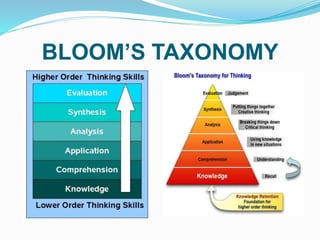
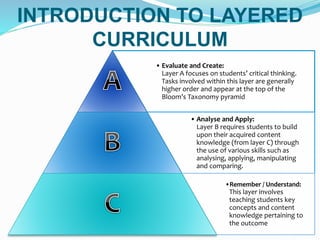
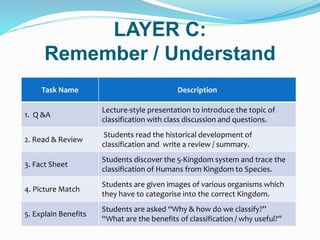
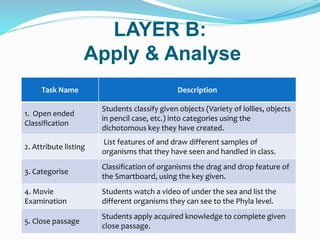
This document outlines the learning outcomes, focus outcome, knowledge and skills, and Bloom's Taxonomy approach for a lesson on classifying living things. The key learning outcomes are to classify living things according to their structural features and identify patterns of similarities and differences. The focus is on describing features of living things. The lesson is broken down into three layers: Layer C involves teaching key concepts and content knowledge; Layer B builds on this through skills like analyzing and applying; Layer A involves higher-order critical thinking tasks like evaluating and creating. Examples of tasks for each layer are provided.