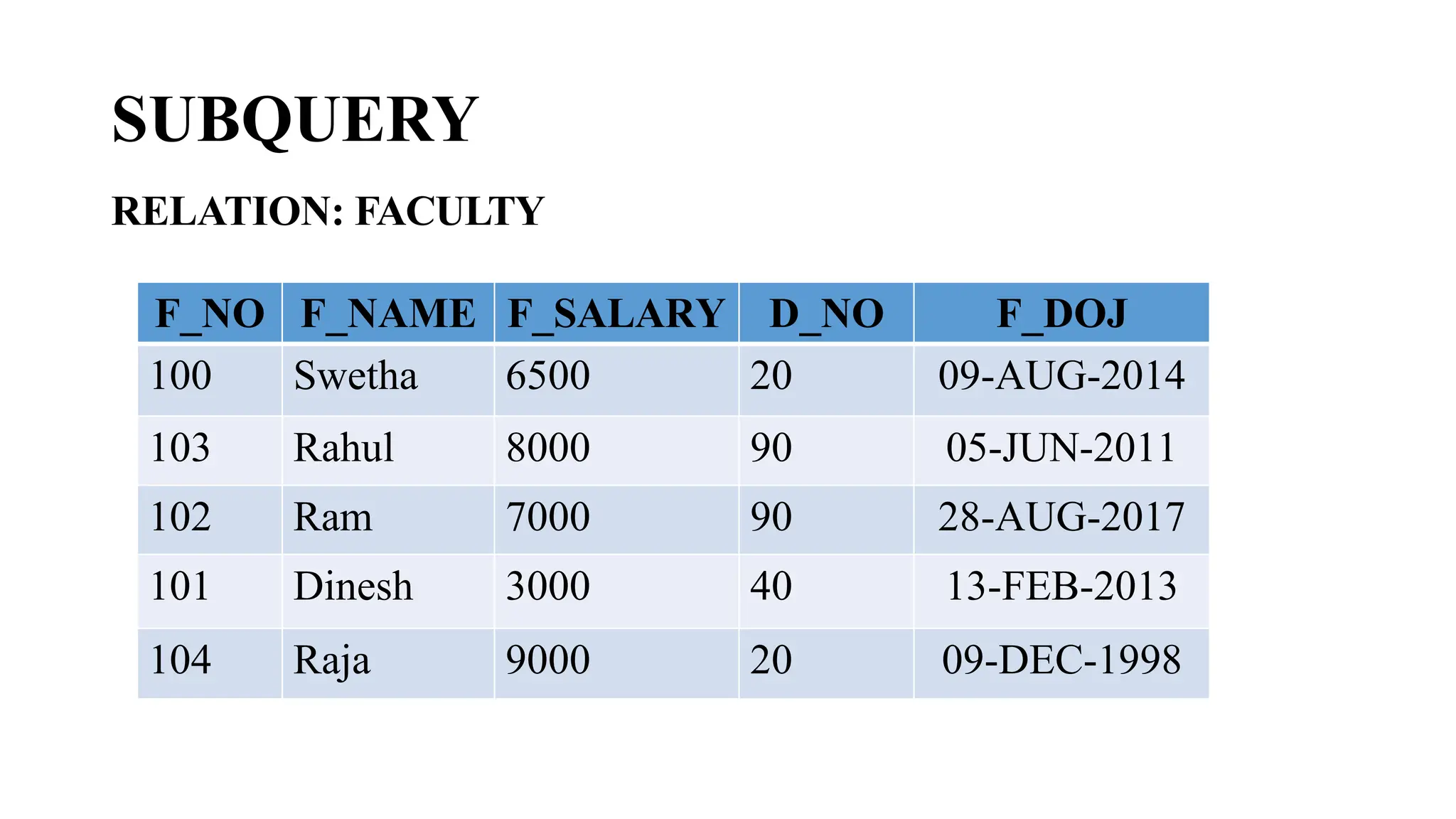
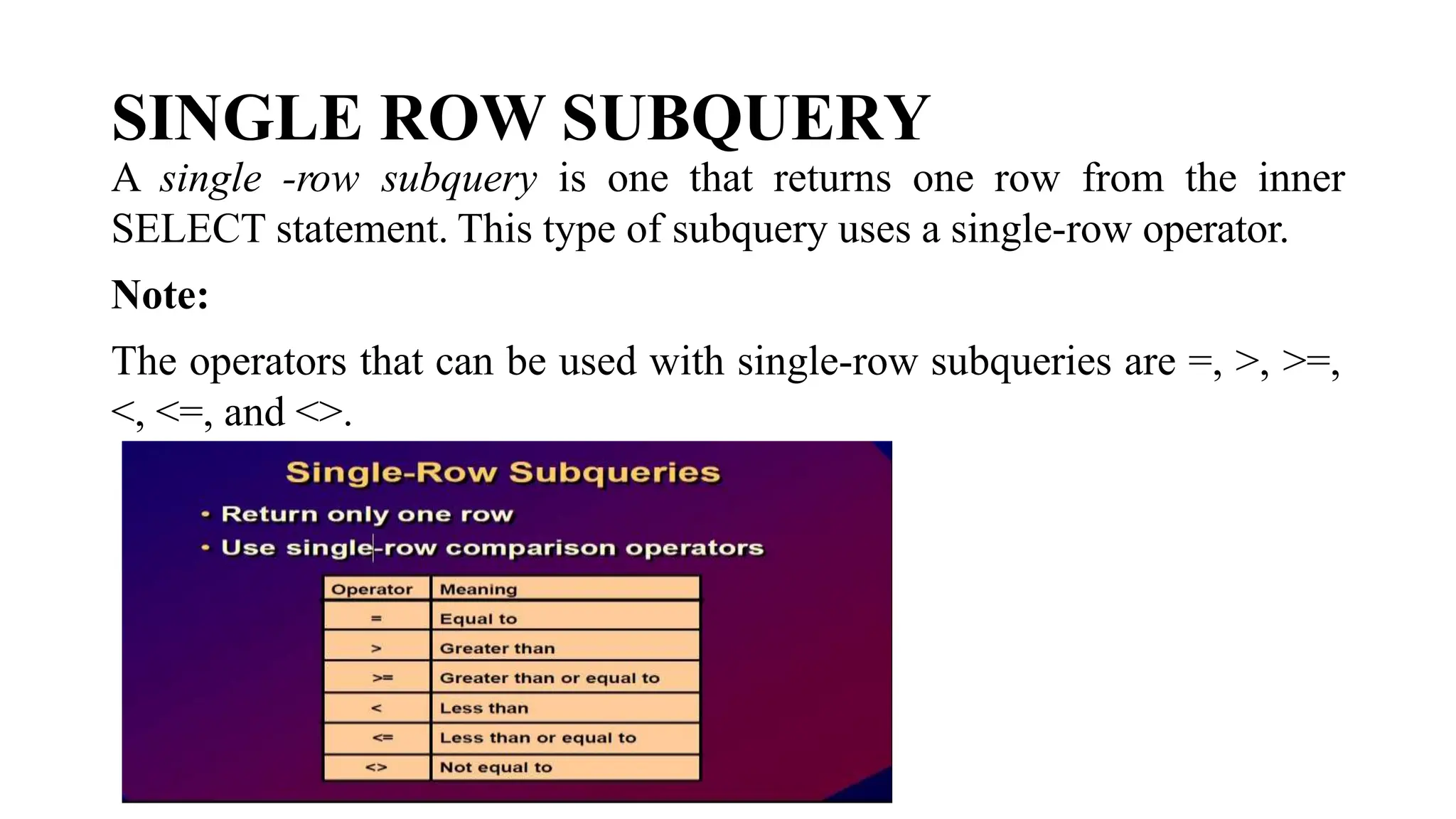
A subquery is a query nested within another query. The inner subquery executes first and its results are used by the outer query. There are different types of subqueries including single-row, multiple-row, multiple-column, and correlated subqueries. Single-row subqueries use operators like = and > to compare a single result, while multiple-row subqueries use operators like IN, ALL, ANY to handle multiple returned rows. Correlated subqueries are executed once for each row returned by the outer query, allowing the queries to reference each other.




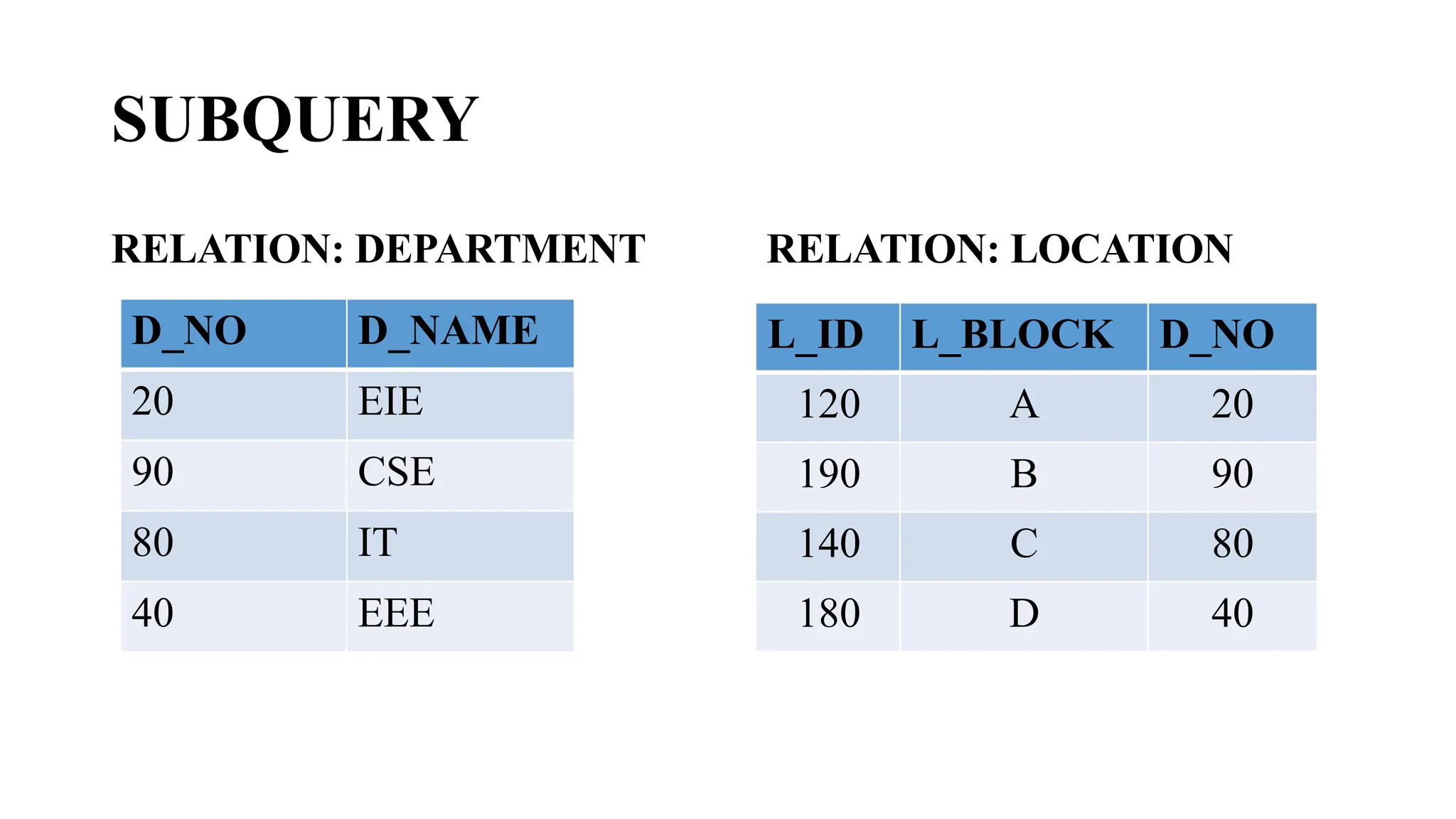



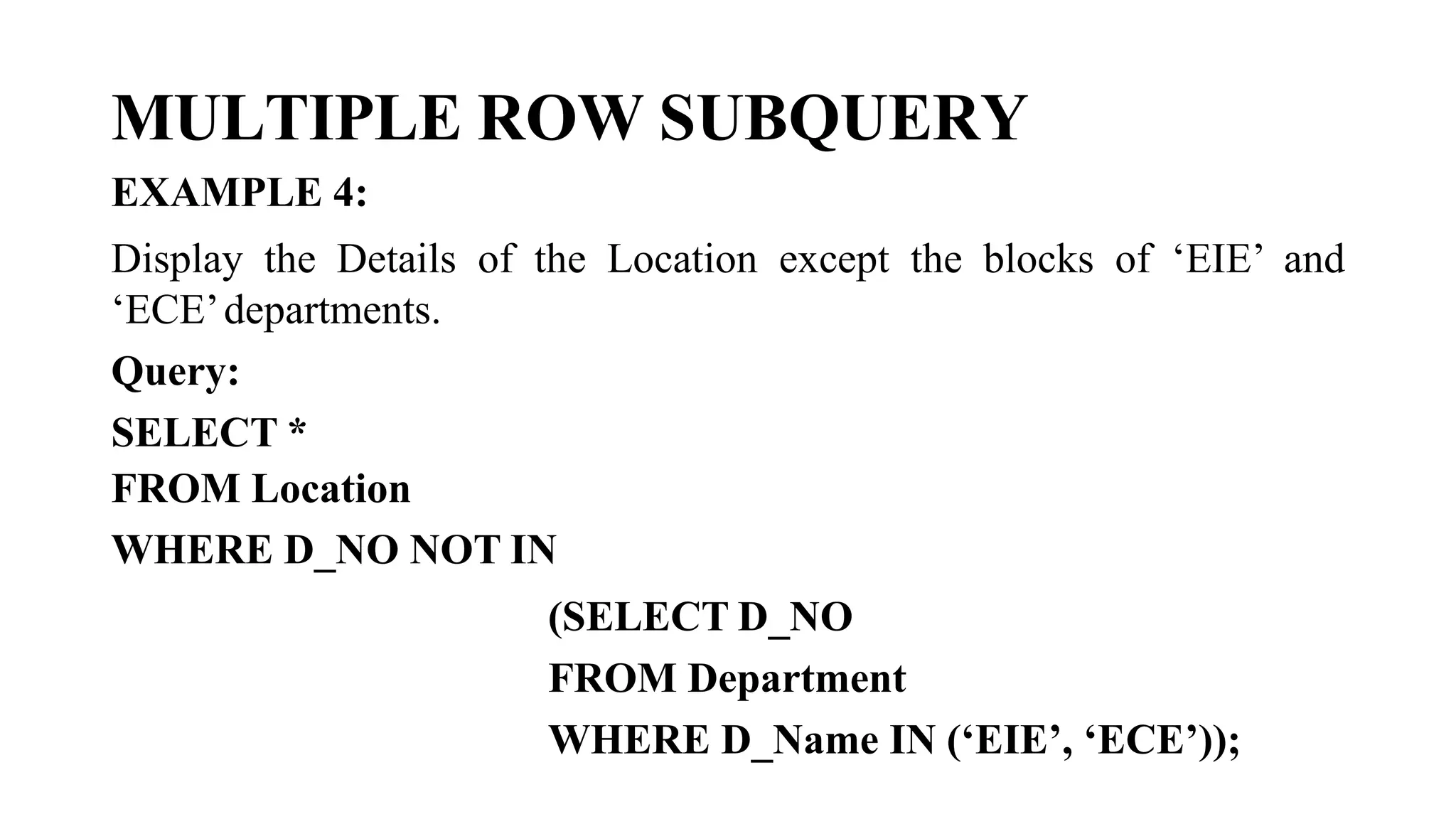
![MULTIPLE ROW SUBQUERY
Multiple-row subqueries are nested queries that can return more than
one row of results to the parent query. Since it returns multiple rows, it
must be handled by set comparison operators (IN,ALL, ANY).
Usage of Multiple Row operators
• [>ALL] More than the highest value returned by the subquery
• [<ALL] Less than the lowest value returned by the subquery
• [<ANY] Less than the highest value returned by the subquery
• [>ANY] More than the lowest value returned by the subquery
• [=ANY] Equal to any value returned by the subquery (same as IN)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/subqueries-231102165202-90e6b2d8/75/SUBQUERIES-pptx-12-2048.jpg)