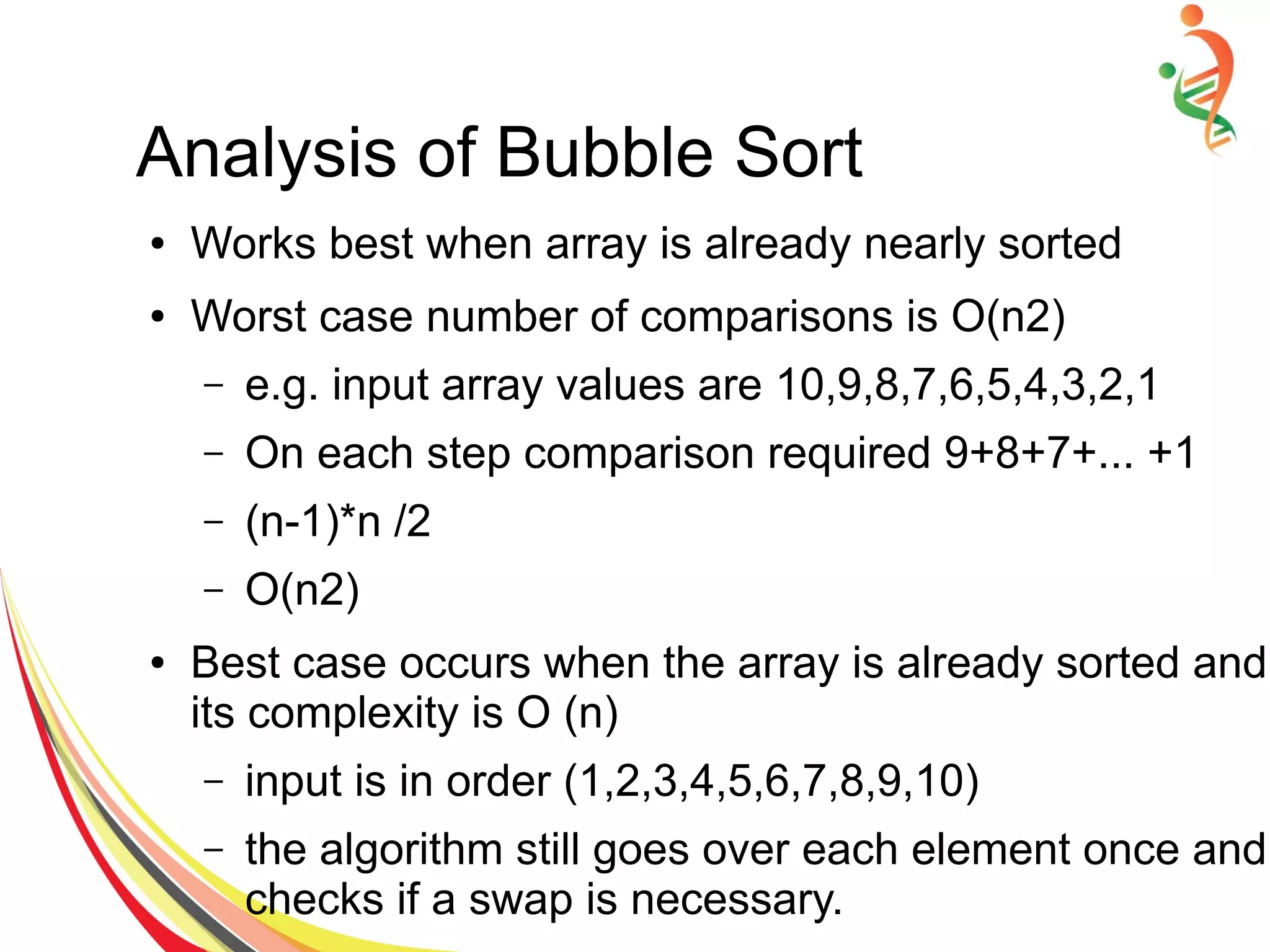
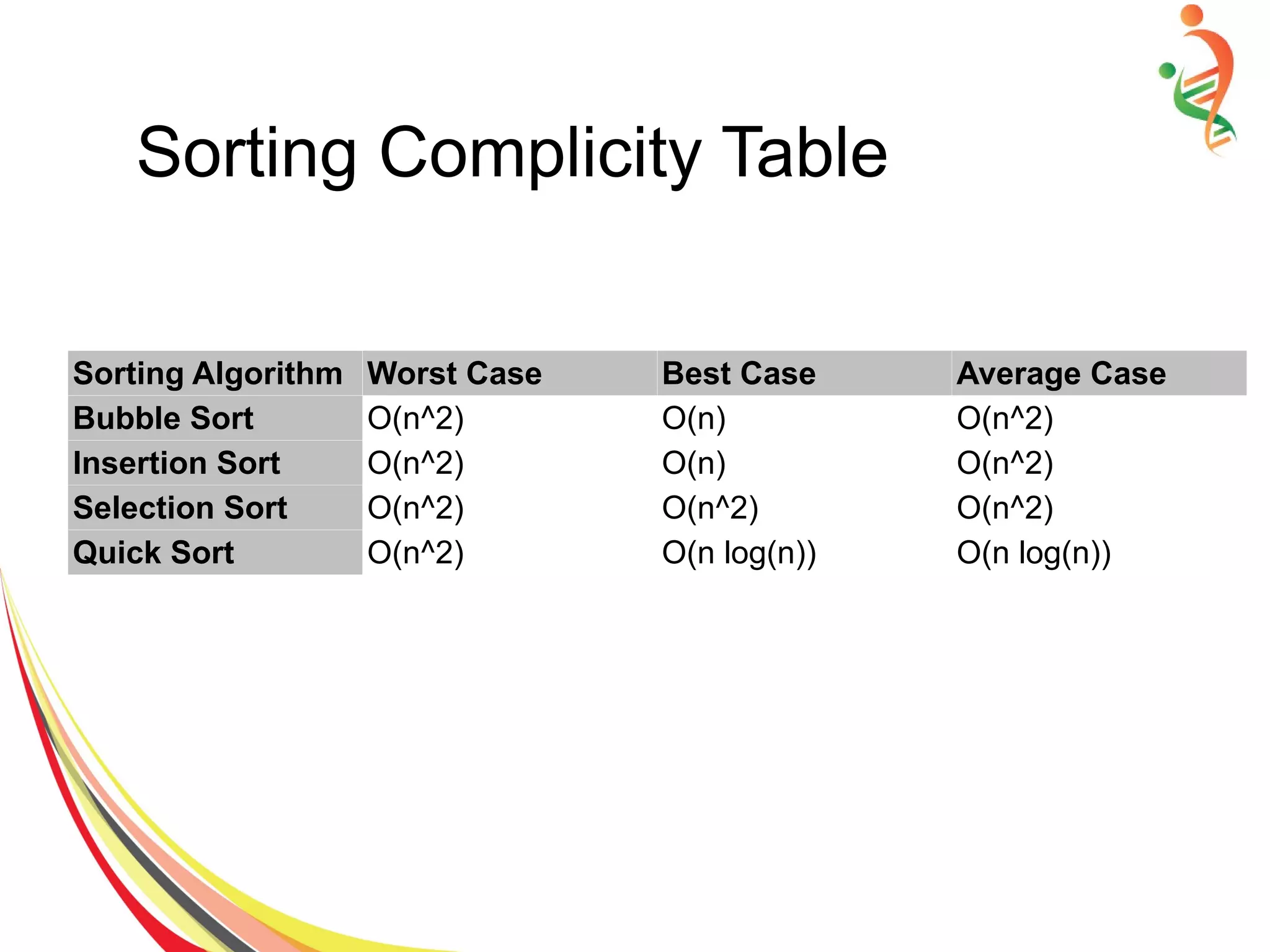
The document provides information on various sorting and searching algorithms, including bubble sort, insertion sort, selection sort, quick sort, sequential search, and binary search. It includes pseudocode to demonstrate the algorithms and example implementations with sample input data. Key points covered include the time complexity of each algorithm (O(n^2) for bubble/insertion/selection sort, O(n log n) for quick sort, O(n) for sequential search, and O(log n) for binary search) and how they work at a high level.



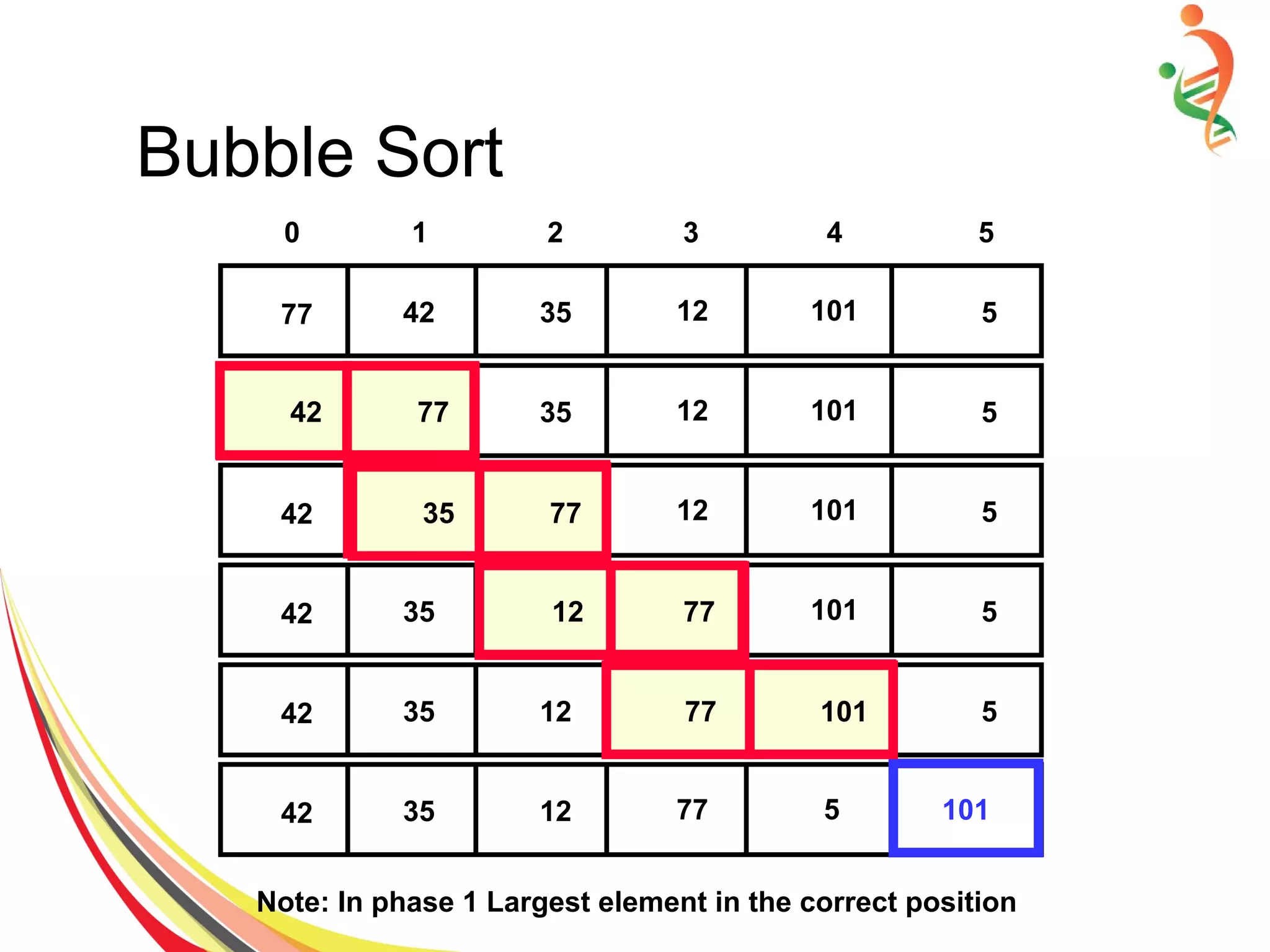
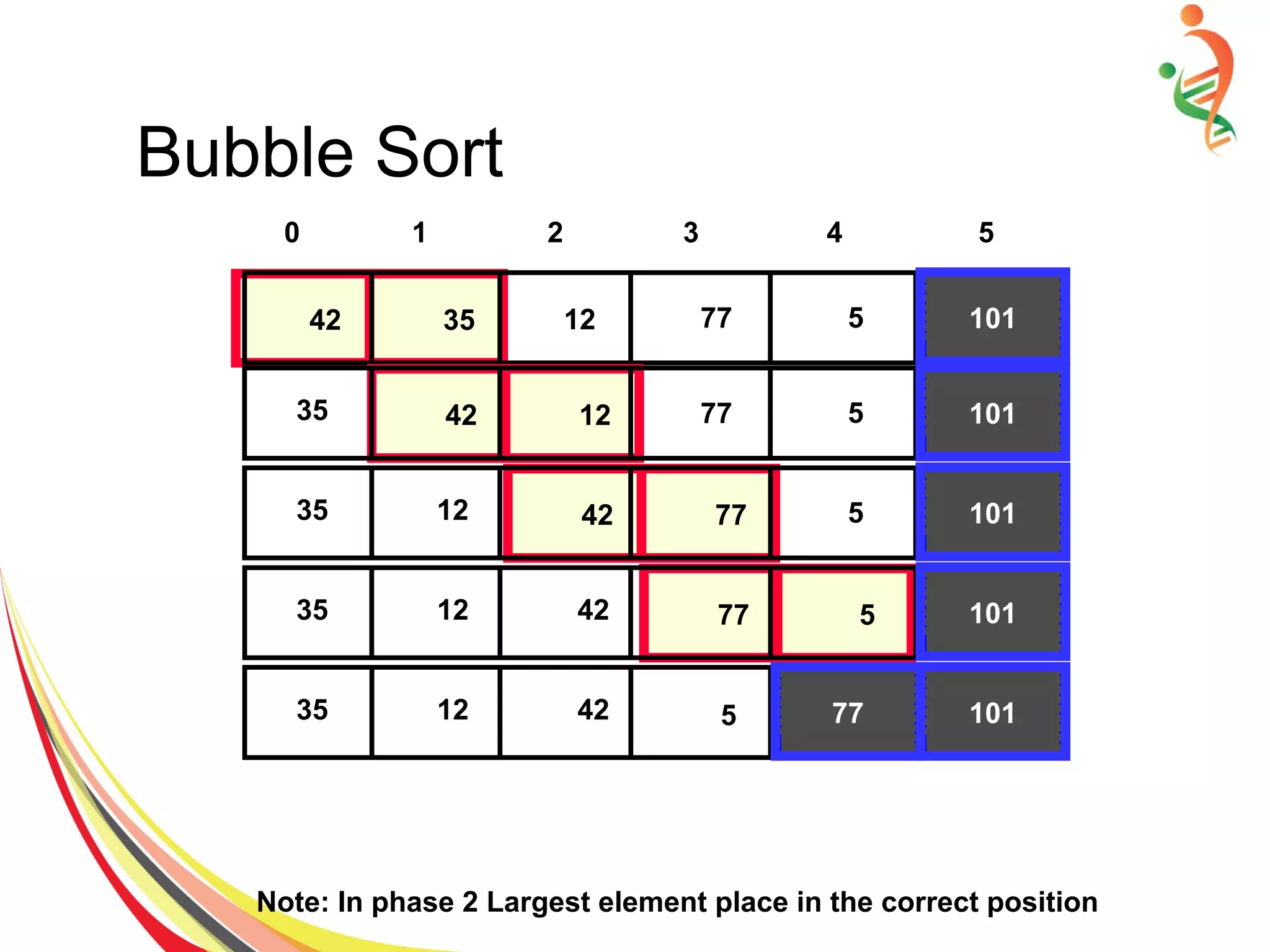
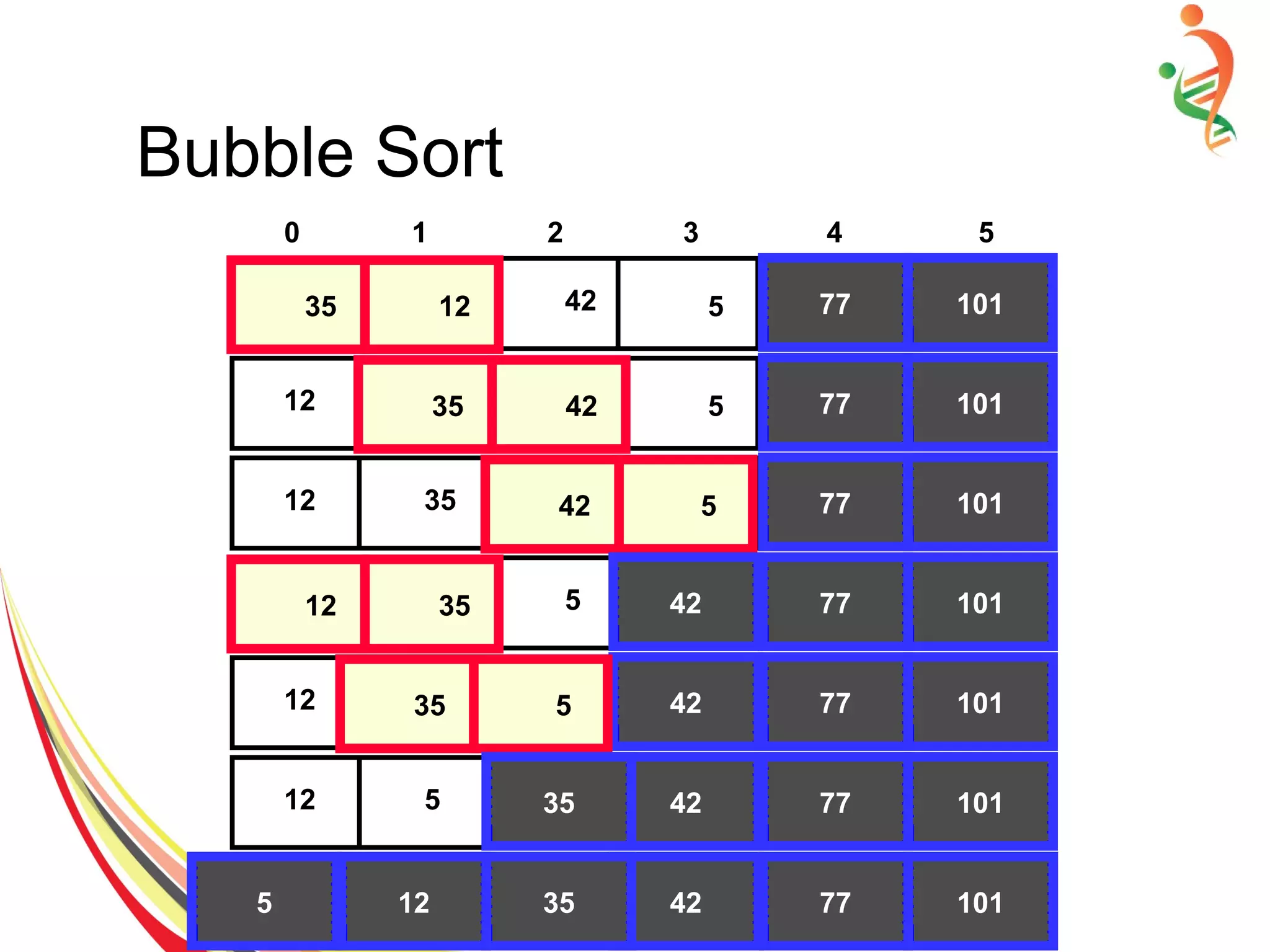
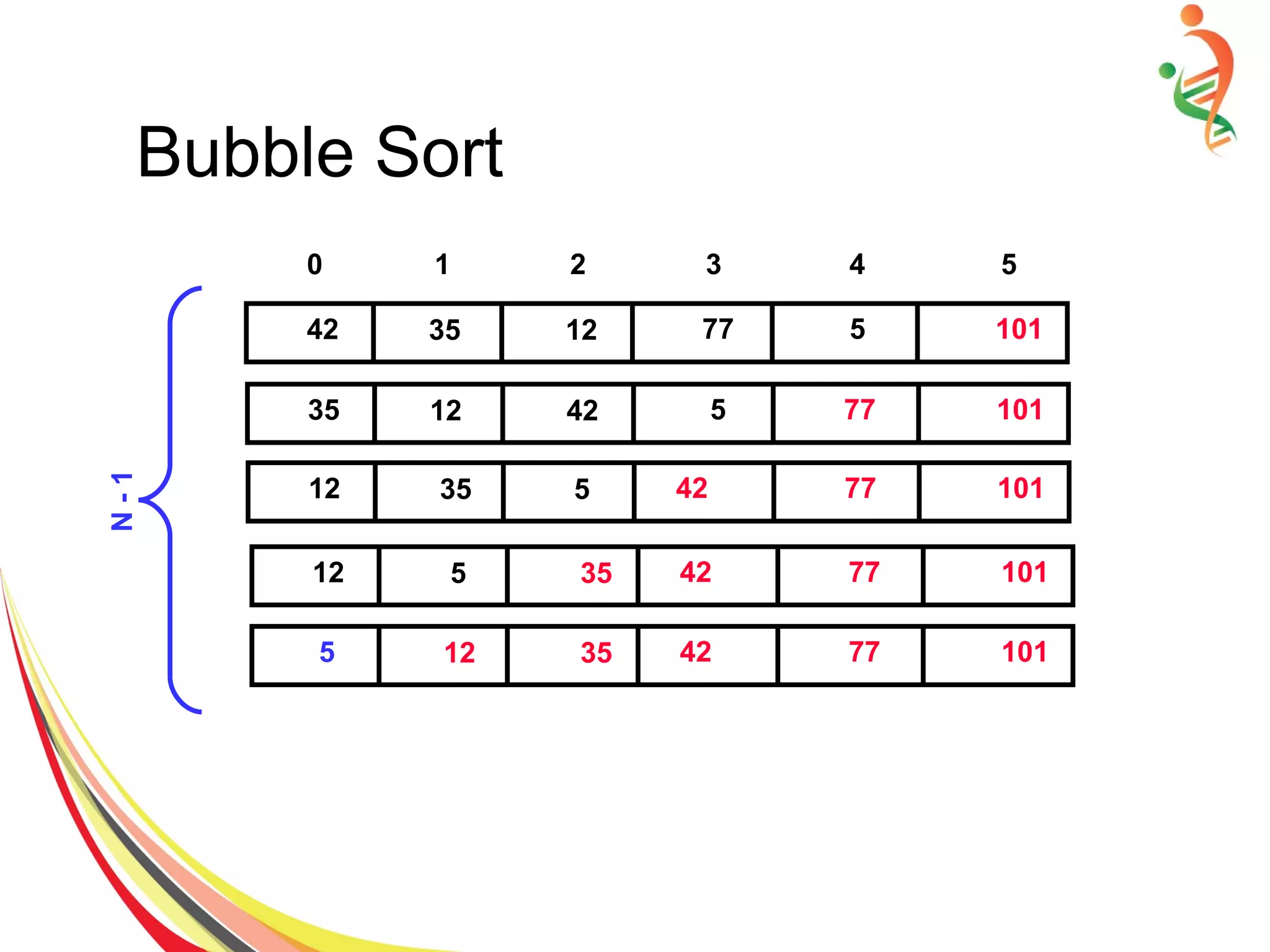
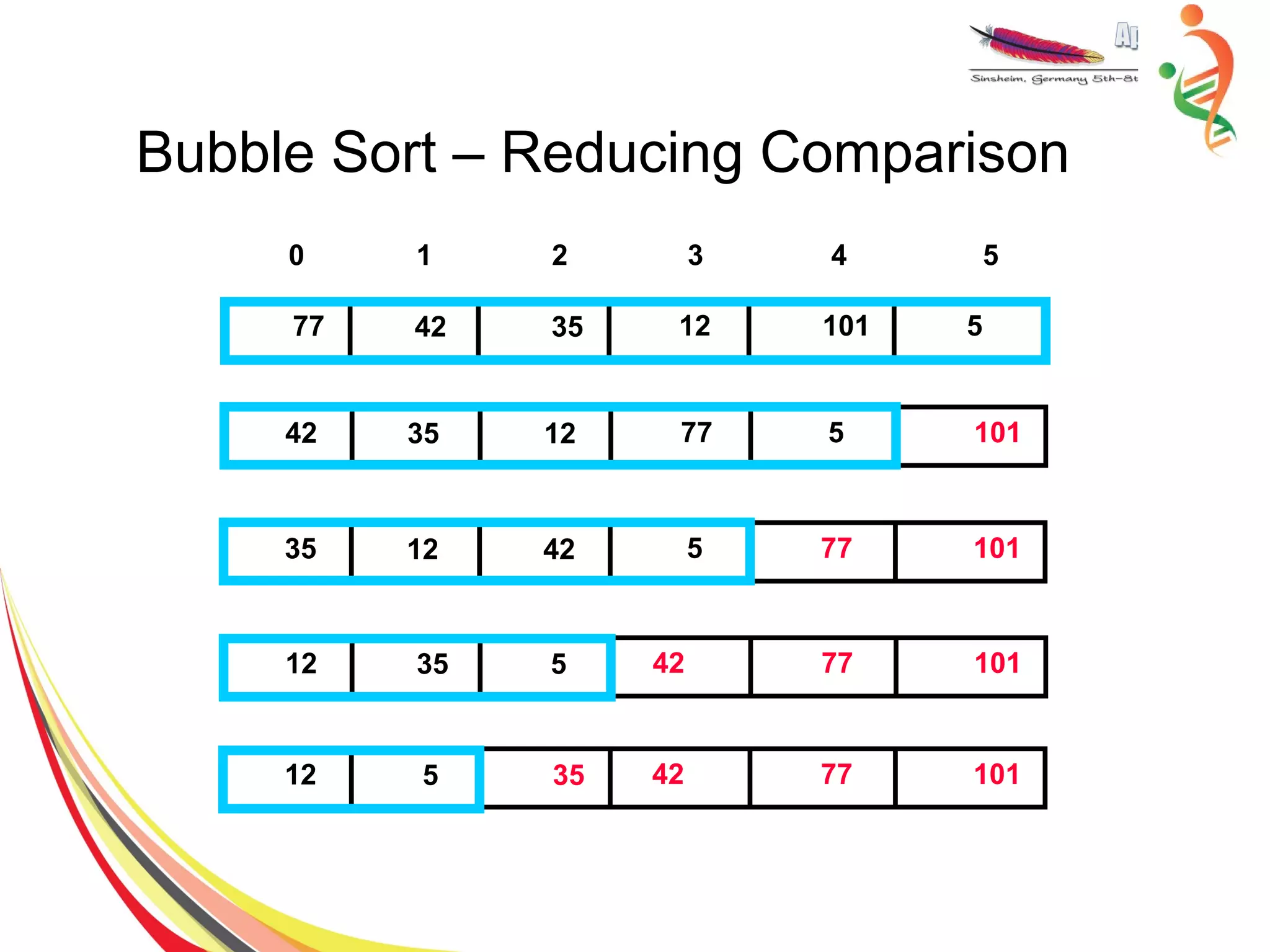
![Algorithm of Bubble Sort
● Declare array on n items
items[n]={4,5,1,8,54,32...32}
● Compare each pair of item and swap if required.
for(int pass=0; pass<n-1; pass ++)
for(int i=0; i<n-pass-1; i++)
If (item[ i ] > item [i+1]) {
tempvar = item[i]
Item[ i ] = item [i+1]
Item[ i+1]=tempvar
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-150528091014-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-4-2048.jpg)
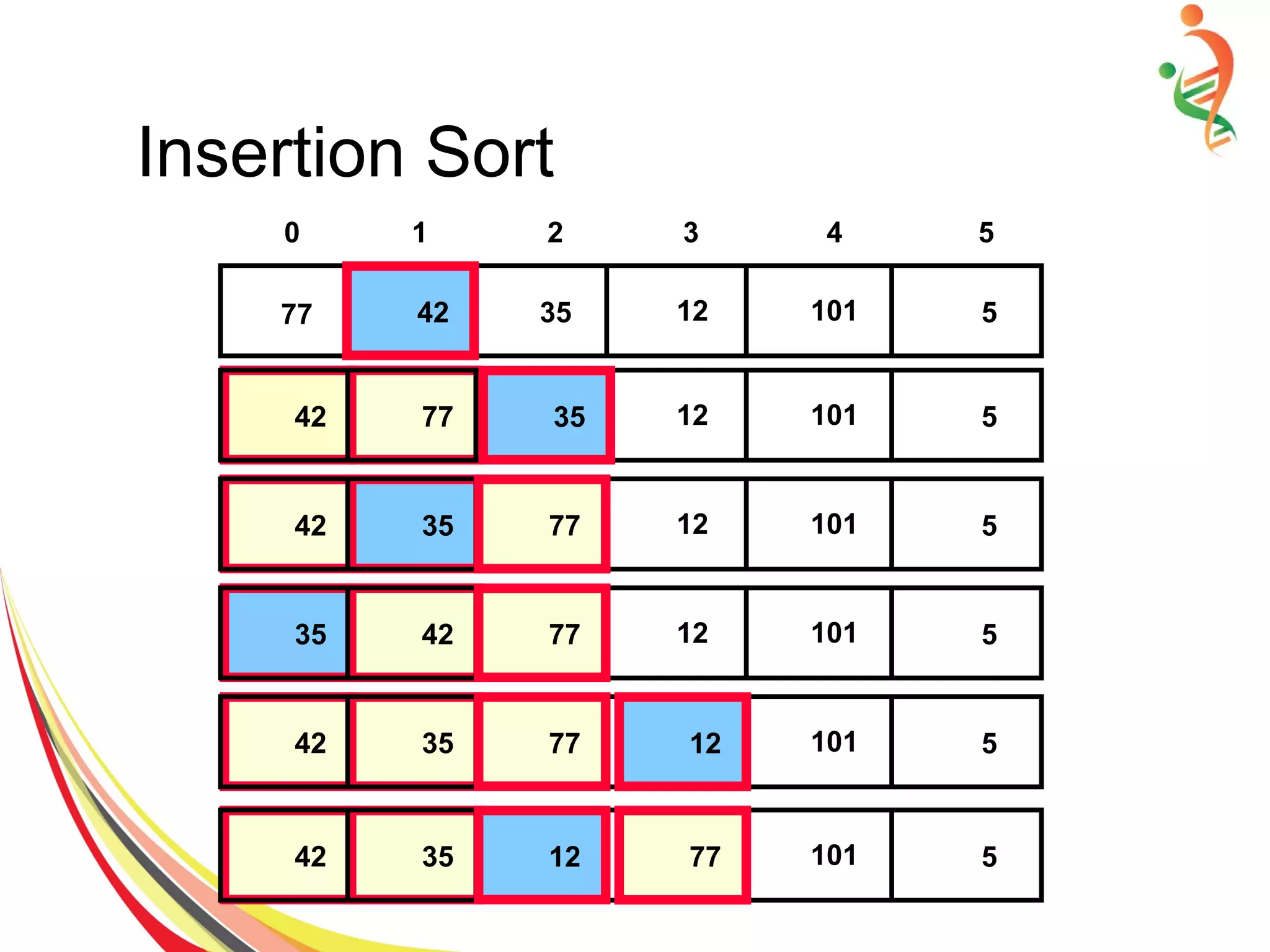
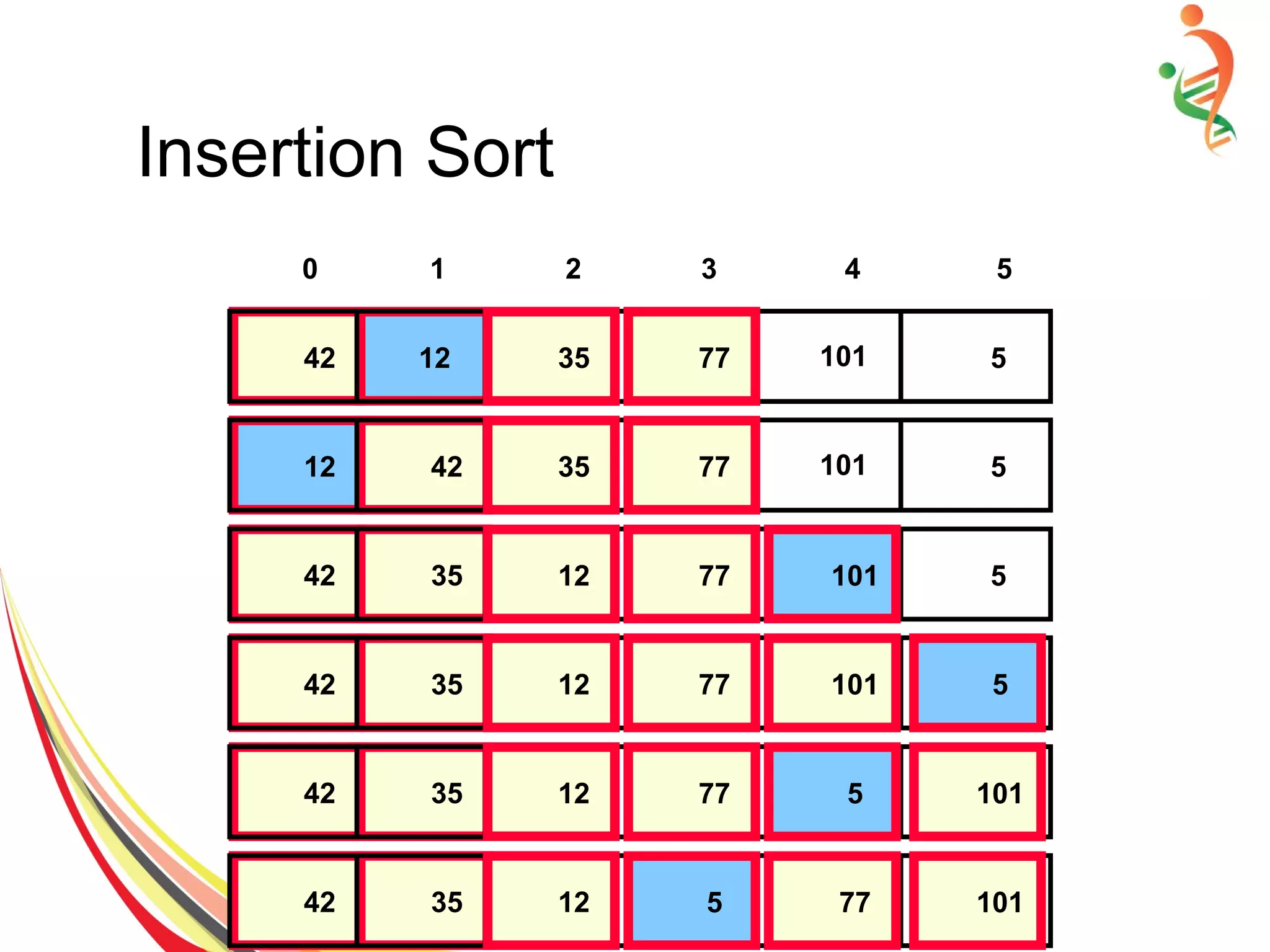
![Insertion Sort
● Sort the elements in range[0,m] form = 0,...,n−1
● No action need form=0
● When going from m to m+1, insert the element
in index m+1, to its appropriate location](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-150528091014-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-11-2048.jpg)
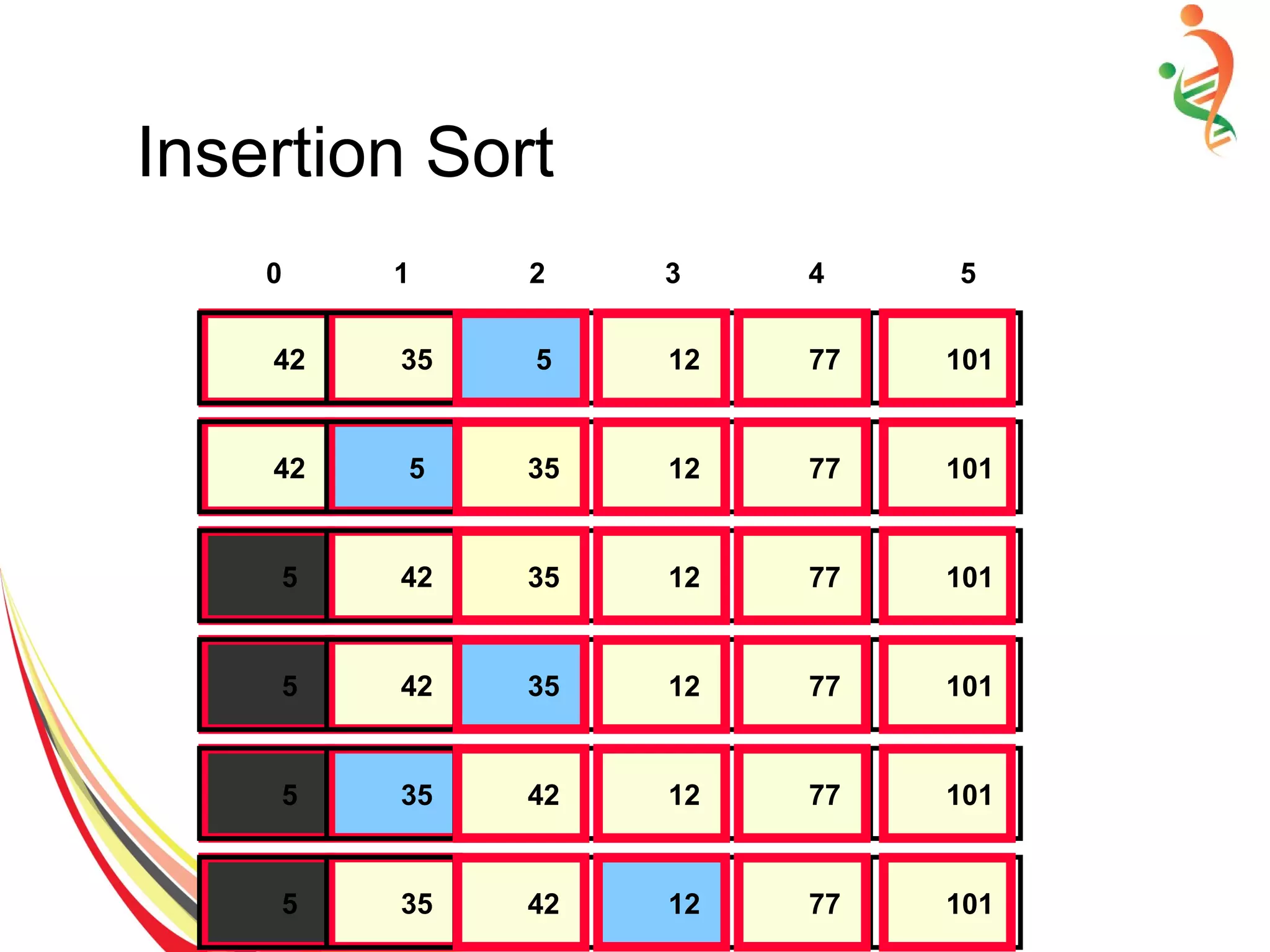
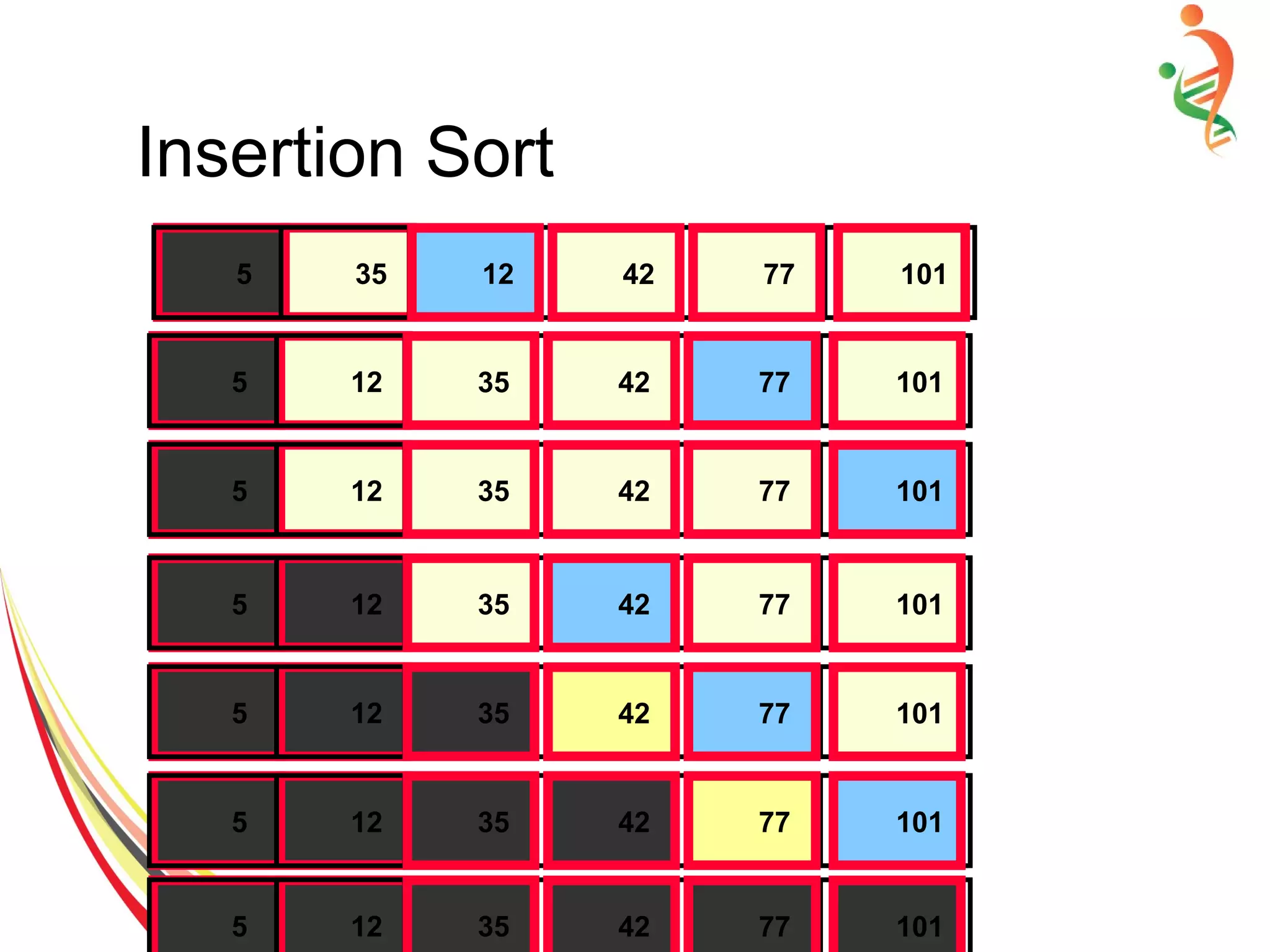
![Algorithm of Insertion Sort
● This algorithm sorts the array a with n elements.
Set a[n] ={ 2,7,5,8,43,23..99}
● for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) //Array start from 0
{
Item tmp = a[i];
for (int j=i; j>0 && tmp < a[j-1]; j--)
a[j] = a[j-1];
a[j] = tmp;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-150528091014-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-12-2048.jpg)

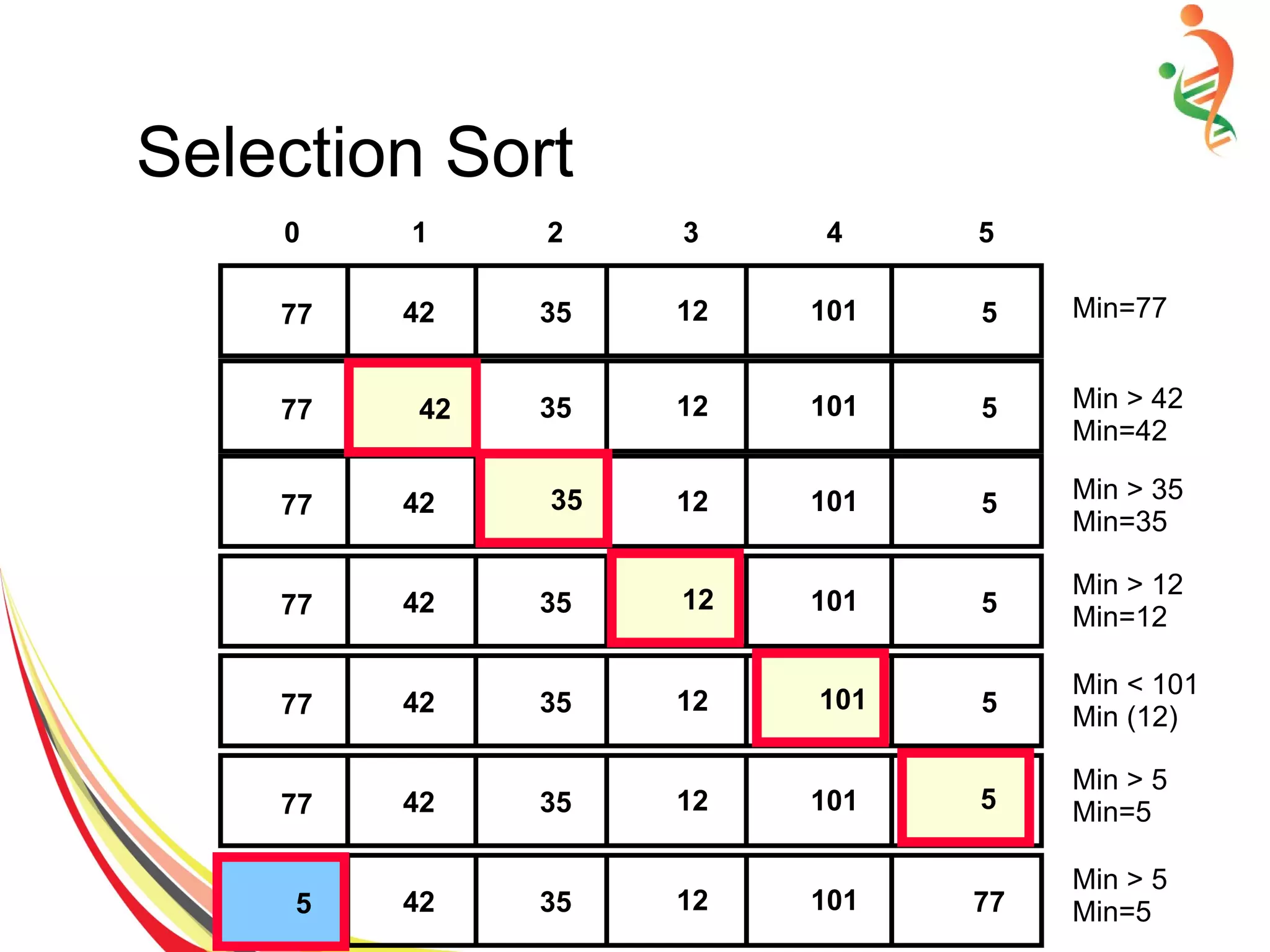
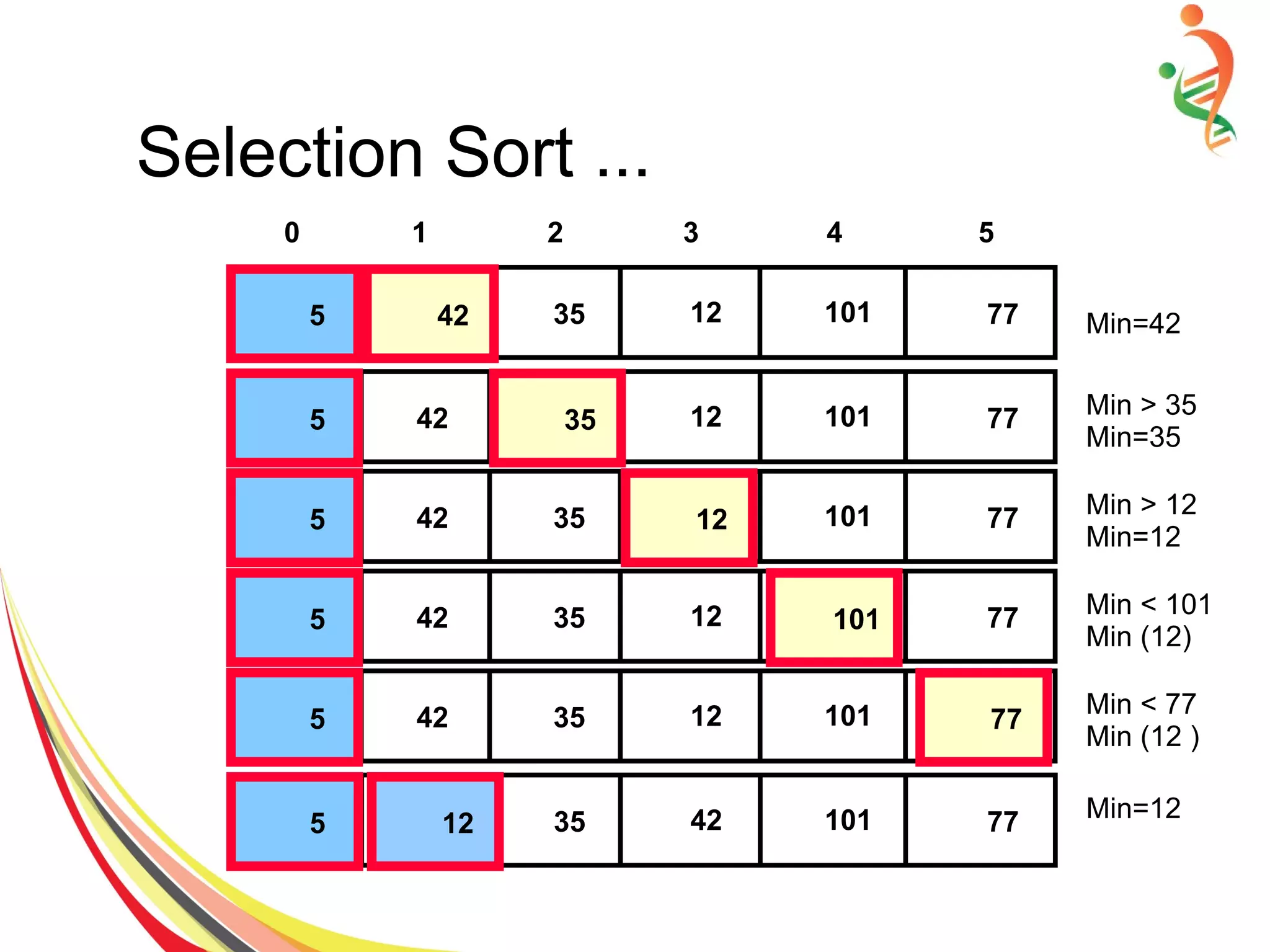
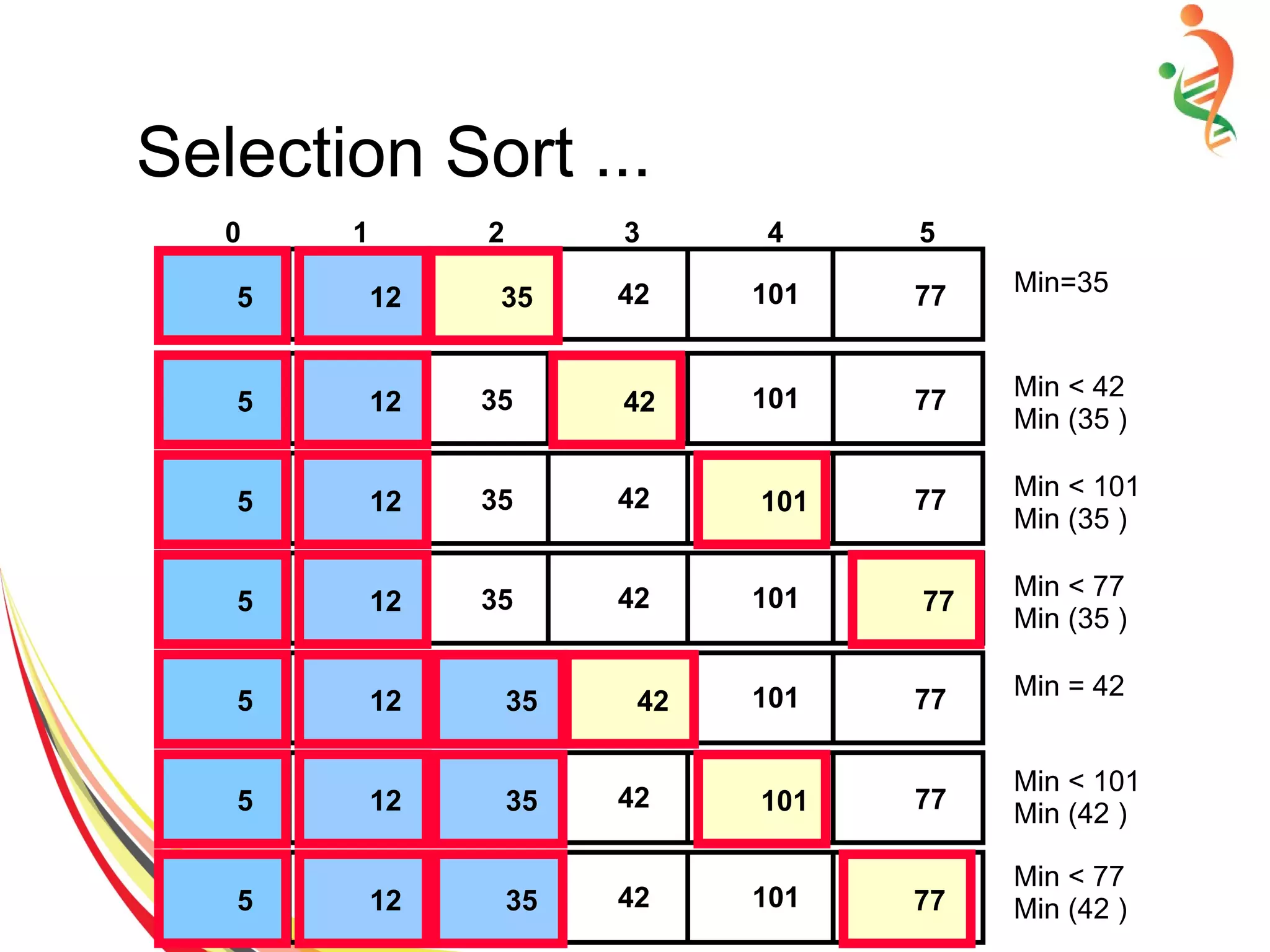
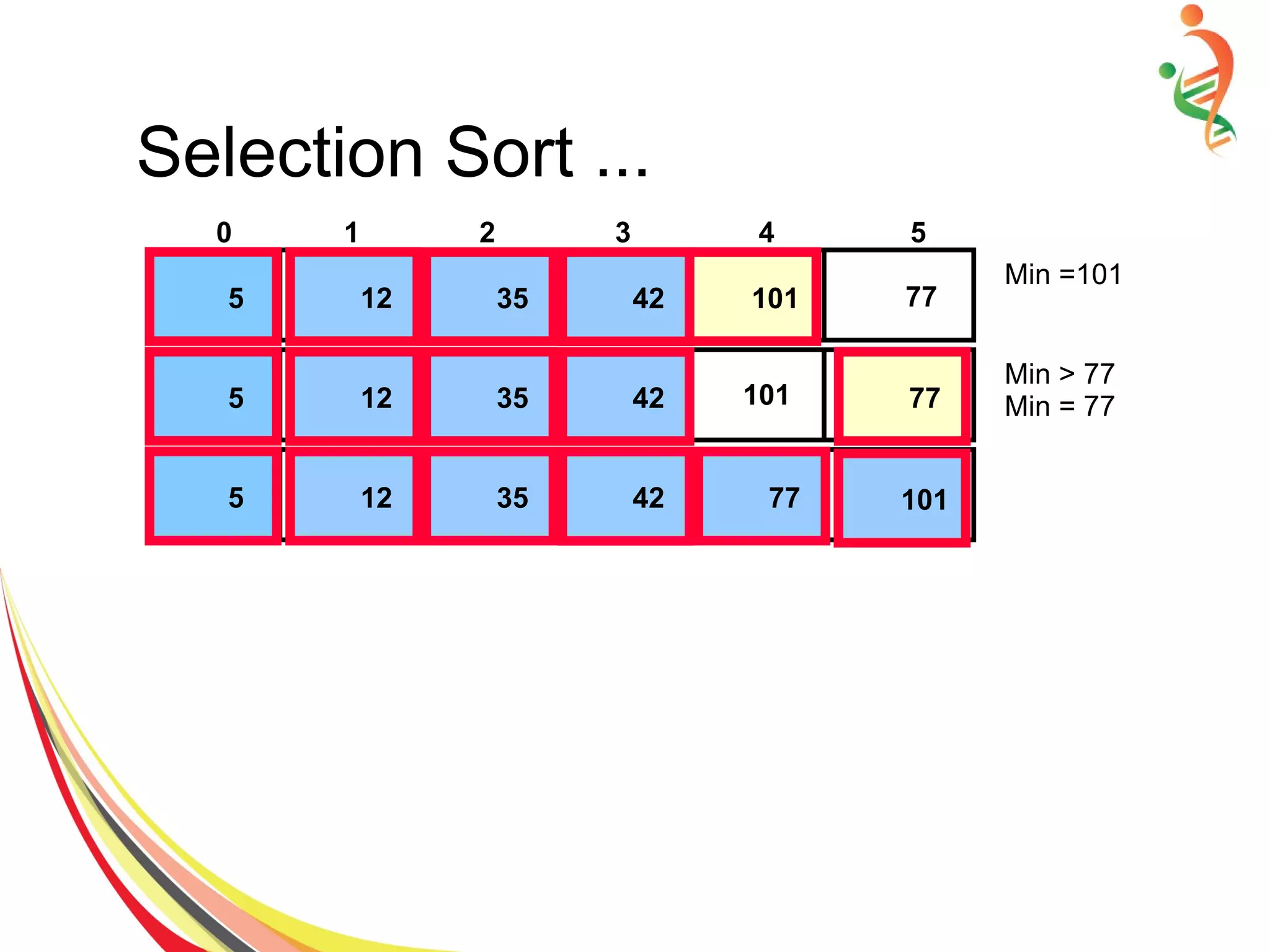
![Selection Sort Algorithm
● Declare array on n items
Set items[n] = { 2,7,5,8,43,23..99}
● Find the min item and and iteratively swap with
first item if required.
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) {
int min = i;
for (int j = i+1; j < n; j++)
if (a[j] < a[min]) min = j;
swap(a[i], a[min]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-150528091014-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-18-2048.jpg)

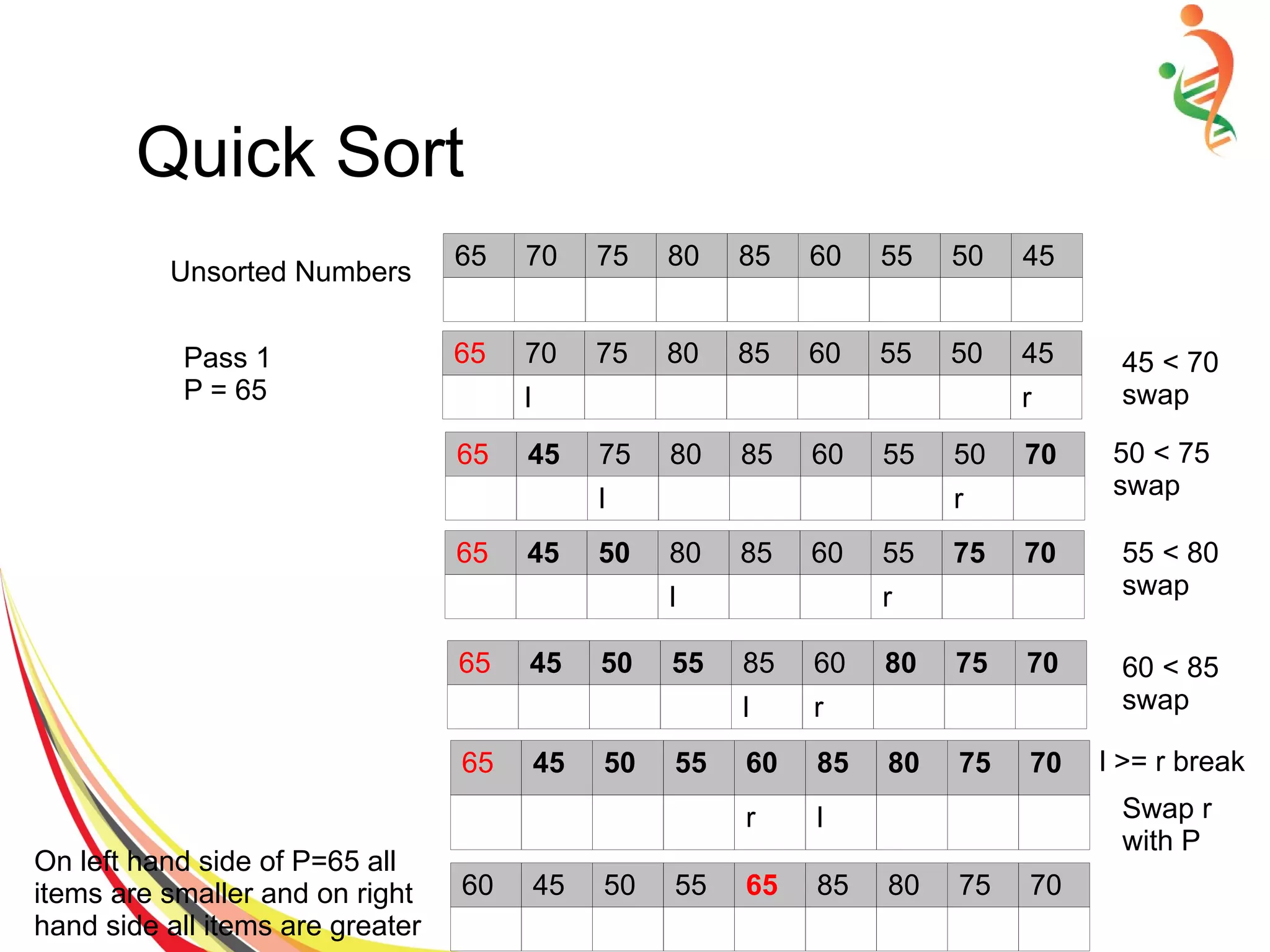
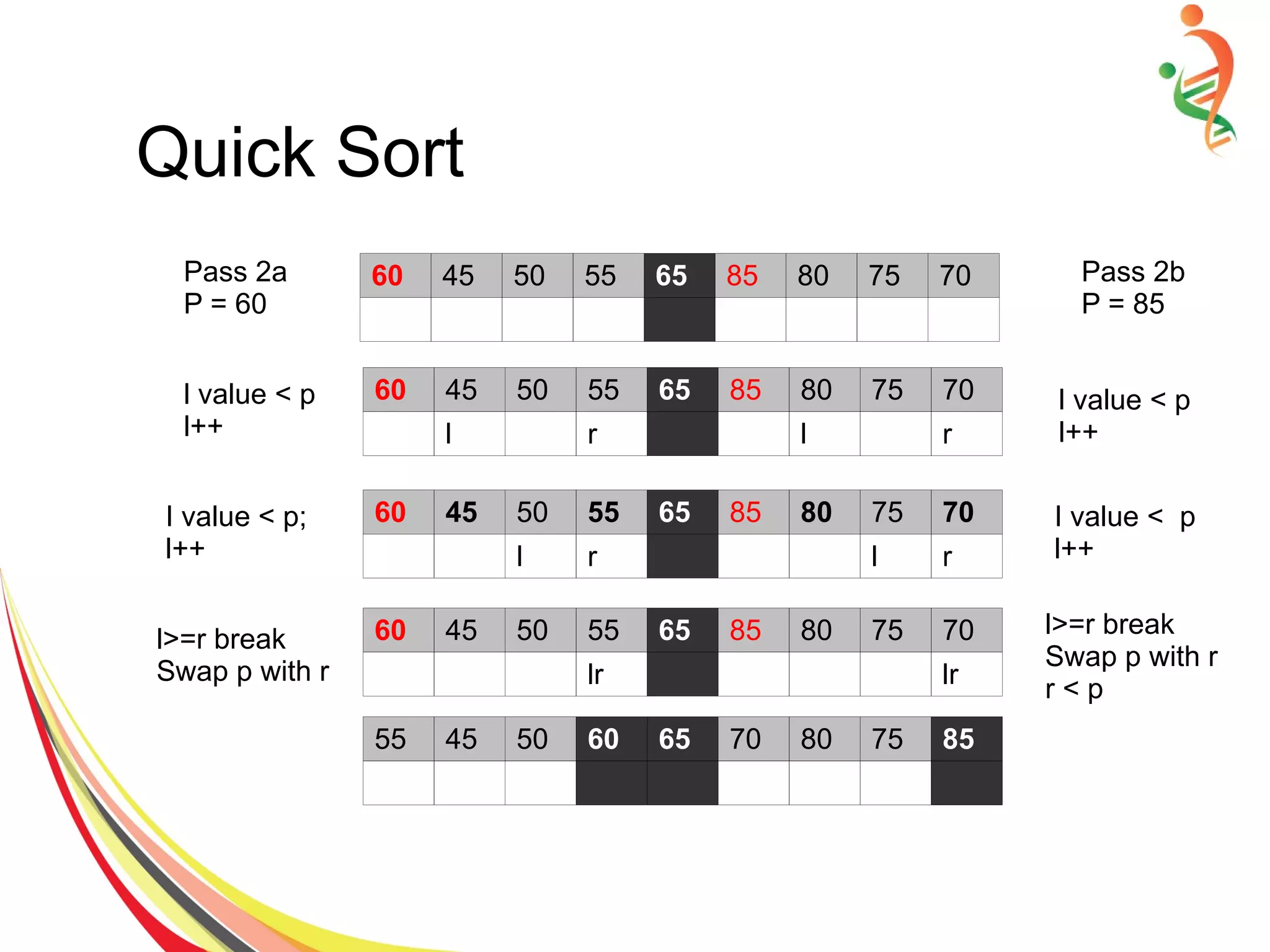
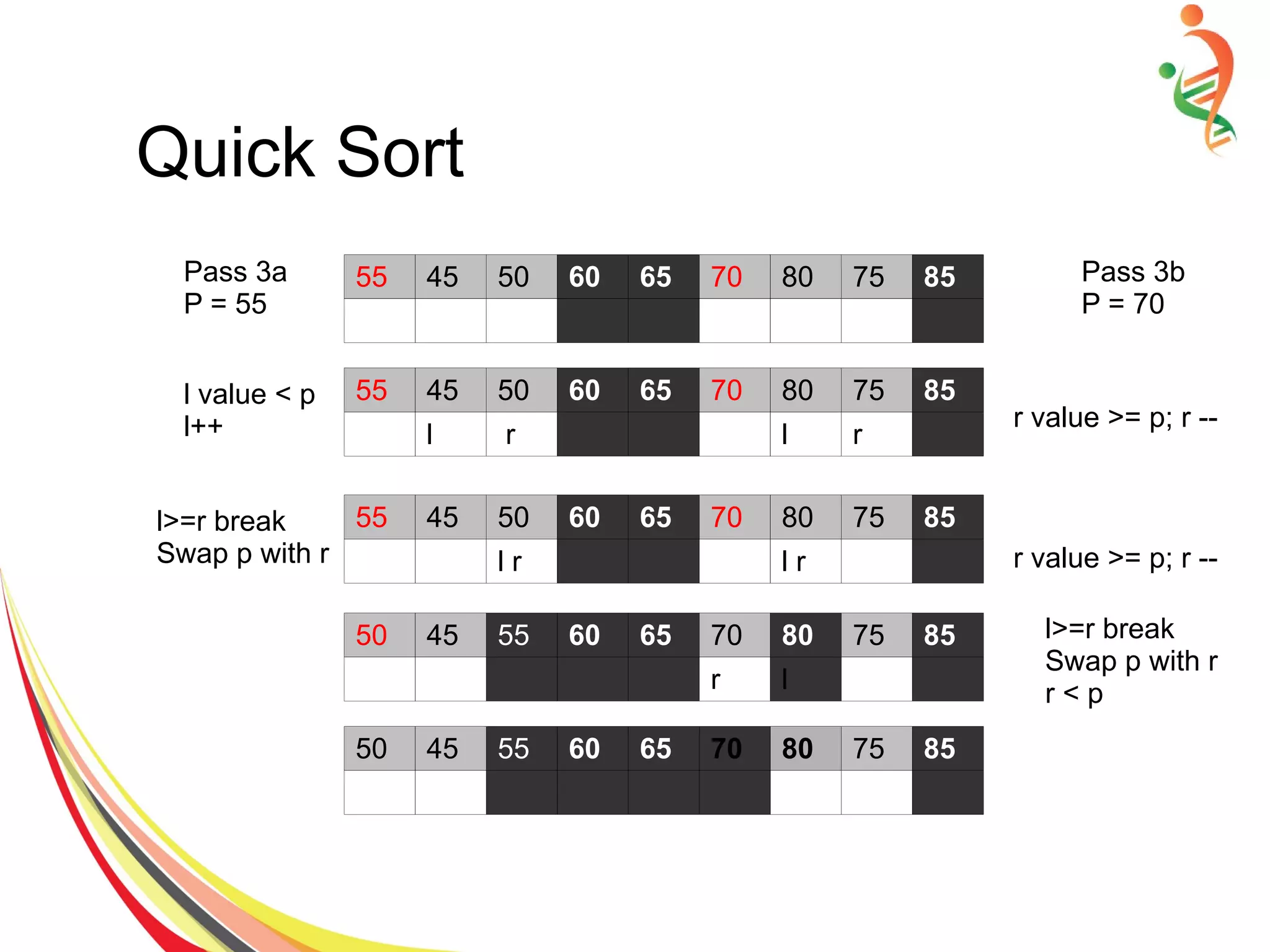
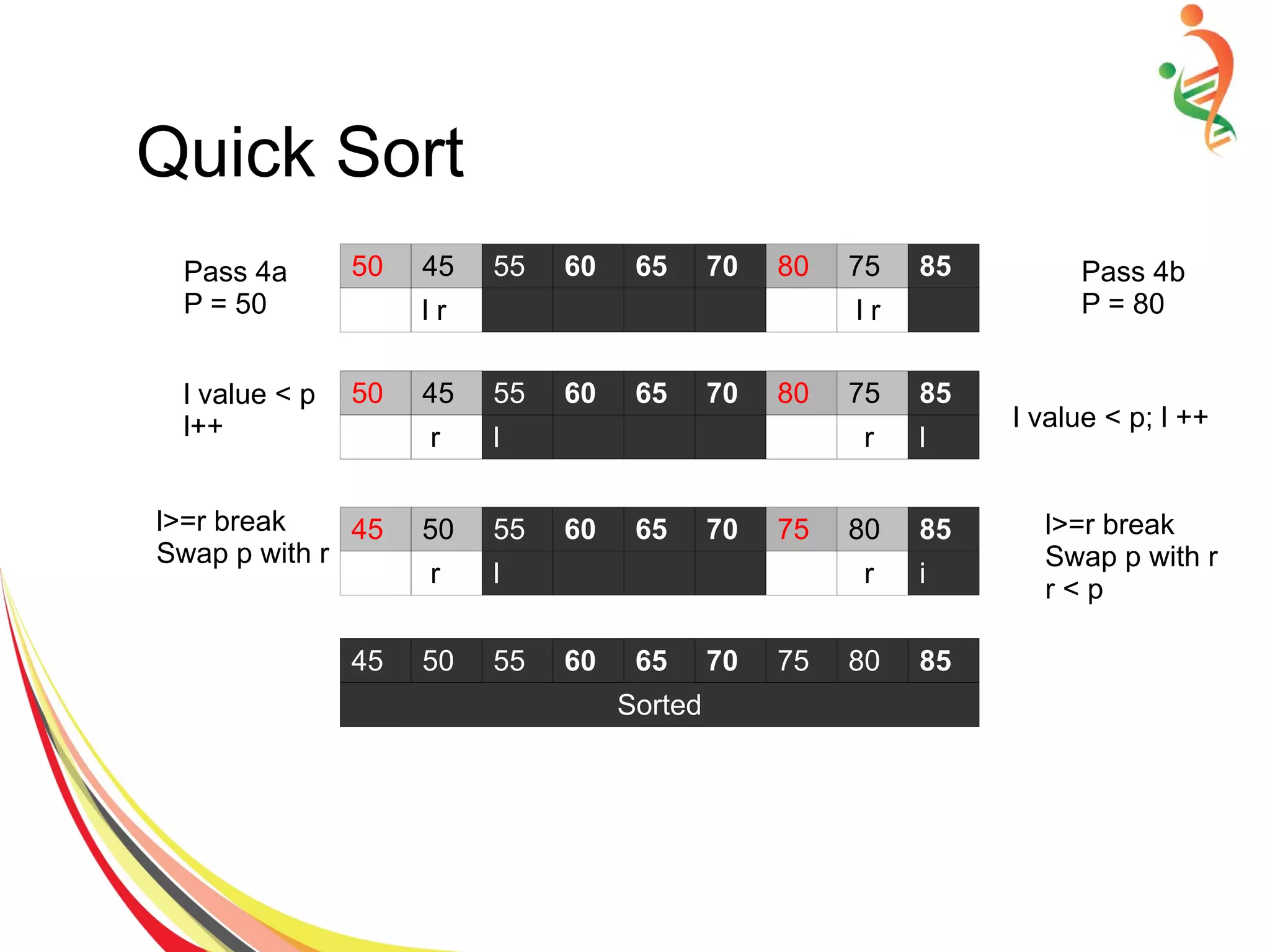
![Quick Sort Algorithm
● Set pivot = a[left], l = left + 1, r = right;
● while l < r, do
– while l < right & a[l] < pivot , set l = l + 1
– while r > left & a[r] >= pivot , set r = r – 1
– if a[l] < a[r], swap a[l] and a[r]
● Set a[left] = a[r], a[r] = pivot
● Terminate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-150528091014-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-24-2048.jpg)


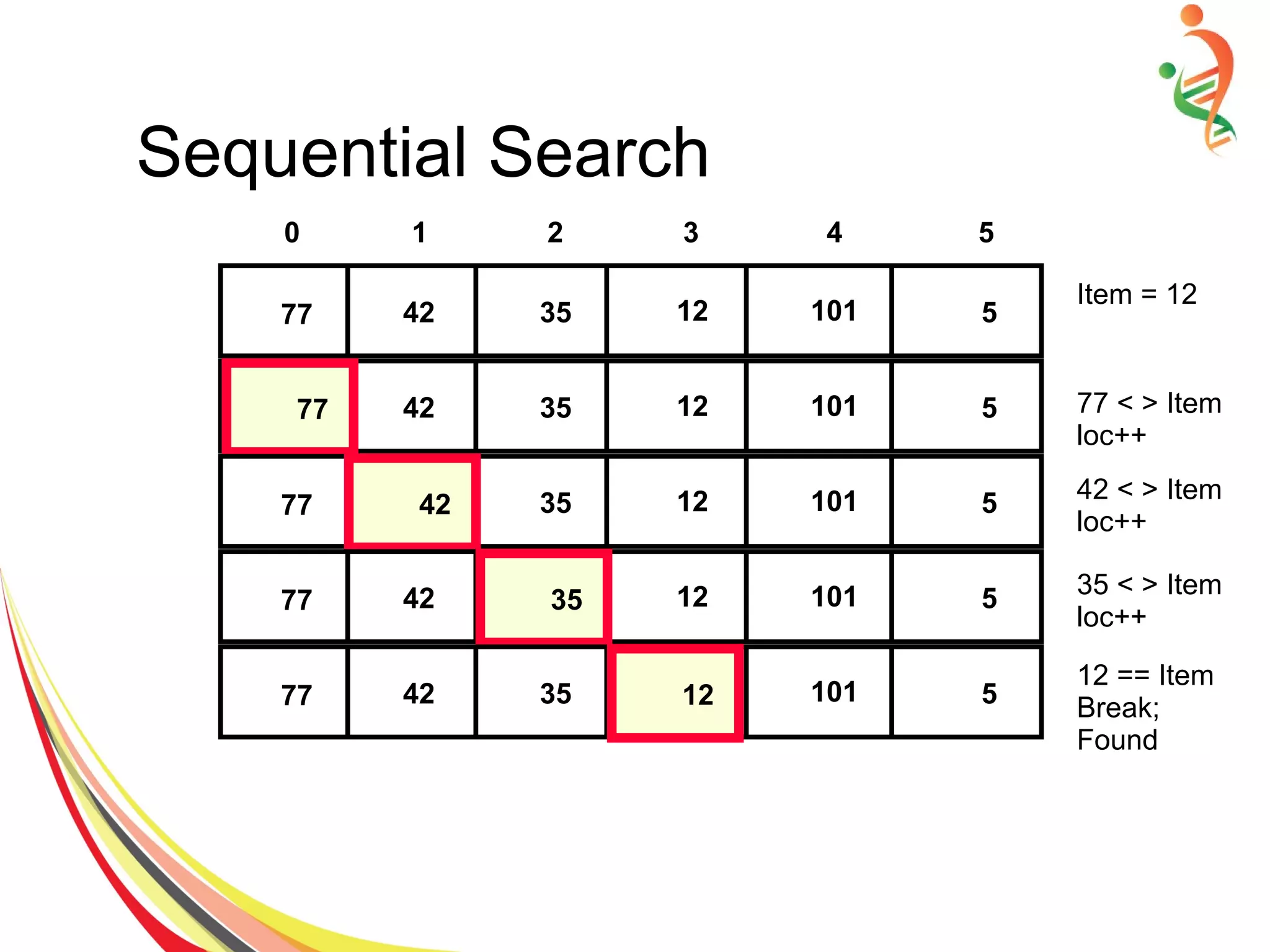
![Sequential Search Algorithm
● Declare array on n items
Set items[n] = { 2,7,5,8,43,23..99}
● Find a number into provided items array.
bool found = false;
for(int loc = 0; loc < n; loc++)
if(items[loc] == item) {
found = true;
break; }
if(found)
return loc;
else
return -1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-150528091014-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-32-2048.jpg)

![Binary Search Algorithm
● Declare array of n items
Set items[n] = { 2,7,5,8,43,23..99}
● Find a number into provided items
array.
● int first = 0; int mid; int last=n -1
● bool found = false;
● while(first <= last && !found) {
– mid = (first + last) / 2 ;
– if(items[mid] ==item)
found=true;
else
if(items[mid] > item)
last=mid-1;
else
first= mid+1;
}
if(found)
return mid;
else
return -1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-150528091014-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-35-2048.jpg)
![Binary Search
1021225102 101
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
110
First =0; Last = 6; Mid=(0+6)/2=3
Item= 101
Items[3]<>10145
1024525102 101 110102
items[mid]< 101; First=4; Last=6; Mid=(4+6)/2=5
Items[5]<>101
1024525102 101 110101
items[mid]> 101; First=4; Last=4; Mid=(4+4)/2=4
Items[4]==101
Found](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sorting-150528091014-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-36-2048.jpg)