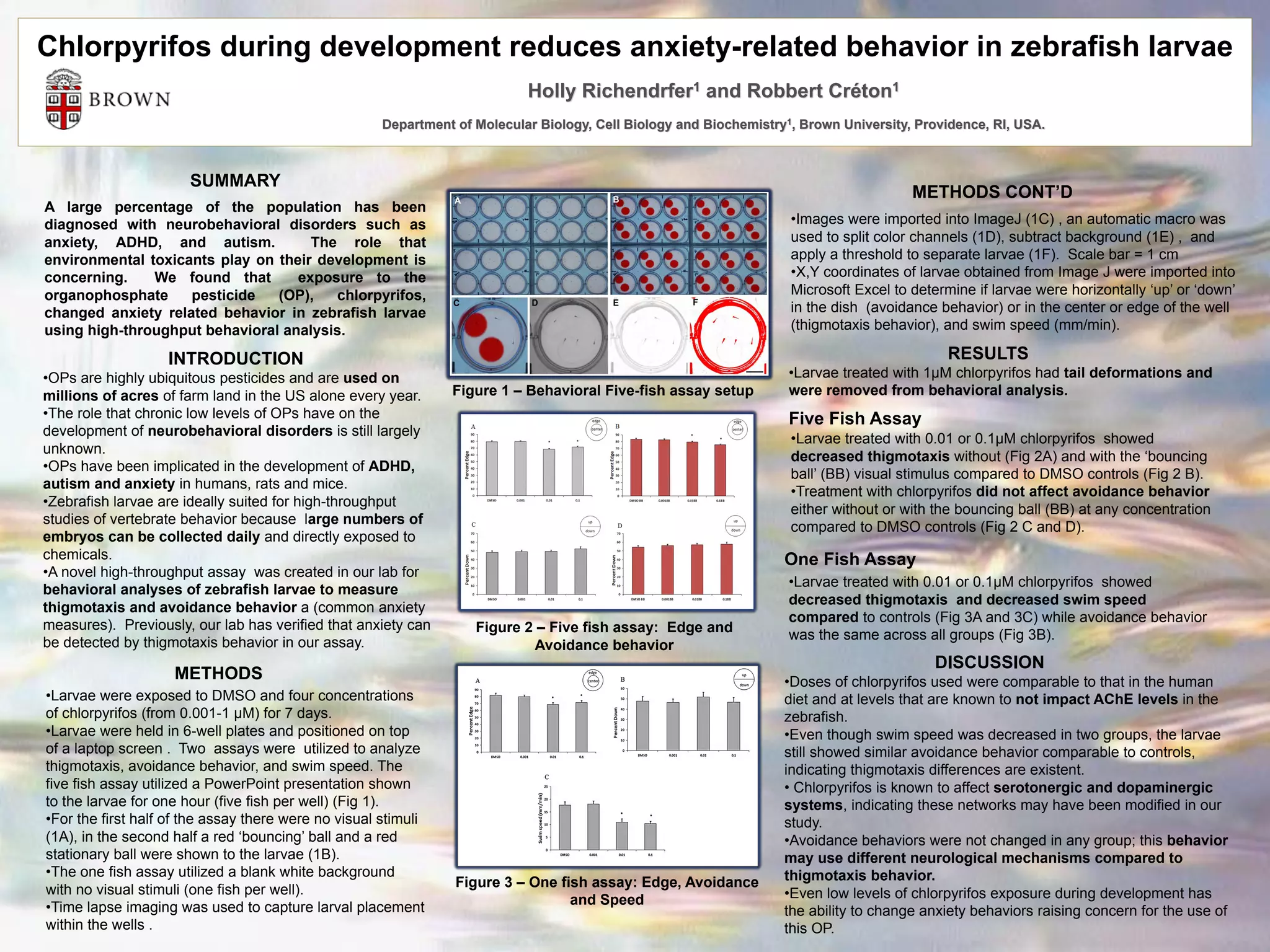
The study found that exposure to the organophosphate pesticide chlorpyrifos during development reduced anxiety-related behavior in zebrafish larvae. Using a novel high-throughput behavioral assay, the researchers determined that larvae treated with low doses of chlorpyrifos showed decreased thigmotaxis, or edge-seeking behavior, without and with a visual stimulus compared to controls, indicating reduced anxiety. Treatment did not affect avoidance behavior. In a separate assay, chlorpyrifos-treated larvae also showed decreased thigmotaxis, swim speed, but no change in avoidance behavior compared to controls. The results suggest that even low levels of chlorpyrifos during development can alter anxiety behaviors through effects on the serotonergic and