Spring Framework & MyBatis_ 스프링프레임워크 & 마이바티스
☆ 무.료 강의자료 제공 中 ★
♡ 좋아요! 하고 더많은 자료 받아보세요 :) :) :) :) !!!!
[ 제 3장 ] _ Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
[ 목 차 ]
3.1 AOP 개요
3.2 AOP HelloWorld
3.2.1 AOP HelloWorld(프로그래밍을 통한 AOP
3.2.2 AOP HelloWorld(XML Schema Based AOP 구현)
3.2.3 HelloWorld(@AspectJ Annotation Based AOP 구현)
3.2.4 생성자 주입(Constructor Injection) – 어노테이션 기반
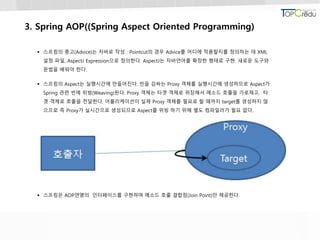
3.3 AOP 충고(Advice)
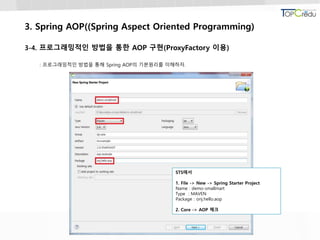
3.4 프로그래밍적인 방법을 통한 AOP 구현 (ProxyFactory 이용)
[#더많은자료, #꿀강의, #꿀강좌, #구로오라클학원 #탑크리에듀]
http://www.topcredu.co.kr/








![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
File -> New -> Spring Legacy Project -> Simple Spring Maven 선택 후 프로젝트 명을 “aophello1” 이
라고 입력 후 “Finish” 클릭
단순히 "Hello AOP..." 이라고 출력하는 PrintMsg 클래스의 메소드 sayHello()가 있고 이 클래스에 주변
충고(어라운드 어드바이스, Around Advice)를 추가해 sayHello() 메소드 실행 전/후 필요한 기능
("메소드 실행 전 안녕...", "메소드 실행 후 안녕...")을 출력하고자 한다.
3-2. AOP HelloWorld
3-2-1. AOP HelloWorld(프로그래밍을 통한 AOP 구현)
[IprintMsg.java]
package aophello1;
public interface IPrintMsg {
public void
sayHello();
}
[PrintMsg.java]
타겟 클래스(충고가 적용될 클래스, 횡단관심사
기능을 구햔한 클래스
본 예제에서는 간단히 로깅만 하기로 한다.
package aophello1;
public class PrintMsg implements IPrintMsg {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Hello AOP...");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-10-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-2. AOP HelloWorld
3-2-1. AOP HelloWorld(프로그래밍을 통한 AOP 구현)
[MyAroundAdvice.java]
어라운드 어드바이스(AroundAdvice)의 구현체, 충고 MethodInterceptor는 메소드 호출용 어라운드 어드바이스의 표준 인터페이스이다.
MethodInvocation은 어드바이스를 추가하기 위한 메소드 호출을 나타내며 이 객체를 사용하면 메소드 호출이 실행되는 시점
(메소드 실행 전/후)을 제어할 수 있다.
package aophello1;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
public class MyAroundAdvice implements MethodInterceptor {
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation)
throws Throwable {
System.out.println("메소드 실행전 안녕...");
Object ret = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("메소드 실행후 안녕...");
return ret;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-11-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-2. AOP HelloWorld
3-2-1. AOP HelloWorld(프로그래밍을 통한 AOP 구현)
[HelloMain.java]
Proxt 빈 객체를 생성후 MyAroundAdvice 및 타겟 객체인 PrintMsg를 위빙하여 프록시 생성
package aophello1;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
public class HelloMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IPrintMsg target = new PrintMsg();
//Proxy 빈껍데기 생성
ProxyFactory pf = new ProxyFactory();
pf.addAdvice(new MyAroundAdvice()); //충고 add
pf.setTarget(target); //타겟 add
PrintMsg proxy = (PrintMsg)pf.getProxy();
proxy.sayHello();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-12-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-2. AOP HelloWorld
3-2-1. AOP HelloWorld(프로그래밍을 통한 AOP 구현)
[HelloMain.java]
Proxt 빈 객체를 생성후 MyAroundAdvice 및 타겟 객체인 PrintMsg를 위빙하여 프록시 생성
package aophello1;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
public class HelloMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IPrintMsg target = new PrintMsg();
//Proxy 빈껍데기 생성
ProxyFactory pf = new ProxyFactory();
pf.addAdvice(new MyAroundAdvice()); //충고 add
pf.setTarget(target); //타겟 add
PrintMsg proxy = (PrintMsg)pf.getProxy();
proxy.sayHello();
}
}
[실행결과]
메소드 실행 전 안녕...
Hello AOP...
메소드 실행 후 안녕...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-13-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-2. AOP HelloWorld
3-2-2. AOP HelloWorld (XML Schema Based AOP 구현)
File -> New -> Spring Legacy Project -> Simple Spring Maven 선택 후 프로젝트 명을 “aophello1” 이
라고 입력 후 “Finish” 클릭
스프링에서 제공하는 aop Namespace를 이용하는 방법으로 타깃 클래스의 sayHello1(), sayHello2() 메
소드 중 sayHello1() 메소드만 주변충고가 적용되도록 구성한 예제이다.
[pom.xml]에 AOP를 위한 라이브러리 추가
<!-- Spring AOP + AspectJ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>${spring-
framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>1.6.11</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.6.11</version>
</dependency>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-14-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-2. AOP HelloWorld
3-2-2. AOP HelloWorld (XML Schema Based AOP 구현)
[IprintMsg.java]
package aophello1;
public interface IPrintMsg {
public void sayHello1();
public void sayHello2();
}
[PrintMsg.java]
package aophello1;
public class PrintMsg implements IPrintMsg {
public void sayHello1() {
System.out.println("Hello AOP1...");
}
public void sayHello2() {
System.out.println("Hello AOP2...");
}
}
[LogginAspect.java]
// XML Schema Based AOP 구현에서는 Aspect클래스에 충고용 메소드를 정의한다.
// 아래 myAdvice가 주변충고용 메소드로 어떤 메소드에 이 충고가 내려갈지는 XML에서 설정을 한다.
// pjp.procees() 메소드를 통해 원래 타겟클래스의 sayHello1() 메소드가 호출된다.
package aophello1;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
public class LoggingAspect {
public void myAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp)
throws Throwable{
System.out.println("메소드 실행전 안녕..."); //메소드 실행 전
Object ret = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("메소드 실행후 안녕..."); //메소드 실행 후
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-15-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-2. AOP HelloWorld
3-2-2. AOP HelloWorld (XML Schema Based AOP 구현)
[Src/main/resources/aophello1.xml]
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.1.xsd ">
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="helloAspect" ref="logging"> <!-- ref에는 충고를 담고있는 Aspect가 온다
<aop:pointcut id="selectSayHello1"
expression="execution(* aophello1.PrintMsg.sayHello1(..))"/>
<!—myAdvice는 Aspect 클래스(logging)의 충고용 메소드-->
<aop:around pointcut-ref="selectSayHello1" method="myAdvice"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
<!-- Definition for printMsg bean, 타겟클래스 -->
<bean id="printMsg" class="aophello1.PrintMsg" />
<!-- Definition for logging aspect 충고들이 오여있는 Aspect클래스-->
<bean id="logging" class="aophello1.LoggingAspect"/>
</beans>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-16-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-2. AOP HelloWorld
3-2-2. AOP HelloWorld (XML Schema Based AOP 구현)
[HelloMain.java]
package aophello1;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class HelloMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aophello1.xml");
IPrintMsg printMsg = (IPrintMsg) ctx.getBean("printMsg");
//sayHello1만 충고가 내려가도록 되어 있다.
printMsg.sayHello1();
printMsg.sayHello2();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-17-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-2. AOP HelloWorld
3-2-3. AOP HelloWorld (@AspectJ Annotation Based AOP 구현)
File -> New -> Spring Legacy Project -> Simple Spring Maven 선택 후 프로젝트 명을 “aophello1” 이라고
입력 후 “Finish” 클릭
스프링에서 제공하는 aop Namespace를 이용하는 방법으로 타깃 클래스의 sayHello1(), sayHello2() 메소드
중 sayHello1() 메소드만 주변충고가 적용되도록 구성한 예제이다.
[pom.xml]에 AOP를 위한 라이브러리 추가
<!-- Spring AOP + AspectJ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>1.6.11</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.6.11</version>
</dependency>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-18-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-2. AOP HelloWorld
3-2-3. AOP HelloWorld (@AspectJ Annotation Based AOP 구현)
[IprintMsg.java]
package aophello1;
public interface IPrintMsg {
public void sayHello1();
public void sayHello2();
}
[PrintMsg.java]
package aophello1;
public class PrintMsg implements IPrintMsg {
public void sayHello1() {
System.out.println("Hello AOP1...");
}
public void sayHello2() {
System.out.println("Hello AOP2...");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-19-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-2. AOP HelloWorld
3-2-3. AOP HelloWorld (@AspectJ Annotation Based AOP 구현)
[LogginAspect.java]
// Aspect클래스로 충고용 메소드 및 포인트컷을 정의한다.
// 아래 myAdvice가 주변충고용 메소드로 메소드 상단에 포인트컷을 정의했다.
// pjp.procees() 메소드를 통해 원래 타겟클래스의 sayHello1() 메소드가 호출된다.
package aophello1;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
@Aspect
public class LoggingAspect {
@Around("execution(* aophello1.PrintMsg.sayHello1())")
public void myAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp)
throws Throwable{
System.out.println("메소드 실행전 안녕..."); //메소드 실행전
Object ret = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("메소드 실행후 안녕..."); //메소드 실행후
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-20-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-2. AOP HelloWorld
3-2-3. AOP HelloWorld (@AspectJ Annotation Based AOP 구현)
[Src/main/resources/aophello1.xml]
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.1.xsd ">
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
<!-- Definition for printMsg bean, 타겟클래스 -->
<bean id="printMsg" class="aophello1.PrintMsg" />
<!-- Definition for logging aspect 충고들이 오여있는 Aspect클래스-->
<bean id="logging" class="aophello1.LoggingAspect"/>
</beans>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-21-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-2. AOP HelloWorld
3-2-3. AOP HelloWorld (@AspectJ Annotation Based AOP 구현)
[HelloMain.java]
package aophello1;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class HelloMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aophello1.xml");
IPrintMsg printMsg = (IPrintMsg) ctx.getBean("printMsg");
//sayHello1만 충고가 내려가도록 되어 있다.
printMsg.sayHello1();
printMsg.sayHello2();
}
}
[결과]
메소드 실행전 안녕...
Hello AOP1...
메소드 실행후 안녕...
Hello AOP2...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-22-320.jpg)


![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-4. 프로그래밍적인 방법을 통한 AOP 구현(ProxyFactory 이용)
[SmallMartInterface.java]
package onj.hello.aop;
public interface SmallMartInterface {
public void getProducts(String productName) throws Exception;
}
[SmallMart.java]
package onj.hello.aop;
public class SmallMart implements SmallMartInterface {
public void getProducts(String productName) throws Exception {
System.out.println("[Target Method]getProduct()..." + productName);
throw new Exception("error..."); //주석으로 막고 실행해 보자.
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-28-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-4. 프로그래밍적인 방법을 통한 AOP 구현(ProxyFactory 이용)
[BeforeLoggingAdvice.java]
package onj.hello.aop;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
public class BeforeLogginAdvice implements MethodBeforeAdvice{
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
String findName = (String)args[0];
System.out.println(method.getName() + "(" + findName + "):: 사전충고");
}
}
/**
* 사전 충고용 인터페이스
* 이메소드는 대상메소드, 그 메소드에 전달할 인자, 대상객체에 대한 접근점 제공
* 메소드 인자에 접근 가능하므로 런타임중에 파라미터를 사용하여 충고 구현 가능
*/
public interface MethodBeforeAdvice {
void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable ;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-29-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-4. 프로그래밍적인 방법을 통한 AOP 구현(ProxyFactory 이용)
[AfterLoggingAdvice.java]
package onj.hello.aop;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
public class AfterLoggingAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice {
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws
Throwable {
System.out.println(method.getName() + "(" + args[0] + ") :: 사후중고" );
}
}
/* 사후 충고(AfterReturning Advice)용 인터페이스 */
public interface AfterReturningAdvice {
void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object
target) throws Throwable;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-30-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-4. 프로그래밍적인 방법을 통한 AOP 구현(ProxyFactory 이용)
[AroundLoggingAdvice.java]
package onj.hello.aop;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
public class AroundLoggingAdvice implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
String findName = (String) invocation.getArguments()[0];
String methodName = (String) invocation.getMethod().getName();
System.out.println("[주변충고]" + methodName + "(" + findName + ") 메소드 실행전");
Object obj = invocation.proceed(); // 타켓클래스의 메소드 호출
System.out.println("[주변충고]" + methodName + "(" + findName + ") 메소드 실행후");
return obj;
}
}
/* 이전에 사전,사후 충고를 엮었는
데 주변충고를 통해 둘 다를 엮을
수 있다.*/
public interface
MethodInterceptor {
Object
invoke(MethodInvocation
invocation) throws Throwable;
}
MethodInterceptor 구현 클래스
(주변충고용 클래스)는 대상 메소
드의 실제 호출여부를 제어하며
proceed를 통해 호출 타깃 메소드
호출하며, 원래 메소드의 리턴을
대체 가능하다.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-31-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-4. 프로그래밍적인 방법을 통한 AOP 구현(ProxyFactory 이용)
[ThrowsLoggingAdvice.java]
package onj.hello.aop;
import org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice;
public class ThrowsLoggingAdvice implements ThrowsAdvice {
public void afterThrowing(Throwable throwable) {
System.out.println("에러 발생...");
}
}
/* 예외가 발생했을 때의 행위를 정의, marker interface */
public interface ThrowsAdvice { }
구현대상이 없지만 아래의 메소드중 하나를 포함해야 한다.
void afterThrowing(Throwable throwable);
void afterThrowing(Method method, Object[] args, Object target, Throwable
throwable);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-32-320.jpg)
![3. Spring AOP((Spring Aspect Oriented Programming)
3-4. 프로그래밍적인 방법을 통한 AOP 구현(ProxyFactory 이용)
[DemoSmallmartApplication.java]
package onj.hello.aop;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoSmallmartApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoSmallmartApplication.class, args);
SmallMartInterface target = new SmallMart();
ProxyFactory pf = new ProxyFactory();
pf.addAdvice(new BeforeLoggingAdvice());
pf.addAdvice(new AfterLoggingAdvice());
pf.addAdvice(new AroundLoggingAdvice());
pf.addAdvice(new ThrowsLoggingAdvice());
pf.setTarget(target);
try {
SmallMartInterface proxy = (SmallMartInterface)pf.getProxy();
proxy.getProducts("생필품");
}
catch(Exception e) {e.printStackTrace(System.out); }
}
}
DemoSmallmartApplication 클래스에서 마우스 우측버튼 ->
Run As -> Spring Boot App 또는 Java Application으로 실
행 가능](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-170209084930/85/Spring-IoC-DI-_-IT-33-320.jpg)

