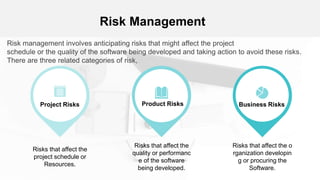
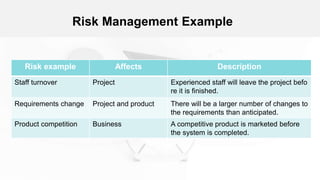
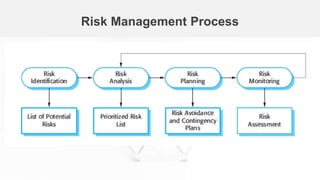
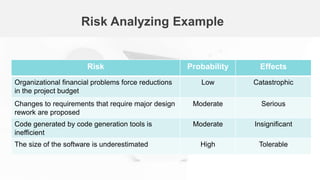
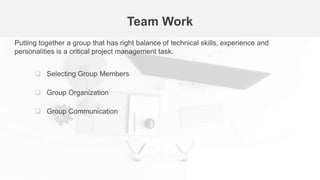
The document outlines the fundamentals of software project management, emphasizing its importance in achieving project goals while adhering to organizational constraints. Key areas include project planning, risk management, and people management, which involve selecting team members, motivating them, and anticipating potential risks. Additionally, it discusses the risk management process, including identification, analysis, planning, and monitoring of risks that could impact the project.